UV-Visible spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique widely used in the field of chemistry. It involves the measurement of the absorption of ultraviolet (UV) and visible light by molecules, providing valuable information about their electronic structure and bonding. This technique has revolutionized the way scientists analyze and study compounds, allowing them to uncover fascinating insights into the molecular world. In this article, we will explore ten astonishing facts about UV-Visible spectroscopy that will broaden your understanding of this indispensable tool in the field of chemistry. From its historical origins to its applications in various industries, UV-Visible spectroscopy has come a long way and continues to play a crucial role in scientific research and analysis. So, let’s dive into the world of UV-Visible spectroscopy and discover some intriguing and awe-inspiring facts!
Key Takeaways:
- UV-Visible Spectroscopy helps scientists analyze light absorption and identify chemicals in a non-destructive way, making it useful in pharmaceuticals, environmental studies, and quality control in industries.
- By using UV-Visible Spectroscopy, scientists can determine the concentration of substances, study chemical structures, and even detect impurities in pharmaceutical drugs, ensuring product safety and efficacy.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy is used to analyze the absorption and transmission of light.
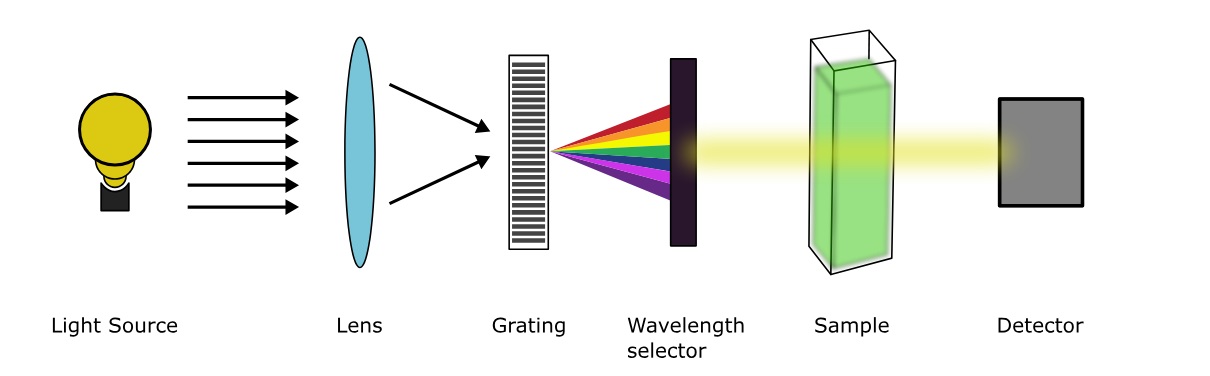
UV-Visible Spectroscopy is a widely used technique in analytical chemistry that involves measuring the absorption and transmission of light in the ultraviolet (UV) and visible (Vis) regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy can identify and quantify sample components.
By analyzing the absorption spectrum of a sample, UV-Visible Spectroscopy can provide valuable information about the presence and concentration of various chemical compounds.
It has applications in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, and forensic science.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy plays a crucial role in pharmaceutical analysis, environmental monitoring, and forensic investigations, helping scientists and researchers gain insights into the composition and properties of different substances.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy is non-destructive and requires minimal sample preparation.
One of the advantages of UV-Visible Spectroscopy is that it is a non-destructive technique, allowing multiple measurements to be taken on the same sample. Additionally, it usually requires minimal sample preparation, making it faster and more convenient.
The Beer-Lambert Law is a fundamental principle used in UV-Visible Spectroscopy.
The Beer-Lambert Law states that the absorbance of a substance is directly proportional to its concentration and the path length of the light passing through it. This law forms the basis for quantitative analysis using UV-Visible Spectroscopy.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy can be used to determine the chemical structure of compounds.
By analyzing the absorption peaks and patterns in a UV-Visible spectrum, scientists can gather information about the chemical structure and functional groups present in a compound.
It is commonly utilized for quality control purposes in industries.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy is extensively employed in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and cosmetics for quality control and assurance, ensuring consistent product standards.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy can be used to study reaction kinetics.
By monitoring how the absorbance of a compound changes over time, UV-Visible Spectroscopy can provide valuable information on reaction rates and mechanisms, helping researchers understand chemical reactions.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy can detect impurities in pharmaceutical drugs.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers use UV-Visible Spectroscopy to detect and quantify impurities in drug formulations, ensuring product safety and efficacy.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy can be coupled with other techniques for enhanced analysis.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy can be combined with other analytical techniques like chromatography or mass spectrometry to provide complementary information and more comprehensive analysis of complex samples.
Conclusion
UV-Visible spectroscopy is a fascinating field that has revolutionized the way we understand and analyze various substances. Through the absorption and emission of light, scientists are able to investigate the electronic structure and properties of materials in a non-destructive manner.
This article highlighted 10 astonishing facts about UV-Visible spectroscopy, including its applications in various industries, the principles behind the technique, and its limitations. From its role in drug discovery to its use in environmental monitoring, UV-Visible spectroscopy continues to be a crucial tool in scientific research and analysis.
By understanding these facts, you now have a deeper appreciation for the power of UV-Visible spectroscopy and its impact on our understanding of the world around us.
FAQs
Q: What is UV-Visible spectroscopy?
A: UV-Visible spectroscopy is a technique used to measure the absorption and emission of ultraviolet and visible light by substances to determine their electronic structure and properties.
Q: What are the applications of UV-Visible spectroscopy?
A: UV-Visible spectroscopy has a wide range of applications including pharmaceutical analysis, environmental monitoring, forensic science, and materials research.
Q: How does UV-Visible spectroscopy work?
A: UV-Visible spectroscopy works by passing a beam of light through a sample and measuring the intensity of the light before and after it interacts with the sample. The absorption or emission of certain wavelengths of light indicates the presence of specific substances or electronic transitions.
Q: What are the limitations of UV-Visible spectroscopy?
A: UV-Visible spectroscopy is limited by the need for a relatively concentrated sample, interference from impurities, and the inability to provide detailed structural information.
Q: Can UV-Visible spectroscopy be used for quantitative analysis?
A: Yes, UV-Visible spectroscopy can be used for quantitative analysis by measuring the amount of light absorbed or emitted by a sample and correlating it with the concentration of the substance of interest.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
