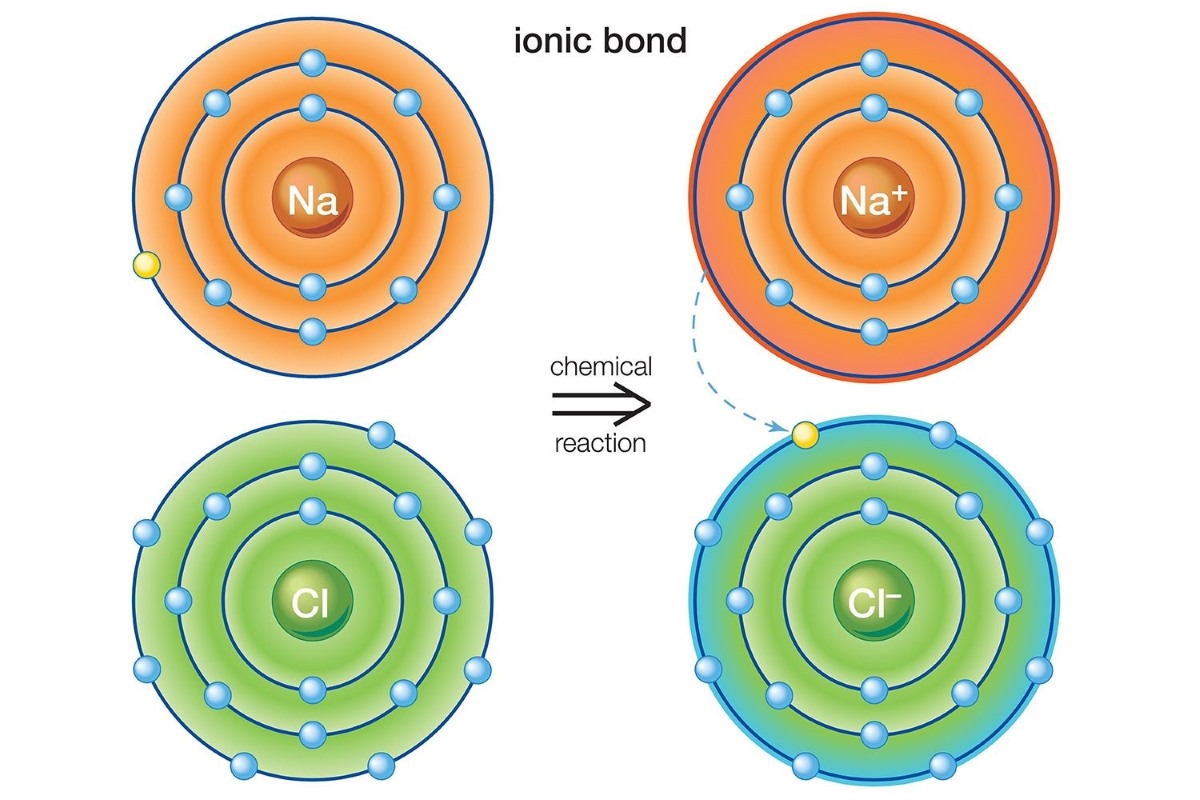
When it comes to chemical bonding, one type that stands out is the ionic bond. This fascinating phenomenon occurs when atoms transfer electrons to achieve stability, resulting in the formation of compounds with unique properties. Ionic bonds are commonly found in compounds such as salts, minerals, and many biochemical molecules.
Curious about the intricate nature of ionic bonds? In this article, we will explore 20 intriguing facts about ionic bonding that will not only deepen your understanding of chemistry but also captivate your curiosity. From the historical discoveries to the applications in various fields, these facts shed light on the significance of ionic bonds in our daily lives.
Key Takeaways:
- Ionic bonds create strong attractions between positively and negatively charged ions, forming stable compounds with high melting points and conductivity in water.
- Ionic compounds play a crucial role in biological processes, have unique crystalline appearances, and are essential in the formation of salts and minerals.
What is an ionic bond?
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs when one atom transfers an electron to another atom, resulting in the formation of ions. This transfer of electrons creates a strong electrostatic attraction between the positively charged ion (cation) and the negatively charged ion (anion).
Ionic bonds often form between metals and non-metals.
In most cases, ionic bonds are formed between a metal atom and a non-metal atom. This is because metals tend to have a low electronegativity, meaning they have a greater tendency to give up electrons, while non-metals have a high electronegativity, leading to a greater ability to attract electrons.
Ionic bonds result in the formation of a crystal lattice structure.
When an ionic bond is formed, the positively and negatively charged ions arrange themselves in a repeating three-dimensional pattern, known as a crystal lattice. This lattice structure gives ionic compounds their characteristic high melting and boiling points.
Ionic compounds are often solid at room temperature.
Due to their strong electrostatic interactions, most ionic compounds exist in a solid state at room temperature. Common examples include sodium chloride (table salt) and calcium carbonate (chalk or limestone).
Ionic compounds can conduct electricity when dissolved in water.
When an ionic compound dissolves in water, the ions separate from each other and are free to move. This allows them to conduct electricity, making aqueous solutions of ionic compounds good conductors of electricity.
Ionic bonds are stronger than covalent bonds.
Compared to covalent bonds, which involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, ionic bonds are generally stronger. This is because the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions is stronger than the bond resulting from the sharing of electrons.
Ionic bonds give rise to the formation of stable compounds.
Due to their strong nature, ionic bonds lead to the creation of stable compounds. The transfer of electrons allows atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration, similar to that of noble gases.
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
Due to the strong attractions between ions within the crystal lattice, ionic compounds require a significant amount of energy to break the bonds and change their state. Hence, they exhibit high melting and boiling points.
Ionic compounds often have a crystalline appearance.
Because of their ordered arrangement in the crystal lattice, many ionic compounds exhibit a crystalline appearance. This can be observed in various minerals and gemstones.
Ionic bonds are essential for many biological processes.
Ionic bonds play a crucial role in many biological processes, such as nerve function, muscle contraction, and enzyme activity. These bonds help maintain the overall stability and functionality of biological molecules.
Ionic compounds can be formed by the transfer of multiple electrons.
In some cases, more than one electron can be transferred between atoms to form ionic bonds. This leads to the formation of ions with multiple charges, such as Fe2+ and Fe3+ in iron compounds.
Ionic bonding is influenced by the size of ions.
The size of ions plays a role in determining the strength of the ionic bond. Smaller ions have stronger attractions due to their closer proximity to each other, while larger ions have weaker attractions.
Ionic bonds can be represented using Lewis dot structures.
Lewis dot structures, which involve representing atoms and their valence electrons as dots, can be used to depict ionic bonding. The transfer of electrons can be shown through the arrows pointing from one atom to another.
Ionic compounds can have varying solubility in water.
Not all ionic compounds are equally soluble in water. Solubility depends on factors such as the strength of the attractions between ions and the interactions between ions and water molecules.
Ionic bonds are responsible for the color of many transition metal compounds.
The presence of d-orbitals in transition metals allows for the absorption and reflection of certain wavelengths of light, giving rise to the vibrant colors observed in many ionic compounds containing transition metals.
Ionic compounds have high electrical stability.
The strong electrostatic attractions in ionic compounds make them highly stable when it comes to electrical influences, such as electric fields or external charges.
Ionic bonds can exhibit some degree of covalent character.
In certain cases, ionic bonds can exhibit partial covalent character, making them polar covalent bonds. This occurs when the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms is not large enough to form a purely ionic bond.
Ionic compounds can form complex structures.
By combining different ions, ionic compounds can form complex structures, such as zeolites or perovskites, which have unique properties and applications in various fields, including catalysis and electronics.
Ionic compounds can undergo dissociation in solution.
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, their ions separate and become hydrated. However, in some cases, these compounds can also dissociate into individual ions without water molecules attached to them, depending on the concentration and conditions.
Ionic bonding plays a crucial role in the formation of salts and minerals.
Salts and minerals, such as sodium chloride and calcium carbonate, are formed through the process of ionic bonding. These compounds are vital in various geological processes and have many practical applications in industry and everyday life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ionic bonding is a fascinating concept in the world of chemistry. Through the exchange of electrons between atoms, ions are formed, creating a strong attraction between positively and negatively charged species. This type of bonding is responsible for the formation of countless compounds and plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. Understanding the intricacies of ionic bonding can provide insights into how different substances interact and how we can harness these interactions for practical applications.By delving into the 20 intriguing facts about ionic bonds, we have explored the fundamental principles behind this type of chemical bonding. From the development of ionic compounds to the properties exhibited by these substances, there is much to learn and appreciate about the way atoms come together to form stable structures. So, whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or simply curious about the world around us, the realm of ionic bonding offers endless possibilities for exploration and discovery.
FAQs
1. What is an ionic bond?
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two ions with opposite charges. These charges are typically generated when atoms either gain or lose electrons, resulting in the formation of positive and negative ions.
2. How are ionic bonds different from covalent bonds?
The key difference between ionic and covalent bonds lies in the sharing of electrons. In ionic bonds, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, while in covalent bonds, electrons are shared between atoms.
3. What are some examples of substances with ionic bonds?
Common examples of substances with ionic bonds include table salt (sodium chloride), potassium iodide, and magnesium oxide.
4. Can ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Yes, ionic compounds can conduct electricity when they are dissolved in water or melted, as the ions in the compound are free to move and carry electric charge.
5. Are ionic bonds stronger than covalent bonds?
Generally, ionic bonds are stronger than covalent bonds due to the strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. However, the strength of a bond can vary depending on the specific elements involved.
6. What are some real-life applications of ionic bonding?
Ionic bonding is essential for many aspects of daily life, including the conduction of electricity in batteries, the formation of crystals, and the functioning of biological processes such as nerve signaling.
7. Can ionic bonds form between nonmetals?
No, ionic bonds typically form between metals and nonmetals, where the metal atom donates electrons to the nonmetal atom.
8. How do you represent ionic bonds in chemical equations?
Ionic bonds can be represented by writing the chemical formula of the ionic compound, indicating the ions involved and their respective charges.
9. Can ionic compounds be broken down into their constituent elements?
Yes, ionic compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements through various chemical reactions, such as electrolysis or heating.
10. Why are ionic bonds often called electrovalent bonds?
Ionic bonds are sometimes referred to as electrovalent bonds because they involve the transfer of electrons and the presence of electrostatic forces between the ions.
Exploring ionic bonds is just the beginning of your chemistry journey. Dive deeper into the fascinating world of electronegativity and discover how it influences chemical bonding. Expand your knowledge with a wide range of captivating chemistry facts that will leave you craving more. Don't forget to investigate the intriguing properties of salts, such as sea salt, and their role in our daily lives.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
