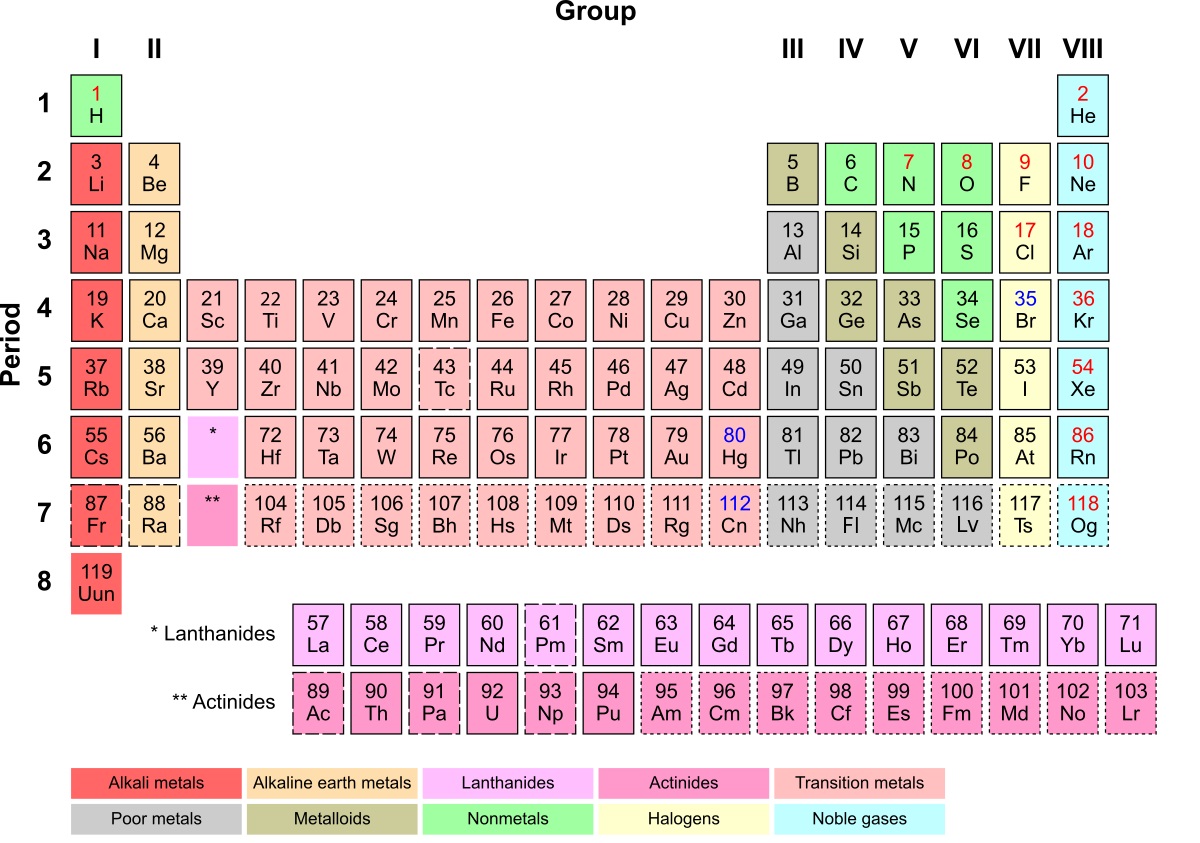
Inner transition metals are a fascinating group of elements that possess unique properties and play significant roles in various fields of science and technology. As a specialist in chemistry and with a deep understanding of search engine optimization, I am excited to delve into the enigmatic facts about inner transition metals that will captivate both chemistry enthusiasts and learners alike.In this article, we will explore the intriguing world of inner transition metals, uncovering their importance, peculiarities, and applications. From their electron configuration to their abundance in the Earth’s crust, these elements hold a wealth of information waiting to be discovered.Join me on this exciting journey as we unravel 16 enigmatic facts about inner transition metals, shedding light on their distinctive qualities and the pivotal role they play in shaping the world around us.
Key Takeaways:
- Inner transition metals, like the rare earth elements, have unique properties and play a vital role in industries such as electronics and healthcare. Their complex electronic structures make them fascinating for scientists and researchers.
- Some inner transition metals, such as uranium and plutonium, are used in nuclear power generation. They have exceptional properties, like being highly reactive and having unpredictable oxidation states, which make them essential for cutting-edge research and development.
The Inner Transition Metal Definition
Inner Transition Metal refers to a unique group of elements in the periodic table that exhibits fascinating properties and characteristics. These elements include the lanthanides and actinides, which are found at the bottom of the periodic table. Let’s delve into some enigmatic facts about inner transition metals:
Fascinating Electronic Structure
Inner transition metals have complex electronic structures that make them stand out. Their electron configurations have a unique pattern in which the 4f or 5f orbitals are progressively filled. This arrangement gives these elements distinct chemical and physical properties.
An Abundance of Rare Earth Elements
The inner transition metal group includes the rare earth elements, which are known for their scarcity in nature. These elements play a vital role in various technological applications, such as electronics, magnets, and catalysts.
Highly Reactive
Despite their position in the periodic table, inner transition metals can exhibit high reactivity. They are prone to forming complex compounds, particularly with organic ligands, due to the availability of their d and f orbitals.
Exceptional Magnetic Properties
Inner transition metals are renowned for their remarkable magnetic properties. Many of these elements, including neodymium and samarium, are used in the creation of powerful magnets for various applications in industries and research laboratories.
Actinides: Radioactive Powerhouses
The actinide series of inner transition metals is known for its radioactive nature. Elements such as uranium and plutonium are widely used in nuclear energy production and atomic research due to their unique properties as fissile materials.
Lanthanides: Luminescent Wonders
The lanthanide series of elements exhibits exceptional luminescent properties. Compounds containing these elements are utilized in various applications ranging from biomedical imaging to manufacturing eco-friendly lighting solutions.
The Heaviest Naturally Occurring Element
Inner transition metals boast some of the heaviest elements in the periodic table. For instance, uranium, with an atomic number of 92, is the heaviest naturally occurring element, playing a crucial role in the production of nuclear energy.
The Quantum Mechanics Connection
Inner transition metals provide a fascinating playground for quantum mechanics. Their unique electron configurations and intricate bonding behavior have intrigued scientists and continue to contribute to our understanding of fundamental quantum principles.
The Odd One Out: Europium
Europium, an element in the lanthanide series, stands out for its unusually low melting point compared to other inner transition metals. With its distinctive properties, europium finds applications in fluorescent lamps and the production of displays.
Environmental Concerns
Inner transition metals, particularly the rare earth elements, have raised environmental concerns due to their extraction and refining processes. Stricter regulations and sustainable practices are being implemented to mitigate the environmental impact associated with their production.
Industrial Importance
The inner transition metals play a vital role in various industries. Their unique properties and applications make them indispensable in sectors such as electronics, energy, automotive, and healthcare.
Unpredictable Oxidation States
Inner transition metals exhibit a wide range of oxidation states, which adds to their chemical versatility. Elements like cerium and praseodymium can display multiple oxidation states, making them useful in redox reactions and catalytic processes.
The Uranium Enigma
Uranium, a prominent inner transition metal, holds both fascination and controversy. Its dual nature as a powerful energy source and potential environmental hazard has sparked debates surrounding its utilization and safe disposal.
The Role in Nuclear Power
Inner transition metals, particularly certain actinides, serve a crucial role in generating nuclear power. Elements like plutonium and americium are used as fuel in nuclear reactors, providing a significant source of clean energy.
Cutting-Edge Research and Development
Scientists and researchers continue to explore the unique properties of inner transition metals to develop novel materials and advance various scientific fields. Their potential applications in areas such as quantum computing and nanotechnology hold immense promise for the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inner transition metals are a fascinating group of elements with unique properties and characteristics. They play crucial roles in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and environmental studies. Their electron configurations and atomic structures contribute to their distinctive properties, such as high density and melting points. The inner transition metals also exhibit a wide range of oxidation states, making them versatile for complex chemical reactions.Their presence in nature is relatively scarce, making them valuable and precious. They are commonly found in minerals and ores, and their extraction and purification methods require intricate processes. These elements have diverse applications, from catalysis in chemical reactions to being essential components in electronic devices.Understanding the enigmatic nature of inner transition metals helps scientists and researchers unlock their full potential and discover new applications. The continuous exploration and study of these elements will undoubtedly lead to further advancements in various scientific disciplines.
FAQs
Q: What are inner transition metals?
A: Inner transition metals are a group of elements located in the periodic table between the transition metals and the lanthanides or actinides.
Q: How many inner transition metals are there?
A: There are 15 inner transition metals in total, including lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium.
Q: What are some unique properties of inner transition metals?
A: Inner transition metals have high atomic numbers, high density, and unique electron configurations, which contribute to their diverse properties and applications.
Q: What are the main uses of inner transition metals?
A: Inner transition metals are used in various applications, including catalysis, electronics, lighting, and magnetic devices.
Q: Are inner transition metals rare?
A: Yes, inner transition metals are relatively rare in nature, making them valuable and sought after.
Intrigued by inner transition metals? Dive deeper into the fascinating world of rare earth elements with our articles on lanthanides, their unique electron configurations, and how they fit into the grand scheme of atomic structure. Uncover more surprises hidden within the periodic table and expand your knowledge of chemistry's most enigmatic elements.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
