Henry’s Law is a fundamental principle in the field of chemistry that helps explain the behavior of gases in liquids. Named after the English physician and chemist William Henry, this law states that the amount of gas dissolved in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the liquid. While Henry’s Law may seem like a complex concept, it is actually quite fascinating and can have practical applications in various fields such as environmental science, biology, and even beverage carbonation. In this article, we will explore some surprising facts about Henry’s Law that you may not be aware of. So, get ready to dive into the captivating world of chemistry and uncover some intriguing insights about this timeless scientific principle.
Key Takeaways:
- Henry’s Law explains how gases dissolve in liquids based on pressure. It’s like squeezing a sponge – the more pressure, the more gas can dissolve!
- Henry’s Law affects everything from scuba diving to chemical reactions. It’s like a secret code for understanding how gases behave in liquids!
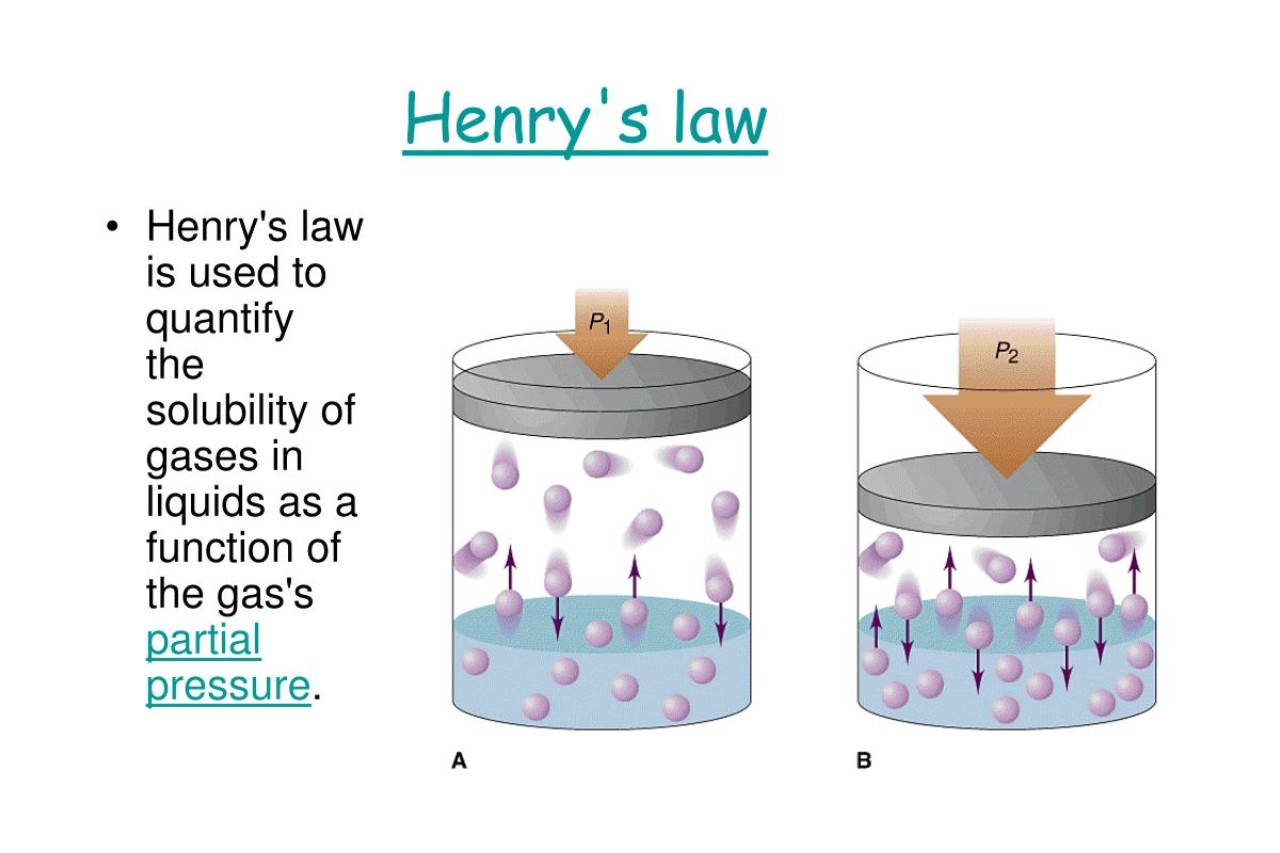
Henry’s Law explains how gases dissolve in liquids.
Henry’s Law states that the amount of gas that dissolves in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the liquid. In other words, the more pressure there is on a gas, the more of it will dissolve into the liquid.
Henry’s Law applies to a wide range of gases.
Whether it’s oxygen dissolving in water or carbon dioxide in a carbonated beverage, Henry’s Law is applicable to various gases. It helps us understand the solubility and behavior of gases in different liquids.
Temperature affects the solubility of gases according to Henry’s Law.
As the temperature of a liquid increases, the solubility of gases decreases. This means that gases are more soluble in colder liquids and less soluble in warmer liquids.
Henry’s Law is crucial in understanding gas exchange in our bodies.
When we breathe, gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in our lungs. Henry’s Law helps explain how these gases dissolve and are transported in our bloodstream, ensuring the proper functioning of our respiratory system.
The concentration of dissolved gases can affect chemical reactions.
Dissolved gases can play a significant role in chemical reactions that occur in solutions. Understanding Henry’s Law helps chemists and scientists predict and control the behavior of these reactions.
It was named after the British chemist William Henry.
Henry’s Law was first formulated and published by William Henry in the early 19th century. His research and observations contributed greatly to our understanding of gas solubility.
Henry’s Law is used in various practical applications.
This law is widely applied in industries such as brewing, wastewater treatment, and even scuba diving. It helps in determining appropriate gas concentrations and pressures for specific processes.
Henry’s Law can be mathematically expressed.
The relationship between the concentration of a gas in a liquid and its partial pressure can be expressed using the Henry’s Law equation:
C = k · P
Where C is the concentration of the gas, P is the partial pressure, and k is the Henry’s Law constant specific to the gas and solvent.
Henry’s Law has some limitations.
While Henry’s Law provides valuable insights into gas solubility, it is mainly applicable to ideal solutions and assumes constant temperature. In reality, deviations can occur, especially with non-ideal solutions.
Overall, these 9 surprising facts about Henry’s Law showcase its significance in understanding gas solubility, chemical reactions, and numerous practical applications. The law named after William Henry continues to be a fundamental concept in the field of chemistry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Henry’s Law is a fundamental principle in Chemistry that helps us understand the relationship between the concentration of a gas and its partial pressure in a solution. It was first proposed by the English chemist William Henry in the early 19th century and has since played a crucial role in various fields, including environmental science, physics, and engineering.Through Henry’s Law, we have learned some fascinating and surprising facts about the behavior of gases in solutions. We have discovered that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to its partial pressure, i.e., as the pressure increases, the solubility also increases. This principle has significant implications, such as in understanding the solubility of gases in natural water bodies and the efficiency of gas exchange in biological systems.Henry’s Law is a valuable tool that scientists and engineers use to study and predict the behavior of gases in various systems. It has paved the way for advancements in fields such as chemical engineering, environmental monitoring, and medical research. By understanding the underlying principles of Henry’s Law, we can continue to unlock further insights into the behavior of gases and their interactions with liquids.
FAQs
1. What is Henry’s Law?
Henry’s Law is a principle in Chemistry that describes the relationship between the concentration of a gas and its partial pressure in a solution. It states that the solubility of a gas is directly proportional to its partial pressure.
2. Who discovered Henry’s Law?
Henry’s Law was first proposed by the English chemist William Henry in the early 19th century. He conducted extensive experiments to elucidate the solubility of gases in liquids and formulated the fundamental principle that bears his name.
3. How does Henry’s Law affect natural water bodies?
Henry’s Law is significant in understanding the solubility of gases in natural water bodies. It influences the concentration of gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, in water, which, in turn, impacts the health and survival of aquatic organisms. It also plays a role in the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and water bodies.
4. Can Henry’s Law be applied to all gases?
Henry’s Law applies to ideal gases and their interactions with liquids. However, it may not hold true for gases that deviate significantly from ideal behavior or when complex interactions occur between the gas and the liquid molecules.
5. How is Henry’s Law used in research and engineering?
Henry’s Law is widely used in various scientific disciplines. It is applied in environmental monitoring to determine the concentration of gases in water bodies. Moreover, it plays a crucial role in chemical engineering processes, such as gas absorption and stripping, as well as in medical research and the development of gas exchange devices.
Dive deeper into fascinating chemistry concepts! Unravel the mysteries of chemical equilibrium and how it affects reactions. Explore the captivating world of physical chemistry, where matter and energy intertwine. Discover <Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures> and its impact on gas mixtures. Whether you're a curious learner or a seasoned scientist, these articles will spark your imagination and expand your understanding of the remarkable phenomena that shape our world. Get ready to embark on a thrilling journey through the realm of chemistry!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
