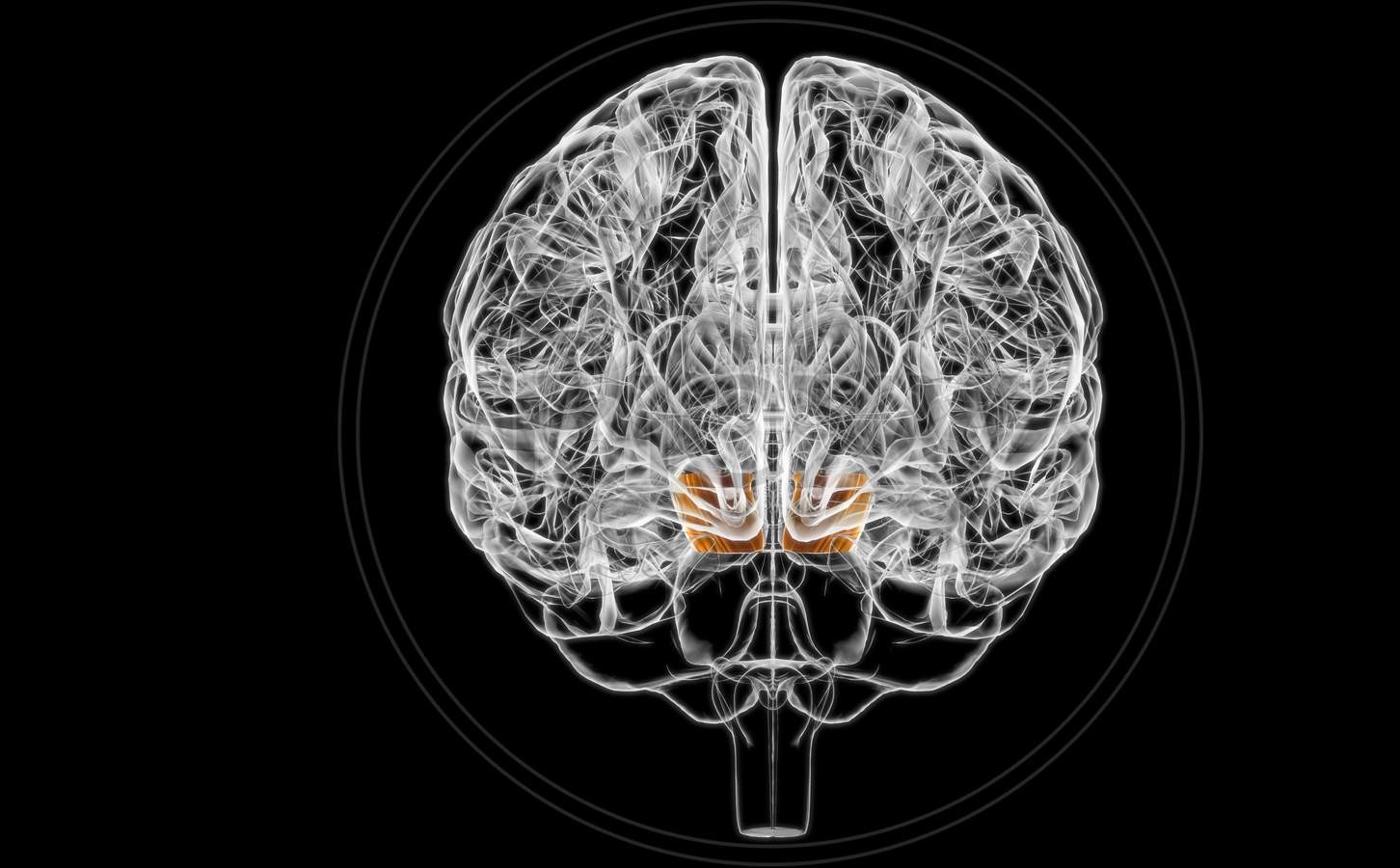
The cerebral peduncle is an essential part of the brain that plays a crucial role in our overall neurological functioning. Comprising of various nerve fibers and structures, the cerebral peduncle serves as a communication pathway between the brainstem and the cerebral cortex. Its functions include transmitting motor signals, coordinating body movements, and relaying sensory information.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of the cerebral peduncle and uncover 12 captivating facts about this vital brain structure. From its anatomical features to its involvement in neural disorders, we will explore the fascinating aspects of the cerebral peduncle, shedding light on its significance in our understanding of human anatomy and cognitive processes.
Key Takeaways:
- The cerebral peduncle is a crucial part of the brain that helps with movement and communication. It connects the cerebrum and spinal cord, and damage to it can cause coordination issues.
- Understanding the cerebral peduncle’s role in motor function and sensory processing can deepen our knowledge of the brain’s intricate workings and its importance in our daily activities.
The Cerebral Peduncle is Part of the Midbrain
The cerebral peduncles are located in the midbrain, which is the middle part of the brainstem. It acts as a bridge, connecting the higher centers of the brain to the spinal cord.
It Consists of Three Main Structures
The cerebral peduncle is composed of three main structures: the crus cerebri, substantia nigra, and the tegmentum. Each structure has its own unique functions within the brain.
The Crus Cerebri Carries Motor Information
The crus cerebri, also known as the cerebral crus, is the largest part of the cerebral peduncle. It contains nerve fibers that transmit motor information from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord and other parts of the body.
The Substantia Nigra Plays a Role in Movement
The substantia nigra is a darkly pigmented area within the cerebral peduncle that produces dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in controlling movement and coordination.
The Tegmentum Contains Various Nerve Pathways
The tegmentum, located in the posterior part of the cerebral peduncle, contains several important nerve pathways involved in sensory processing, motor control, and regulation of arousal and consciousness.
It Connects the Cerebrum and the Spinal Cord
The cerebral peduncle serves as a vital conduit for communication between the cerebrum, which is responsible for higher cognitive functions, and the spinal cord, which controls voluntary and involuntary movements.
Damage to the Cerebral Peduncle Can Cause Motor Coordination Issues
If the cerebral peduncle is damaged, it can result in motor coordination problems such as muscle weakness, difficulty in controlling movements, and impaired balance.
It Plays a Role in Eye Movement
The cerebral peduncle is involved in controlling voluntary eye movements. It works in conjunction with other brain regions to ensure smooth and coordinated eye movements.
The Cerebral Peduncle Contains Myelinated Nerve Fibers
The nerve fibers within the cerebral peduncle are heavily myelinated, meaning they are insulated with a fatty substance called myelin. This insulation enhances the speed and efficiency of nerve signal transmission.
It Receives Input from the Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia, a group of structures involved in motor control, sends input to the cerebral peduncle. This input helps modulate motor activities and maintain balance and posture.
The Cerebral Peduncle Has an Important Role in the Startle Reflex
The startle reflex, a rapid and involuntary response to a sudden stimulus, involves the activation of the cerebral peduncle. It helps to prepare the body for a quick response to potential threats.
Disorders Involving the Cerebral Peduncle Can Lead to Movement Disorders
Disorders that affect the cerebral peduncle, such as Parkinson’s disease, can result in movement disorders characterized by tremors, rigidity, and difficulty initiating or controlling movements.
In conclusion, the cerebral peduncle is a vital structure within the brain that bridges the gap between the cerebrum and the spinal cord. It plays a critical role in motor function, sensory processing, and coordination. Understanding these captivating facts about the cerebral peduncle can deepen our knowledge of the brain’s intricate workings.
Conclusion
Cerebral peduncles are an intriguing part of the human brain that play a crucial role in various functions. These structures, located in the midbrain, serve as a pathway for transmitting information between different regions of the brain.
Throughout this article, we have explored 12 captivating facts about cerebral peduncles. From their anatomical features to their involvement in motor control and sensory processing, these facts shed light on the significance of cerebral peduncles in our daily lives.
Whether you are a medical professional, a student, or simply fascinated by the wonders of the human body, understanding the role of cerebral peduncles provides insights into the complexity and brilliance of our neurological systems.
So next time you marvel at the complexities of the human brain, remember the cerebral peduncles and their remarkable contributions to our cognitive and physical abilities.
FAQs
1. What are cerebral peduncles?
Cerebral peduncles are structures located in the midbrain that serve as a pathway for transmitting information between different regions of the brain.
2. What is the function of cerebral peduncles?
The main function of cerebral peduncles is to carry motor commands from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord and other parts of the body, allowing for voluntary movement. They also play a role in the processing of sensory information.
3. How do cerebral peduncles contribute to motor control?
Cerebral peduncles contain the corticospinal tracts, which are responsible for transmitting motor commands from the motor cortex to the spinal cord. This enables the execution of voluntary movements.
4. Can damage to cerebral peduncles lead to motor deficits?
Yes, damage to cerebral peduncles can result in motor deficits such as weakness, loss of coordination, and difficulties with fine motor skills.
5. Are cerebral peduncles involved in sensory processing?
Yes, cerebral peduncles are also involved in the processing of sensory information. They play a role in transmitting sensory signals from the spinal cord and other sensory organs to the cerebral cortex.
6. Are cerebral peduncles unique to humans?
No, cerebral peduncles are found in all mammals, including humans.
7. Can cerebral peduncles be seen on imaging studies?
Yes, cerebral peduncles can be visualized on imaging studies such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans.
8. Do cerebral peduncles have any other functions besides motor control and sensory processing?
While motor control and sensory processing are the primary functions of cerebral peduncles, they also contribute to other processes, such as eye movement control and arousal.
9. Are there any diseases or conditions associated with cerebral peduncles?
Yes, cerebral peduncles can be affected in certain neurological disorders such as stroke, brain tumors, and Parkinson’s disease.
10. Can cerebral peduncles regenerate or repair themselves after injury?
Unfortunately, cerebral peduncles have limited regenerative capacity, and significant damage to these structures may result in long-term impairments.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
