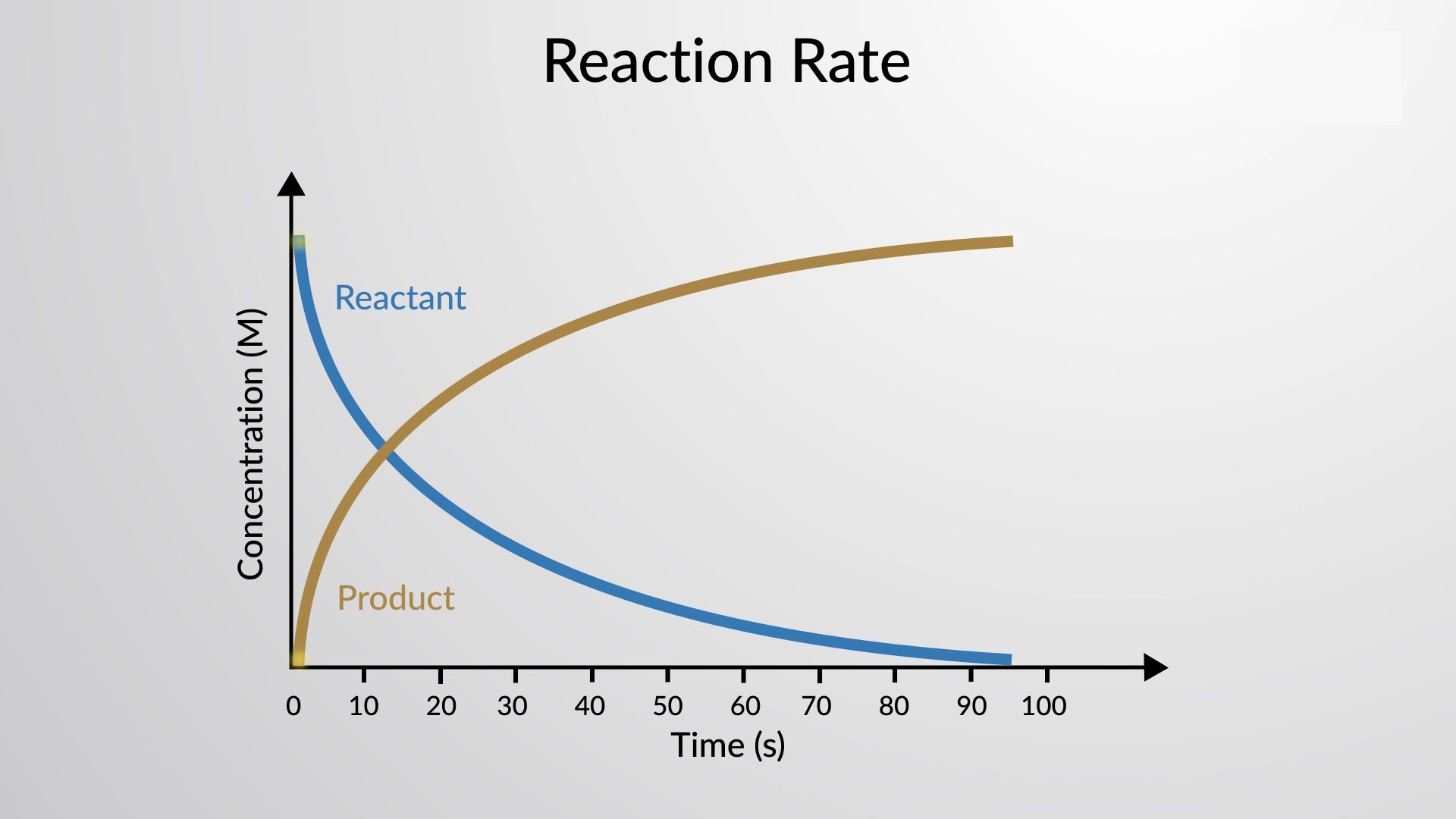
Reaction rate is a fundamental concept in chemistry that measures the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place. Understanding reaction rates is crucial in various applications, from designing efficient industrial processes to predicting the behavior of medications in our bodies.
In this article, we will take a deep dive into the world of reaction rates and explore 20 surprising facts that you may not have known. These facts will not only expand your knowledge of chemistry but also showcase the fascinating intricacies of how reactions occur.
So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to discover some intriguing facts about reaction rates that will leave you amazed!
Key Takeaways:
- Reaction rates can vary greatly, from lightning-fast to snail-paced, and are influenced by factors like temperature, concentration, and catalysts.
- Factors like surface area, pressure, and even the presence of a magnetic field can impact how fast chemical reactions occur.
Reaction rates can vary greatly.
The rate at which a reaction occurs can range from extremely fast to infinitesimally slow, depending on various factors.
Temperature affects reaction rates.
Higher temperatures generally lead to faster reaction rates due to increased molecular collisions and energy.
Concentration influences reaction rates.
Higher concentrations of reactants typically result in faster reaction rates because there are more particles available for collision.
Catalysts can speed up reactions.
Catalysts are substances that can increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process.
Surface area impacts reaction rates.
A larger surface area allows for more contact between reactant particles, leading to faster reaction rates.
Pressure affects reaction rates in gases.
High pressure can increase the rate of gas-phase reactions by forcing particles closer together, promoting collisions.
Reactant particle size matters.
Smaller reactant particles tend to have faster reaction rates because they have higher collision frequencies.
Nature of reactants influences reaction rates.
Reactants with stronger bonds or higher activation energies generally have slower reaction rates.
Reaction rates can be influenced by light.
Photoreactions are chemical reactions that are initiated or affected by light, altering the rate of the reaction.
Some reactions can be spontaneous.
Spontaneous reactions occur naturally without any external energy input, resulting in a rapid rate of reaction.
Reaction rates can be measured using a stopwatch.
A simple way to measure reaction rates is by timing how long it takes for a reaction to reach completion or a certain point.
Reactions can occur in multiple steps.
Complex reactions often involve a sequence of elementary steps, each with its own rate determining factor.
Reaction rates can be influenced by a magnetic field.
Magnetoreactions are reactions that are influenced by the presence of a magnetic field, affecting the rate at which they occur.
pH can impact reaction rates.
Changes in pH can affect the ionization of reactants and alter reaction rates, particularly in acid-base reactions.
Mixing can increase reaction rates.
Stirring or agitating reactants can enhance reaction rates by increasing the likelihood of collisions between particles.
Reaction rates can be affected by the presence of impurities.
Impurities in reactants can hinder or facilitate reactions, depending on their chemical properties and interactions.
Reaction rates can be influenced by the presence of a catalyst.
Enzymes and other types of catalysts can significantly increase reaction rates by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
Reaction rates can be influenced by the pressure of reactants.
In gas-phase reactions, increasing the pressure of reactants can lead to a higher collision frequency and, consequently, a faster reaction rate.
Reaction rates can be influenced by the presence of a solvent.
In solution-phase reactions, the nature and properties of the solvent can affect the reaction rate by influencing the solubility and mobility of the reactants.
Reaction rates can be influenced by the concentration of catalysts.
The concentration of catalysts can have a significant impact on reaction rates, with higher concentrations often resulting in faster reactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding reaction rates is crucial in the field of chemistry. The rate at which a reaction occurs can provide valuable insights into the underlying chemical processes, and it plays a significant role in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental studies. By considering factors that affect reaction rates, such as temperature, concentration, catalysts, and surface area, scientists can manipulate and control chemical reactions for desired outcomes.
By delving into the surprising facts about reaction rates, we can appreciate the intricacies of chemical reactions and how they impact our daily lives. From the astonishing speed at which certain reactions occur to the extraordinary influence of catalysts, reaction rates continue to fascinate and challenge scientists worldwide. Exploring these facts not only enriches our understanding of chemistry but also highlights the dynamic nature of the world around us.
FAQs
1. What is reaction rate?
The reaction rate refers to the speed of a chemical reaction. It measures how quickly reactants are converted into products.
2. What factors affect reaction rates?
Several factors influence reaction rates, including temperature, concentration of reactants, catalysts, and surface area.
3. How does temperature affect reaction rates?
In general, increasing the temperature increases the reaction rate. This is because higher temperatures provide more energy for reactant molecules to collide and react.
4. What role do catalysts play in reaction rates?
Catalysts increase the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. They provide an alternative reaction pathway with lower energy barriers.
5. Can reaction rates be slowed down or sped up?
Yes, reaction rates can be modified by adjusting the conditions. For instance, decreasing the temperature or concentration can slow down the reaction, while increasing them can speed it up.
6. What are some real-life examples of reaction rates?
Reaction rates are evident in everyday life. Examples include food spoilage, the burning of fuels, rusting of metals, and the digestion of food in our bodies.
Reaction rates hold countless surprises, but kinetics, rate constants, and second-order reactions offer even more intriguing facts. Delving deeper into kinetics reveals 16 fascinating phenomena that shape our understanding of chemical processes. Rate constants, often overlooked, harbor 13 mind-blowing truths waiting to be explored. Second-order reactions, seemingly complex, conceal 11 unbelievable facts that challenge our perceptions. Unraveling these mysteries promises a thrilling journey through the heart of chemistry, where curiosity and knowledge intertwine. Embark on this adventure and discover the secrets that lie within these captivating subjects.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
