When it comes to the world of physics, the Beer-Lambert Law stands out as a fundamental principle in the study of light absorption. This law, named after August Beer and Johann Lambert who independently discovered it in the 19th century, provides a mathematical relationship between the concentration of a chemical species and the amount of light it absorbs. While this law may seem straightforward on the surface, delving deeper reveals some surprising and fascinating facts. In this article, we will explore 13 surprising facts about the Beer-Lambert Law, shedding light on its applications, limitations, and impact in various scientific fields. So sit back, grab a cold one if you’d like, and let’s dive into the intriguing world of the Beer-Lambert Law!
Key Takeaways:
- The Beer-Lambert Law, named after scientists Beer and Lambert, explains how the concentration of a substance affects the amount of light it absorbs. It’s like a mathematical equation for measuring solute concentration in a solution.
- This law is used in various scientific fields and helps determine unknown concentrations, analyze molecular structures, and ensure accurate measurements in industries like pharmaceuticals and food production. However, it has limitations and scientists must consider them when applying the law.
The Origin of Beer-Lambert Law
The Beer-Lambert Law, also known as the Beer-Lambert-Bouguer Law, was named after two scientists: August Beer and Johann Heinrich Lambert. They independently derived the law in the 18th and 19th centuries, respectively. Who would have thought that a scientific principle would be associated with beer?
The Law’s Relationship with Light Absorption
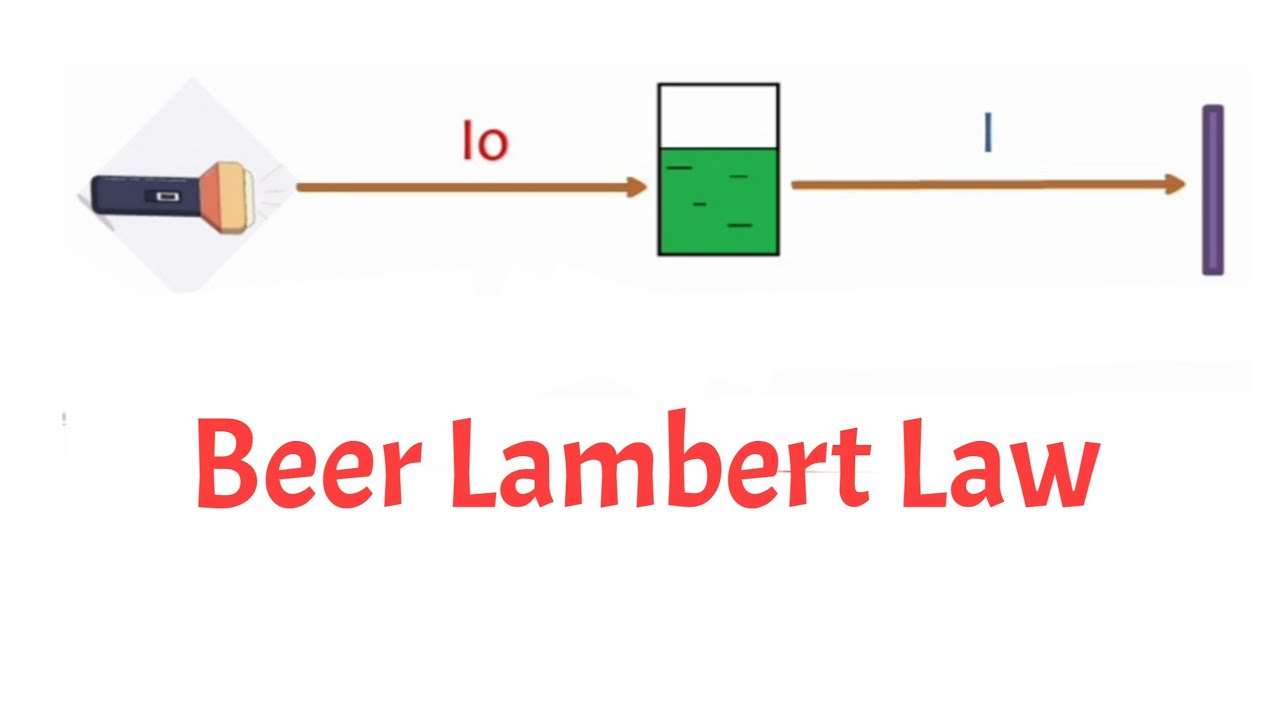
The Beer-Lambert Law is a fundamental principle in physics that describes how the concentration of a solute in a solution affects the amount of light it absorbs. The law states that the absorbance of light is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute and the path length of light through the solution. In simpler terms, the more solute present in a solution, the more light it absorbs.
It Applies to Various Fields
The Beer-Lambert Law is not limited to a specific branch of science. It is widely applicable in chemistry, physics, biochemistry, and even environmental science. This law provides a foundation for spectrophotometry, the technique used to measure the absorption of light by a substance.
The Relationship Between Absorbance and Concentration
According to the Beer-Lambert Law, the absorbance of light is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute. This means that as the concentration increases, so does the absorbance. It’s like a mathematical equation where the concentration and absorbance go hand in hand.
It Helps Determine Unknown Concentrations
One of the practical applications of the Beer-Lambert Law is its ability to determine the concentration of unknown substances. By measuring the absorbance of a sample and comparing it to a calibration curve, scientists can accurately determine the concentration of the solute in the solution. This makes it a valuable tool in chemical analysis.
It Accounts for Light Scattering
In addition to light absorption, the Beer-Lambert Law also accounts for light scattering, which can occur when light interacts with suspended particles or molecules in a solution. This incorporation of light scattering in the law makes it even more versatile and applicable in various scientific studies.
The Use of Spectrophotometers
Spectrophotometers are instruments commonly used to measure the absorbance of light in accordance with the Beer-Lambert Law. These devices emit a beam of light at a specific wavelength through a sample solution and measure the amount of light absorbed. Spectrophotometers are essential tools in many research and laboratory settings.
The Absorption Spectrum
When a substance is subjected to different wavelengths of light, it produces a characteristic absorption spectrum. This spectrum provides information about the substance’s chemical and physical properties. The Beer-Lambert Law is used to analyze and interpret the absorption spectrum of a compound.
Different Types of Absorbers
According to the Beer-Lambert Law, any compound that absorbs light can be considered an absorber. Examples include colored dyes, pigments, and even certain biological molecules such as chlorophyll. The law allows scientists to quantify the concentration of these absorbers in a solution.
The Importance of Path Length
The path length refers to the distance that light travels through a solution. According to the Beer-Lambert Law, the longer the path length, the more light is absorbed. Scientists can adjust the path length to optimize the measurement of absorbance in order to accurately determine the concentration of the solute.
Beer-Lambert Law and Molecular Structure
The Beer-Lambert Law provides valuable insights into the molecular structure of substances. By understanding how a compound absorbs light, scientists can gain information about its chemical bonds, electronic configuration, and even its spatial arrangement. This information is crucial for various disciplines, including pharmaceutical research.
Quantitative Analysis Applications
The Beer-Lambert Law is extensively used in quantitative analysis, particularly in determining the concentration of various substances. It is widely employed in industries such as pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and food production to ensure accurate measurements and quality control.
The Limitations of the Beer-Lambert Law
Although the Beer-Lambert Law is a powerful tool in many scientific fields, it does have limitations. For example, it assumes that the solution is dilute and that the solute and solvent do not interact with each other. It may also be affected by temperature, pH, and other factors. Scientists must consider these limitations when applying the law.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Beer-Lambert Law is a fundamental concept in the field of physics that helps us understand the relationship between the concentration of a substance and the amount of light it absorbs. It has numerous applications in various scientific disciplines, including chemistry, biochemistry, and environmental science.By understanding the key principles behind the Beer-Lambert Law, scientists and researchers can accurately determine the concentration of a substance in a solution, monitor chemical reactions, analyze the composition of complex mixtures, and even assess the quality of substances in industries such as brewing and pharmaceuticals.The Beer-Lambert Law is a powerful tool that continues to contribute to our understanding of how light interacts with matter. Its applications are vast and extend beyond the confines of physics, making it an essential concept in the world of science and research.
FAQs
1. What is the Beer-Lambert Law?
The Beer-Lambert Law, also known as Beer’s Law, describes the relationship between the concentration of a solution and the amount of light it absorbs.
2. How is the Beer-Lambert Law derived?
The Beer-Lambert Law is derived from the absorption of light by a material and is based on the assumption that the concentration of the absorbing species is directly proportional to the amount of light absorbed.
3. What are the key components of the Beer-Lambert Law equation?
The key components of the Beer-Lambert Law equation are the molar absorptivity (?), the path length (l), and the concentration of the solution (c).
4. What are some real-life applications of the Beer-Lambert Law?
The Beer-Lambert Law has various applications, including determining the concentration of analytes in solutions, monitoring chemical reactions, analyzing the composition of mixtures, and assessing the quality of substances in industries such as brewing and pharmaceuticals.
5. Are there any limitations or assumptions associated with the Beer-Lambert Law?
Yes, the Beer-Lambert Law assumes that the absorbing species are uniformly distributed and that there are no interactions or reactions between the absorbing species. Additionally, it assumes that the incident light is monochromatic and that the path length through the solution is constant.
Unraveling the mysteries of Beer-Lambert Law is just the beginning! Dive deeper into scientific wonders by exploring fascinating facts about spectroscopy. This powerful analytical technique harnesses light's interaction with matter, revealing secrets hidden within molecules. From identifying unknown substances to studying chemical structures, spectroscopy opens doors to groundbreaking discoveries across various fields. Whether you're a curious mind or seasoned scientist, prepare to be captivated by spectroscopy's limitless potential. Embark on an enlightening journey through its history, applications, and surprising facts that will leave you marveling at the invisible world around us.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
