Hund’s Rule is a fundamental principle in chemistry that governs the arrangement of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. Named after Friedrich Hund, a German physicist, Hund’s Rule has played a crucial role in understanding the behavior and properties of atoms and molecules.
In this article, we will explore 18 intriguing facts about Hund’s Rule, shedding light on its significance and implications in the field of chemistry. From its historical origins to its practical applications, we will delve into the intricacies of this rule and its impact on our understanding of electron configurations.
Whether you’re a student just beginning your journey into the world of chemistry, or a seasoned professional seeking to brush up on your knowledge, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of Hund’s Rule and its relevance in the study of atomic structure and chemical bonding.
Key Takeaways:
- Hund’s Rule explains how electrons behave in atoms and molecules, helping scientists understand and predict the unique properties of elements. It’s like a rulebook for electron behavior in the tiny world of chemistry!
- By following Hund’s Rule, scientists can figure out how electrons fill up the available spaces in atoms and molecules, leading to cool discoveries and advancements in science and technology.
Hund’s Rule: The Basics
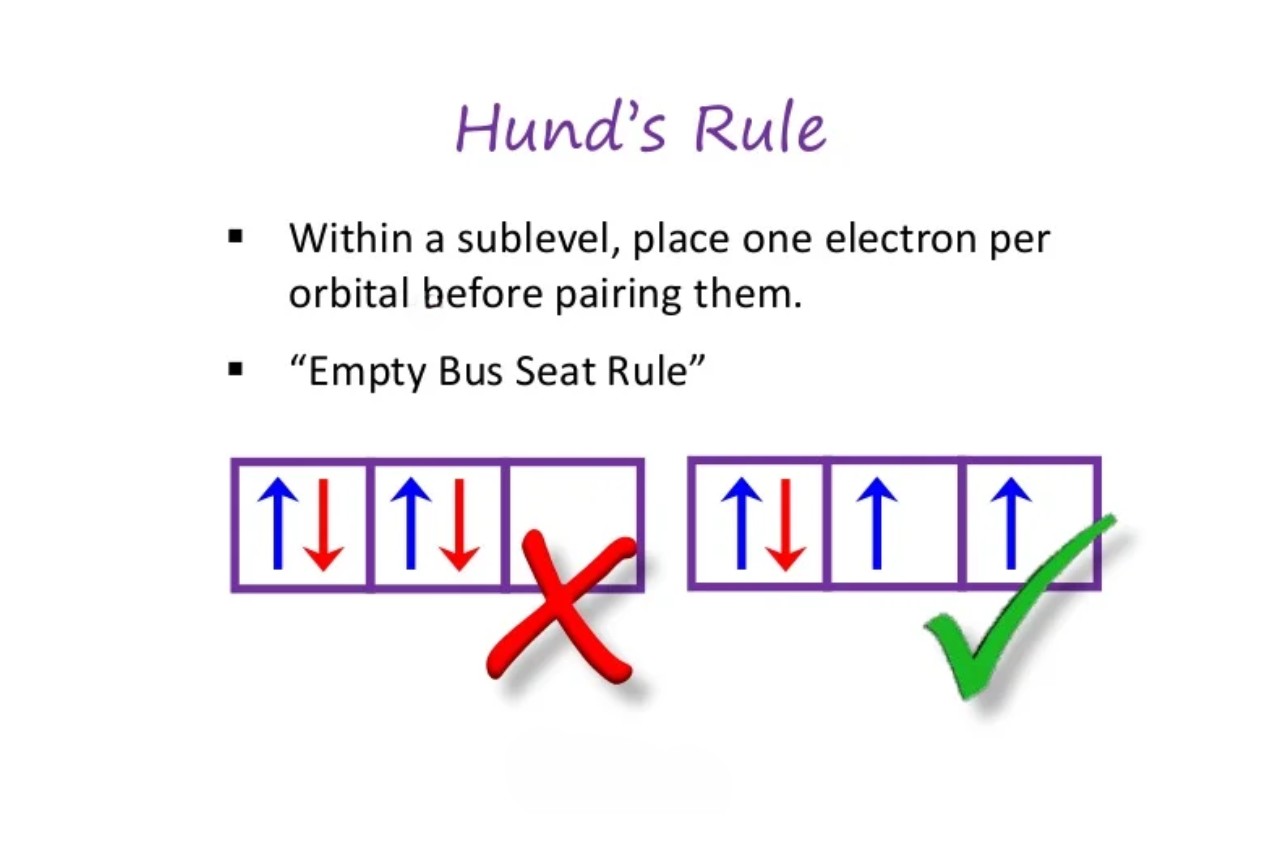
Hund’s Rule, also known as Hund’s first rule, is a fundamental principle in quantum mechanics that helps explain the electron behavior in atoms and molecules. It states that when filling an atom’s orbitals, electrons will occupy separate orbitals of the same energy before pairing up.
Named After Friedrich Hund
Hund’s Rule is named after the German physicist Friedrich Hund, who formulated the rule in Hund made significant contributions to the understanding of atomic structure and electron configurations.
Explains Electron Spin
Hund’s Rule provides an explanation for the phenomenon of electron spin. It states that electrons will first fill up empty orbitals of the same energy with parallel spins before occupying orbitals with opposite spins.
Maximizes Electron Repulsion
One of the key aspects of Hund’s Rule is that it helps maximize electron repulsion. By occupying separate orbitals with parallel spins, the electrons experience less repulsion and the overall stability of the atom or molecule increases.
Determines Electron Configurations
Hund’s Rule plays a crucial role in determining the electron configurations of elements. It provides a set of guidelines for how electrons fill up the available orbitals in an atom, leading to the unique arrangement of electrons in each element.
Applies to Both Atoms and Molecules
Hund’s Rule is applicable not only to individual atoms but also to molecules. It governs the distribution of electrons in molecular orbitals, aiding in the determination of molecular properties.
Key Principle in Chemistry
Hund’s Rule is a fundamental principle in chemistry that helps explain various phenomena such as chemical bonding, molecular structure, and the behavior of electrons in chemical reactions. Its understanding is crucial in the study of atomic and molecular properties.
Influences Periodic Trends
Hund’s Rule has a significant impact on periodic trends such as atomic radius and ionization energy. The electron configuration of an element, determined by Hund’s Rule, affects its physical and chemical properties, leading to observed variations across the periodic table.
Relates to Electron Affinity
Hund’s Rule also has implications for electron affinity, which is the energy change associated with gaining an electron. The electron configuration facilitated by Hund’s Rule influences an atom’s ability to accept additional electrons.
Key in Understanding Magnetism
Hund’s Rule is essential in understanding the magnetic properties of elements. The arrangement of electrons in orbitals with parallel spins contributes to the overall magnetic behavior exhibited by a material or substance.
Governs Ground State Configurations
Hund’s Rule governs the determination of ground state electron configurations, which represent the lowest energy arrangement of electrons in an atom or molecule. It provides insights into the stability and reactivity of chemical species.
Extends to Excited States
While Hund’s Rule primarily applies to ground state electron configurations, it also extends to excited states. Even in higher energy levels, electrons tend to occupy separate orbitals before pairing up, following Hund’s Rule.
Supports the Pauli Exclusion Principle
Hund’s Rule works in harmony with the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. These principles together provide a comprehensive understanding of electron behavior.
Account for Unique Properties of Transition Metals
Hund’s Rule helps explain the unique properties of transition metals, such as their characteristic color, variable oxidation states, and magnetic behavior. The partially filled d orbitals in transition metals follow Hund’s Rule, leading to these distinct characteristics.
Pioneering Work in Quantum Mechanics
Friedrich Hund’s formulation of Hund’s Rule represents a pioneering contribution to the development of quantum mechanics. It provided a theoretical framework that enabled a deeper understanding of the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules.
Basis for Aufbau Principle
The Aufbau Principle, which describes the building up of electron configurations from the lowest energy levels to higher ones, relies on Hund’s Rule. The principle follows the guidelines set by Hund’s Rule for the distribution of electrons in orbitals.
Essential for Spectroscopy
Hund’s Rule plays a crucial role in spectroscopic techniques, such as electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). It helps determine the energy levels and transitions of electrons, aiding in the interpretation of spectroscopic data.
Continues to Shape Chemistry Research
Hund’s Rule remains a fundamental concept in chemistry and continues to shape research in various fields. Its application extends beyond atomic and molecular studies, contributing to the advancement of materials science and theoretical chemistry.
Overall, Hund’s Rule provides essential insights into the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules. It allows scientists to understand and predict the unique properties of elements and compounds, contributing to advancements in many areas of science and technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hund’s rule is an important principle in chemistry that helps us understand the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules. By following Hund’s rule, we can determine the most stable and energetically favorable electron configurations. This rule states that electrons fill up orbitals of the same energy level one by one before pairing up. This leads to the electrons being spread out as much as possible, minimizing their repulsion and increasing the stability of the system. Hund’s rule has significant implications in understanding chemical bonding, the behavior of transition metals, and the magnetic properties of materials.
FAQs
Q: What is Hund’s rule?
A: Hund’s rule is a principle in chemistry that states that electrons fill up orbitals of the same energy level one by one before pairing up.
Q: Why is Hund’s rule important?
A: Hund’s rule is important because it helps us understand the arrangement of electrons in atoms and molecules. By following this rule, we can determine the most stable and energetically favorable electron configurations.
Q: How does Hund’s rule affect electron configurations?
A: Hund’s rule leads to the spread of electrons as much as possible, minimizing their repulsion and increasing the stability of the system.
Q: What are the implications of Hund’s rule in chemistry?
A: Hund’s rule has significant implications in understanding chemical bonding, the behavior of transition metals, and the magnetic properties of materials.
Hund's Rule provides a solid foundation for understanding electron behavior in atomic orbitals, but there's still more to explore! If you're curious about how electrons are represented using specific notation, our article on electron configuration notation will satisfy that curiosity. Unravel the intricacies of electron arrangements and gain a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of chemistry.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
