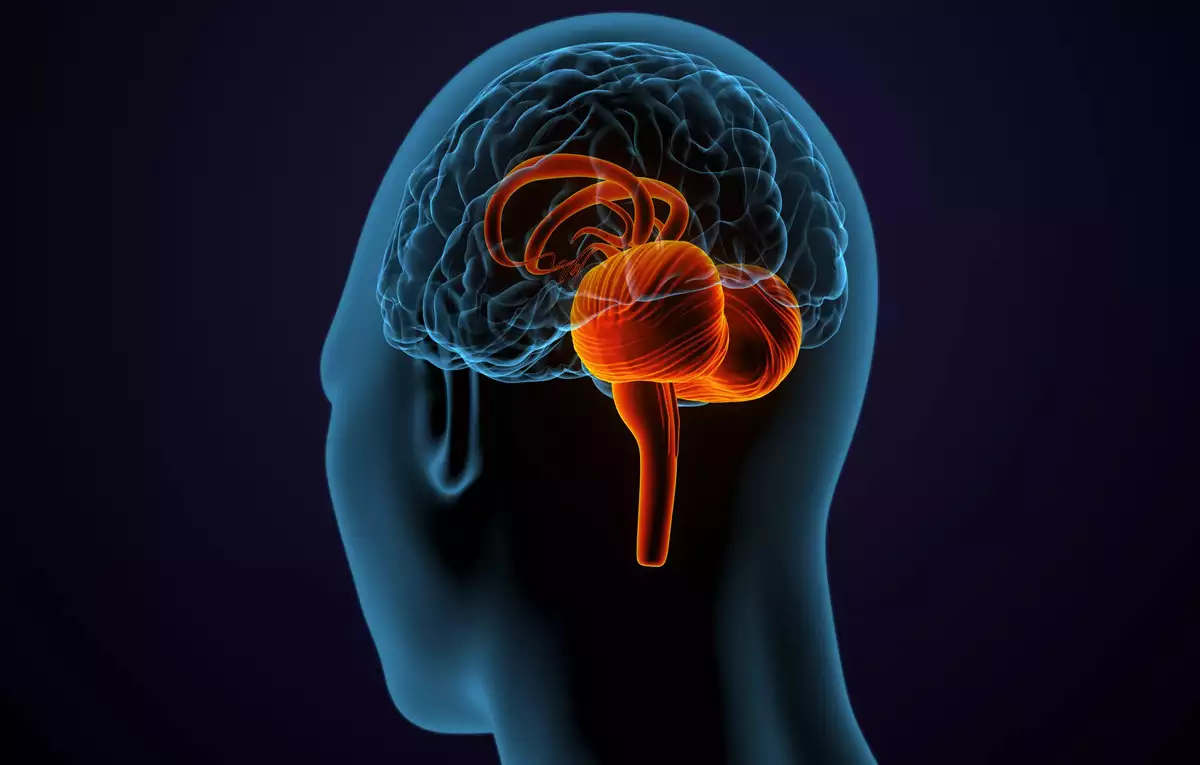
The human brain is a fascinating organ, responsible for controlling our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Within this complex network of neurons and synapses lies a remarkable structure known as the cerebellum. Often overshadowed by its more famous counterpart, the cerebrum, the cerebellum plays a crucial role in our daily lives. This small but mighty part of the brain is responsible for coordinating movement, maintaining balance, and even influencing cognition.
In this article, we will delve into the incredible world of the cerebellum and explore eleven mind-boggling facts that will leave you in awe of this often overlooked brain region. From its intricate structure and evolutionary significance to its role in motor learning and even its potential for neuroplasticity, the cerebellum is a treasure trove of astonishing information. So, let’s dive in and discover the hidden wonders of the cerebellum!
Key Takeaways:
- The cerebellum, also known as the “little brain,” is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and even cognitive functions like attention and memory. It’s like the brain’s secret multitasking powerhouse!
- Despite its small size, the cerebellum contains more neurons than any other part of the brain, allowing it to process and integrate sensory information rapidly. It’s like a supercharged computer chip for our body’s movements and coordination!
The cerebellum contains over half of the brain’s neurons.
Did you know that despite its small size, the cerebellum contains a whopping 50 to 80 billion neurons? This accounts for more than half of all the neurons in the brain! These densely packed nerve cells allow the cerebellum to process an incredible amount of information.
The cerebellum coordinates movement and balance.
The primary function of the cerebellum is to coordinate and regulate our movements. Whether it’s walking, running, or even playing a musical instrument, the cerebellum helps us perform these actions smoothly and efficiently. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in maintaining our balance and posture.
The cerebellum is involved in cognitive functions.
While traditionally known for its role in motor coordination, recent studies have shown that the cerebellum also plays a part in cognitive functions. It contributes to attention, language processing, working memory, and even emotional regulation.
The cerebellum has multiple lobes and regions.
Similar to the cerebral cortex, the cerebellum is divided into several lobes and regions. These divisions are responsible for specific functions such as motor planning, sensory integration, and cognitive processing.
The cerebellum receives input from all over the body.
To carry out its coordinating role effectively, the cerebellum receives input from various parts of the body, including the spinal cord, cerebral cortex, and sensory organs. This information allows the cerebellum to adjust and fine-tune movements accordingly.
The cerebellum has more neurons than the rest of the brain combined.
Despite its compact size, the cerebellum contains more neurons than any other part of the brain. This dense neuronal population enables it to process and integrate sensory information rapidly.
The cerebellum plays a role in procedural memory.
Procedural memory, which involves learning and remembering motor skills, is heavily dependent on the cerebellum. From riding a bike to tying shoelaces, the cerebellum plays a vital role in storing and retrieving these learned movements.
The cerebellum can continue to develop throughout life.
Unlike other brain regions, the cerebellum has the ability to generate new neurons and connections throughout our lives. This capacity for neuroplasticity allows the cerebellum to adapt and learn from new experiences.
Damage to the cerebellum can lead to various motor and cognitive impairments.
When the cerebellum is damaged or affected by injury or disease, it can result in a range of motor and cognitive impairments. These may include difficulties with balance, coordination, speech, and attention.
The cerebellum has connections to other brain regions.
The cerebellum doesn’t work in isolation but is connected to other brain regions, including the cerebral cortex and brainstem. These connections enable seamless communication and integration of information between different parts of the brain.
The cerebellum is highly conserved across species.
The cerebellum’s basic structure and function have remained remarkably similar throughout evolution, suggesting its importance in the central nervous system. This similarity can be observed across a wide range of species, from humans to birds and even fish!
From its role in coordinating movement to its contribution to cognitive functions, the cerebellum continues to reveal its awe-inspiring complexity. These 11 unbelievable facts about the cerebellum offer a glimpse into the remarkable world of this seemingly small yet powerful brain structure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cerebellum is an amazing and complex part of the brain that plays a crucial role in our daily activities. From coordinating movement to maintaining balance and contributing to cognitive functions, the cerebellum is involved in a wide range of processes. Its structure and function have fascinated scientists for centuries, leading to numerous discoveries and ongoing research.We have learned some truly unbelievable facts about the cerebellum, such as its staggering number of neurons, the intricate connections it forms with other brain regions, and its role in motor learning and skill acquisition. The cerebellum’s ability to adapt and fine-tune our movements is truly remarkable.Understanding the cerebellum is essential for advancing our knowledge of neurological disorders and developing effective treatments. By continuing to study this extraordinary brain structure, we can unlock further insights into the mysteries of human brain function.
FAQs
1. What is the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is a region located in the back of the brain, below the cerebrum. It is responsible for the coordination of voluntary movements, balance, and muscle tone.
2. How many neurons are in the cerebellum?
The cerebellum contains roughly 69 billion neurons, which is more than half of the total number of neurons in the entire brain.
3. What happens if the cerebellum is damaged?
Damage to the cerebellum can result in various motor deficits, including difficulties with balance, coordination, and fine motor skills. It can also lead to problems in speech, attention, and cognitive functions.
4. Is the cerebellum only involved in movement?
No, the cerebellum is not just involved in movement. It also contributes to cognitive functions, such as attention, language processing, and working memory.
5. Can the cerebellum regenerate or repair itself?
While the cerebellum has some capacity for regeneration and plasticity, it is limited compared to other parts of the brain. However, with proper rehabilitation and therapy, individuals with cerebellar damage can often regain some lost functions.
6. Are there any disorders specific to the cerebellum?
Yes, there are several disorders that primarily affect the cerebellum. These include cerebellar ataxia, cerebellar hypoplasia, and cerebellar tumors, among others.
7. Can you live without a cerebellum?
No, a fully functional cerebellum is essential for normal movement and balance. Severe damage or complete removal of the cerebellum can have profound and debilitating effects on a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks.
8. Are there any treatments available for cerebellar disorders?
Treatment options for cerebellar disorders depend on the specific condition and its underlying cause. These may include medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery.
9. Can the cerebellum affect emotions?
Although the cerebellum is not traditionally associated with emotions, emerging research suggests that it may play a role in emotional regulation, with connections to regions involved in mood and affect.
10. Can exercise help improve cerebellar function?
Exercise and physical activity have been shown to have positive effects on brain health, including the cerebellum. Regular exercise can enhance motor skills, coordination, and overall brain function.
11. Can genetic factors contribute to cerebellar disorders?
Yes, in some cases, genetic mutations or abnormalities can lead to cerebellar disorders. These genetic factors can interfere with the development or functioning of the cerebellum, resulting in various neurological symptoms and impairments.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
