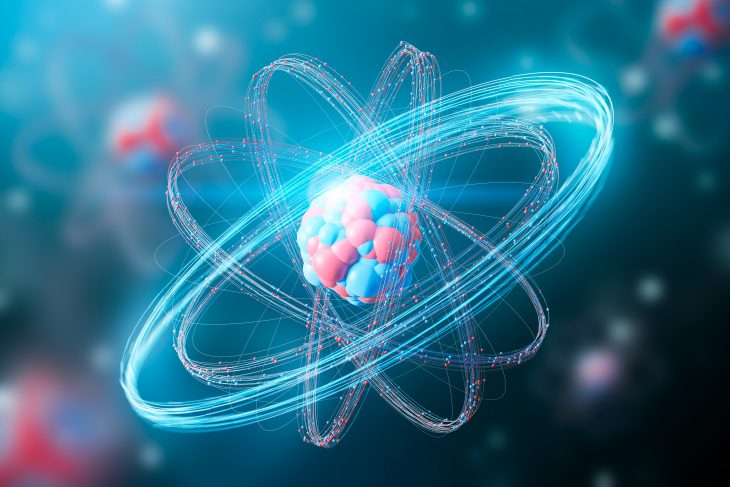
Atoms, the building blocks of matter, are incredibly intriguing. These infinitesimally small particles hold the secrets to understanding the universe. In this article, we will delve into 15 fun facts about atoms that will spark your curiosity and take you on an exciting journey through the microscopic world.
Atoms Are the Smallest Units
Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain the characteristics of a particular element. They cannot be divided further by chemical or physical means.
They Are Mostly Empty Space
Although atoms have a solid appearance in models, they are predominantly empty spaces. The nucleus, consisting of protons and neutrons, occupies only a tiny fraction of the atom’s volume.
Building Blocks of Elements
Atoms combine to form elements, the fundamental substances that make up everything in the universe. There are currently 118 known elements, each with its own unique properties.
Electrons Orbit the Nucleus
Electrons, negatively charged particles, orbit the positively charged nucleus of an atom. These orbits, known as electron shells or energy levels, determine the atom’s chemical behavior.
Subatomic Particles Make Up Atoms
Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge.
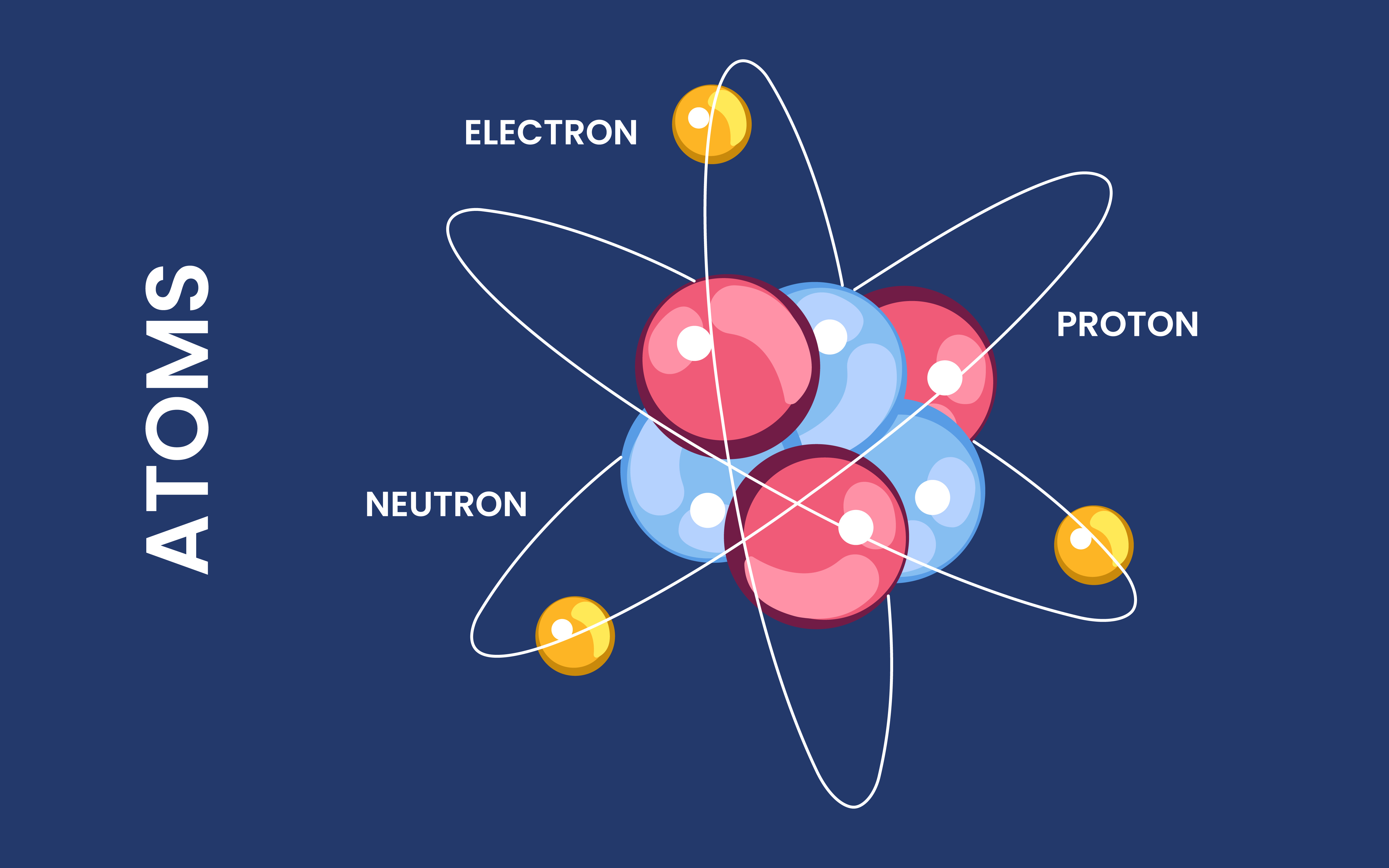
Protons and Neutrons Reside in the Nucleus
The nucleus, located at the center of an atom, contains protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number.
Isotopes Vary in Neutron Number
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different atomic masses. Isotopes can have varying stability and radioactive properties.
Atoms Are Mostly Empty
If you were to remove the empty space from all the atoms that make up the human body, the remaining matter would fit into a volume the size of a sugar cube. Atoms are incredibly small!
They Can Combine to Form Molecules
Atoms can bond together to form molecules through chemical reactions. These molecular combinations give rise to the vast array of substances we encounter in our daily lives.
Atomic Bonding Determines Properties
The way atoms bond to each other influences the physical and chemical properties of substances. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds result in different characteristics such as conductivity, hardness, and melting points.
Atoms Are Constantly in Motion
Atoms are never at rest. They vibrate, rotate, and move within substances. This constant motion is essential for understanding temperature and the behavior of materials.
The Periodic Table Organizes Atoms
The periodic table is a systematic arrangement of elements based on their atomic number and properties. It provides a concise representation of the vast diversity of atoms that exist.
Atomic Structure Revealed by Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy, the study of interactions between matter and electromagnetic radiation, helps scientists uncover details about atoms’ structure, energy levels, and spectral lines, leading to valuable insights.
Nuclear Reactions Release Tremendous Energy
Nuclear reactions, such as those that occur in the sun or during atomic bombs, release enormous amounts of energy. These reactions involve changes in the nucleus of atoms.
Quantum Mechanics Describes Atoms
Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that describes the behavior of atoms and subatomic particles. It provides a framework for understanding the mysterious and fascinating world of atoms.
Conclusion
Atoms are the hidden architects of our world, shaping everything from the air we breathe to the stars that light up the night sky. Understanding their properties and behaviors unlocks a universe of knowledge. Dive into the wonders of atoms, and let their secrets unfold before your eyes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can atoms be destroyed or created?
Atoms cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical reactions. However, nuclear reactions can change the composition of atoms.
How many atoms are in a grain of sand?
A grain of sand contains an astounding number of atoms, estimated to be around 10^18 or one quintillion atoms.
Can atoms exist alone?
Some atoms can exist independently, such as noble gases like helium and neon. However, most atoms prefer to bond with other atoms to form stable structures.
Are all atoms stable?
Not all atoms are stable. Some isotopes exhibit radioactive properties, undergoing spontaneous decay over time.
Can atoms be seen with the naked eye?
Atoms are too small to be seen with the naked eye or even with conventional microscopes. Specialized techniques, such as scanning tunneling microscopes, are needed to observe individual atoms.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
