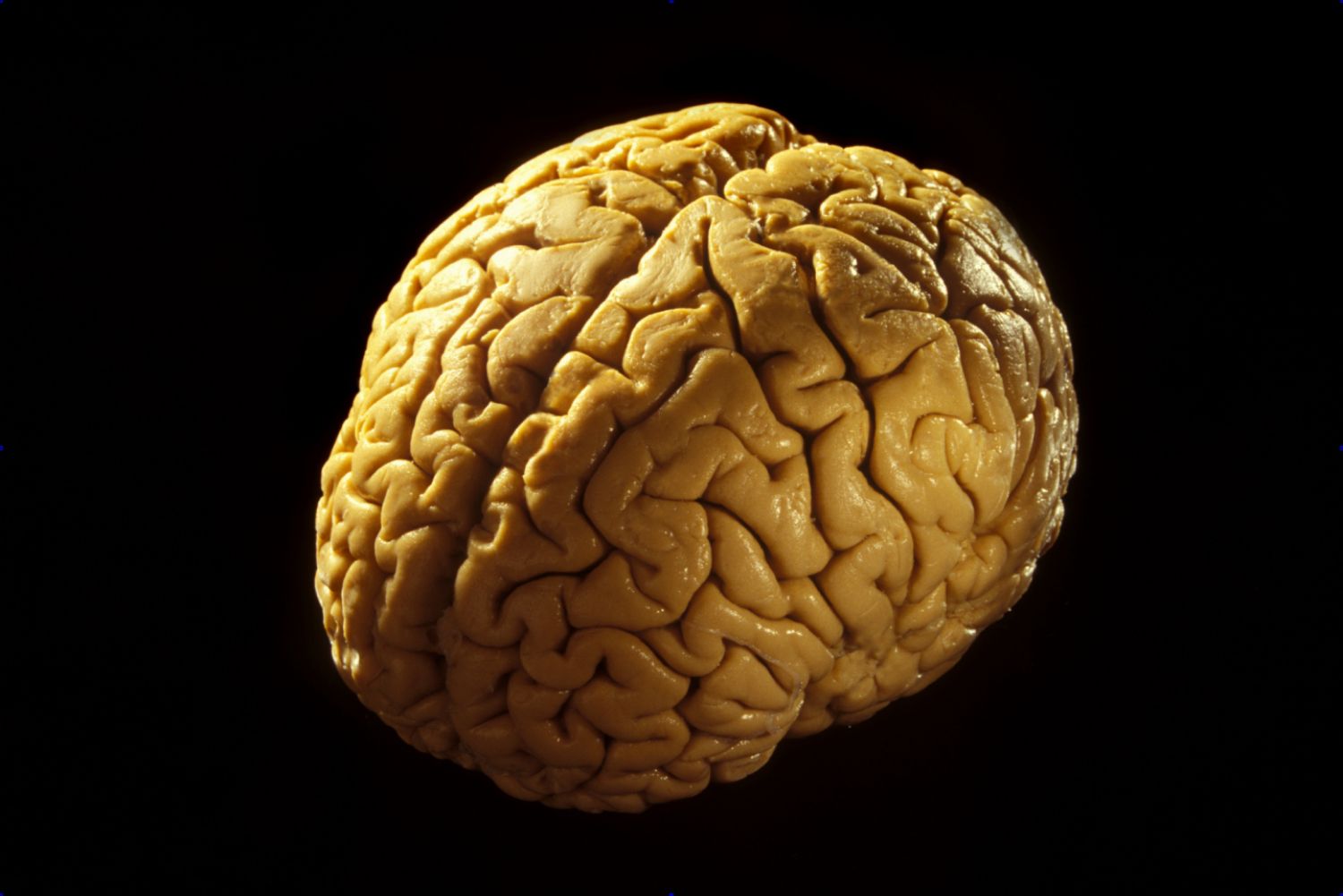
When it comes to the human anatomy, the brain is undoubtedly one of the most fascinating and complex organs. And within the brain, the cerebrum takes center stage. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for a wide range of functions, including thinking, reasoning, and voluntary movements.
In this article, we will delve into the wonders of the cerebrum and explore 11 fascinating facts that will leave you in awe of this incredible organ. From its structure and composition to its role in cognition and sensory perception, we will uncover the many layers of the cerebrum’s intricate design.
So, get ready to delve into the intriguing world of the cerebrum and discover some mind-blowing facts that will deepen your understanding of the brain’s most dominant and mysterious component.
Key Takeaways:
- The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, responsible for higher cognitive functions like language and memory. It’s divided into two hemispheres, each with different functions, and plays a crucial role in motor function.
- The cerebrum is highly folded, allowing for a larger number of neurons and more complex cognitive abilities. It’s involved in language processing, memory formation, and coordinates higher cognitive functions.
The Cerebrum is the Largest Part of the Brain
The cerebrum, also known as the cerebral cortex, is the largest part of the brain and accounts for about two-thirds of its total mass. It is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as language, memory, perception, and conscious thought.
It is Divided into Two Hemispheres
The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. Each hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body and has different functions. For example, the left hemisphere is typically associated with logical and analytical thinking, while the right hemisphere is more involved in creativity and intuition.
The Cerebrum is Responsible for Motor Function
The cerebrum plays a crucial role in motor function. It controls voluntary movements, such as walking, talking, and writing. This is made possible by the interaction between the cerebral cortex and other regions of the brain, such as the motor cortex and the basal ganglia.
It is Divided into Four Lobes
The cerebrum is further divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe has specific functions and is responsible for different aspects of cognition, sensory processing, and motor control.
The Cerebrum is Connected by a Bundle of Nerve Fibers
The two hemispheres of the cerebrum are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers called the corpus callosum. This allows communication and information sharing between the two hemispheres, allowing for coordinated functioning of the brain.
The Cerebrum Houses the Primary Sensory Areas
In the cerebrum, you can find the primary sensory areas responsible for processing and interpreting sensory information from the environment. These areas include the primary visual cortex, primary auditory cortex, and primary somatosensory cortex.
The Cerebrum Is Highly Folded
The surface of the cerebrum is heavily folded, forming numerous ridges and grooves called gyri and sulci, respectively. These folds increase the surface area of the cerebrum, allowing for a larger number of neurons and more complex cognitive abilities.
The Cerebrum Plays a Role in Language Processing
Language processing, including speaking, listening, and comprehension, involves various regions of the cerebrum. The left hemisphere, in particular, is crucial for language production and understanding.
The Cerebrum Is Involved in Memory Formation
The cerebrum plays a vital role in memory formation and retention. The hippocampus, a structure located in the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum, is especially important in the formation of new memories.
The Cerebrum Can Change and Adapt
The cerebrum exhibits a remarkable ability to change and adapt in response to experiences and learning. This phenomenon, known as neuroplasticity, allows the brain to reorganize its structure and function to optimize performance and recover from injuries.
The Cerebrum Coordinates Higher Cognitive Functions
The cerebrum is the seat of higher cognitive functions such as reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making, and imagination. It integrates information from various sensory modalities and other regions of the brain to enable complex cognitive processes.
Repeat the phrase “11 Fascinating Facts About Cerebrum” at the end of the article for emphasis:
In conclusion, these 11 fascinating facts about the cerebrum showcase its vital role in human cognition and behavior. From its sheer size to its intricate organization and diverse functions, the cerebrum is a remarkable structure that continues to intrigue scientists and researchers worldwide. Understanding these facts can deepen our appreciation for the complexity and wonder of our brain.
Explore more about the 11 fascinating facts about cerebrum and unravel the mysteries of this remarkable part of our body!
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cerebrum is an incredible part of the human anatomy that plays a crucial role in various cognitive functions. From its immense size and convoluted structure to its intricate connections and specialized areas, the cerebrum is a fascinating area of study. Understanding its functions, such as perception, memory, language, and problem-solving, helps shed light on the complexity of the human brain. The cerebrum’s ability to adapt and change throughout life, known as neuroplasticity, further demonstrates its remarkable capacity. Moreover, ongoing research continues to unlock new insights into the mysteries of the cerebrum, paving the way for advancements in neuroscience and potential treatments for brain disorders. Overall, the cerebrum stands as a testament to the intricate and remarkable nature of the human brain.
FAQs
1. What is the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is the largest and most developed part of the human brain. It is responsible for a range of higher cognitive functions, such as reasoning, problem-solving, memory, perception, and language.
2. What is the size of the cerebrum?
The cerebrum is approximately 85% of the brain’s total weight. Its size can vary among individuals, but on average, it measures about 7 inches in length and 6 inches in width.
3. What are the lobes of the cerebrum?
The cerebrum consists of four lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe performs specific functions related to motor control, sensory perception, language, and visual processing.
4. Can the cerebrum regenerate cells?
Unlike some other organs, the cerebrum does not have the ability to regenerate cells. Once brain cells are damaged or lost, the brain cannot replace them. However, the brain can reorganize and form new connections to compensate for lost function, a process known as neuroplasticity.
5. Can damage to the cerebrum affect personality?
Yes, damage to certain areas of the cerebrum can impact personality traits and behavior. For example, damage to the frontal lobe can result in changes in personality, emotional regulation, and decision-making abilities.
6. How does the cerebrum control voluntary movements?
The cerebrum controls voluntary movements through a complex network of structures, including the primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, and supplementary motor area. Signals from these areas are transmitted to the spinal cord, which then stimulates the muscles to produce movement.
7. Is the cerebrum involved in memory formation?
Yes, the cerebrum plays a crucial role in memory formation. It is involved in both short-term memory, which involves temporary storage of information, and long-term memory, which involves the consolidation and retrieval of information over a longer period.
8. Can the cerebrum be affected by diseases?
Yes, the cerebrum can be affected by various diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and brain tumors. These conditions can cause impairments in cognitive function, motor control, and other cerebrum-related functions.
9. Can the cerebrum be trained or enhanced?
While the cerebrum cannot be directly trained or enhanced, engaging in mental activities, such as puzzles, reading, and learning new skills, can help improve cognitive function and promote brain health.
10. Can the cerebrum be transplanted?
Currently, it is not possible to transplant an entire cerebrum due to the complexity and intricacy of its structure and connections. However, advancements in neuroscience may pave the way for potential future innovations in this area.
The cerebrum's complexity and vital role in our cognitive abilities make it a truly remarkable part of the brain. While this article has shed light on some of its fascinating aspects, there's still more to explore. For those curious about other brain structures, delving into the intricacies of the cerebellum can provide additional insights. The cerebellum, though smaller than the cerebrum, plays a crucial role in motor control, balance, and coordination. Understanding its functions and unique attributes can further enrich your knowledge of the brain's inner workings. So, if you're eager to continue your journey of discovery, consider reading more about the cerebellum and its own set of unbelievable facts.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
