The human nervous system is a complex and incredible network that plays a vital role in controlling and coordinating the functions of the body. From sending signals to our brain to regulating organ systems, the nervous system is responsible for our ability to perceive, interpret, and respond to the world around us.
In this article, we will explore 14 astonishing facts about the human nervous system that will leave you in awe of its capabilities. From its intricate structure to its remarkable ability to adapt and learn, the nervous system is truly a marvel of biology. So, let’s dive in and uncover the fascinating secrets of this extraordinary system that governs our every move and thought.
Key Takeaways:
- The human nervous system is like a superhighway of communication, with billions of nerve cells transmitting signals at incredible speeds, controlling both voluntary and involuntary actions.
- Our brain, the command center of the nervous system, plays a crucial role in memory, learning, perception of pain, sense of touch, balance, and regulating the body’s internal environment.
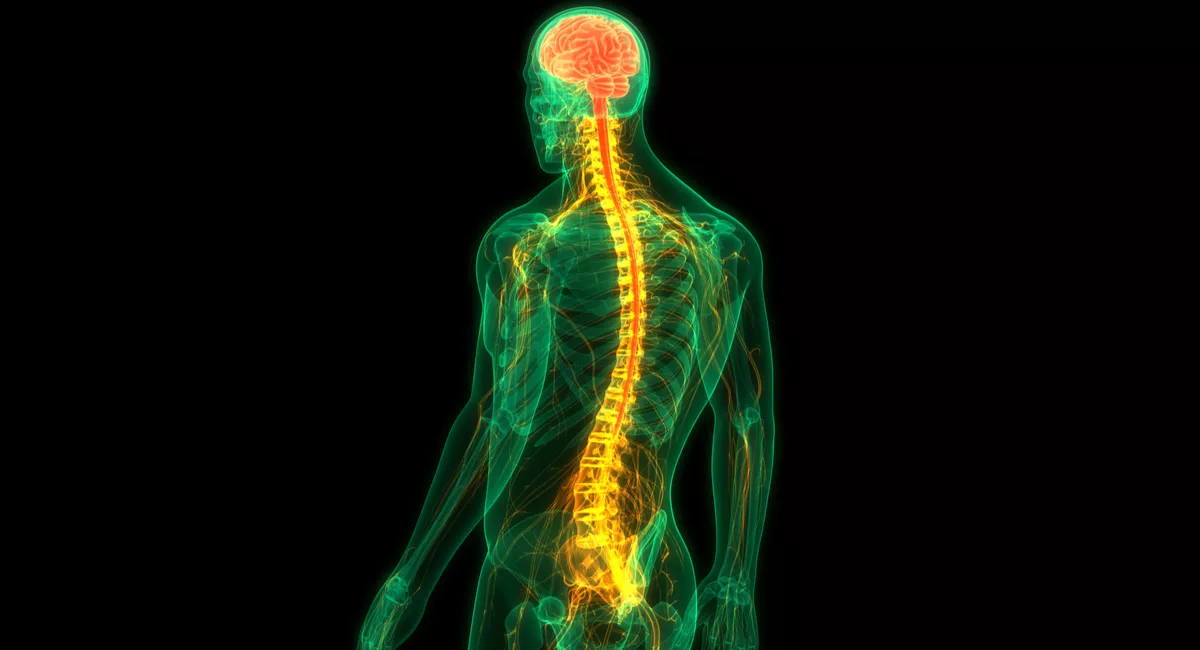
The human nervous system is composed of billions of nerve cells.
The human nervous system consists of a vast network of neurons, estimated to be around 100 billion in number. These specialized cells transmit electrical signals throughout the body, allowing for communication between different parts and organs.
The brain is the command center of the nervous system.
The brain, weighing about 3 pounds, acts as the control center for the entire nervous system. It receives, processes, and interprets information from the body and the external environment, enabling us to think, reason, and make decisions.
The spinal cord connects the brain to the rest of the body.
The spinal cord is a long, tubular bundle of nerves that extends from the base of the brain and runs down the back. It serves as a pathway for transmitting signals between the brain and the body, allowing for voluntary and involuntary movements.
The human nervous system has two main divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord and is responsible for processing and integrating sensory information. On the other hand, the PNS includes all the nerves outside the CNS and connects the body to the CNS.
The human nervous system can transmit signals at incredible speeds.
Nerve impulses can travel at speeds of up to 268 miles per hour (431 kilometers per hour). This allows for swift communication between the brain and various parts of the body, enabling immediate responses to stimuli.
The human nervous system controls both voluntary and involuntary actions.
Voluntary actions, such as walking or writing, are under conscious control and involve the brain’s decision-making processes. Involuntary actions, like digestion or heartbeat, are regulated automatically by the nervous system without conscious effort.
The human brain uses about 20% of the body’s total oxygen and blood supply.
Despite accounting for only 2% of the body’s weight, the brain requires a significant amount of energy to function properly. It relies on a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients delivered by the blood.
The human nervous system continues to develop and change throughout our lives.
Although the majority of brain development occurs during childhood, the human nervous system remains adaptable and capable of forming new connections and altering existing ones through a process known as neuroplasticity.
The human nervous system is involved in the perception of pain.
Pain signals are transmitted through specialized nerves called nociceptors, which detect tissue damage or potential harm. The brain then processes these signals, allowing us to experience and respond to pain.
The human nervous system plays a crucial role in memory and learning.
The brain’s ability to form and store memories is crucial for learning and acquiring new knowledge. Different regions of the brain work together to encode, consolidate, and retrieve information, shaping our ability to remember and recall experiences.
The human nervous system is responsible for our sense of touch.
The skin is richly supplied with nerve endings that detect various sensations such as pressure, temperature, and pain. The nervous system processes these signals, allowing us to perceive and respond to different tactile stimuli.
The human nervous system controls our sense of balance and coordination.
The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, is responsible for maintaining balance and spatial orientation. It sends signals to the brain, which then coordinates muscle movements and helps us maintain an upright posture.
The human nervous system regulates the body’s internal environment.
The autonomic nervous system, a division of the PNS, controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It helps maintain homeostasis by continuously monitoring and adjusting the body’s internal processes.
The human nervous system is vulnerable to various disorders and diseases.
Conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke can significantly impact the functioning of the nervous system, affecting cognition, movement, and overall well-being.
These 14 astonishing facts about the human nervous system only scratch the surface of its complexity and importance. Understanding the intricate workings of this incredible system can help us appreciate the wonders of our own bodies and how we interact with the world around us.
Conclusion
The human nervous system is undoubtedly one of the most fascinating and complex systems in the body. From controlling our every movement to processing information and emotions, it plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Throughout this article, we have explored 14 astonishing facts about the human nervous system, highlighting its incredible capabilities and intricacies.
From the billions of neurons working together to transmit electrical signals to the brain’s central command center, to the adaptability and plasticity of the system, it is clear that the human nervous system is a remarkable product of evolution. The ability to learn, remember, and adapt to new situations showcases the flexibility and resilience of this intricate network.
Furthermore, understanding the human nervous system is not only essential for medical professionals but also for anyone interested in discovering the wonders of our own bodies. The more we learn about it, the more we can appreciate the beauty and complexity of our nervous system.
As research continues to uncover new discoveries, we can only imagine what further astonishing facts will be revealed about the human nervous system in the future. Undoubtedly, it will continue to captivate our minds and expand our understanding of what it means to be human.
FAQs
1. What is the main function of the human nervous system?
The main function of the human nervous system is to coordinate and control the body’s actions and reactions to stimuli. It regulates vital functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion, and enables us to think, learn, and experience emotions.
2. How many neurons are there in the human nervous system?
It is estimated that there are around 86 billion neurons in the human nervous system. These neurons form intricate networks that enable the transmission of electrical impulses throughout the body.
3. Can the human nervous system regenerate?
Although the ability for full regeneration is limited, some parts of the nervous system, such as peripheral nerves, have the potential for partial regeneration. The central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord, has limited regenerative abilities.
4. What happens when the nervous system malfunctions?
When the nervous system malfunctions, it can lead to various neurological disorders and conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke. These conditions can affect motor functions, cognition, and overall wellbeing.
5. Can stress affect the nervous system?
Yes, stress can significantly impact the nervous system. Prolonged or chronic stress can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in the body, leading to adverse effects on mental health, cognitive function, and overall well-being.
Hungry for more captivating facts about the human body? Explore the wonders of neurobiology and learn how nerve cells communicate. Delve into a collection of surprising nerve system facts that will leave you in awe. Lastly, unravel the mysteries of nerve impulses and how they enable our bodies to function seamlessly.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


