Metalloids, also known as semimetals, form an intriguing group of elements on the periodic table. They exhibit properties that are a blend of both metals and nonmetals, making them unique and captivating subjects of study in the field of chemistry. With their intermediate characteristics, metalloids play significant roles in various applications, from electronics and semiconductors to environmental remediation and medicine. In this article, we will explore 17 fascinating facts about metalloids that will help you appreciate their versatility and importance in the world of science. So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the captivating world of metalloids!
Key Takeaways:
- Metalloids, like boron and silicon, are unique elements with both metallic and non-metallic properties. They play a crucial role in technology and everyday life, from electronics to medicine.
- Metalloids, such as arsenic and tellurium, have diverse applications but require responsible handling to minimize environmental impact. Ongoing research continues to uncover their potential in scientific discoveries and future innovations.
Metalloids, the Elements on the Border
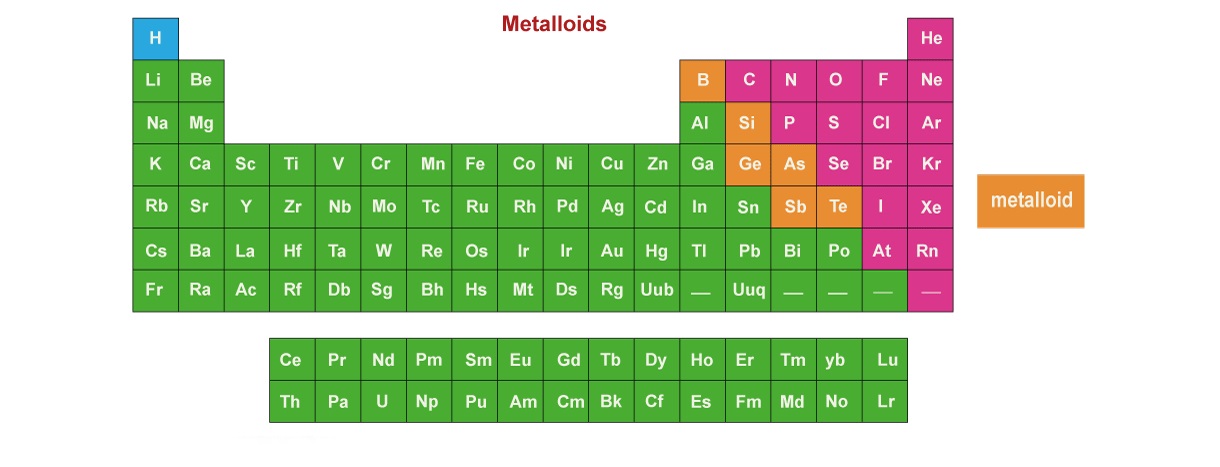
Metalloids are a unique group of elements found on the periodic table, situated between metals and non-metals. These elements possess both metallic and non-metallic properties, making them versatile and intriguing.
The Big 7
There are seven known metalloids: boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, and polonium. Each of these elements exhibits distinct characteristics and finds various applications in different industries.
Semiconductor Wonders
Metalloids are renowned for their semiconducting properties, allowing them to conduct electricity under certain conditions. This quality makes them vital in the manufacturing of electronic devices like transistors and diodes.
Boron, the Lightest Metalloid
Boron, the first element on the metalloid list, is the lightest of the group. Known for its high strength and low density, boron finds use in various applications, including the production of lightweight alloys and heat-resistant materials.
Silicon, the Foundation of Technology
Silicon, perhaps the most well-known metalloid, is an essential component in the production of semiconductors. It is widely used in the electronics industry, playing a crucial role in the development of computers, smartphones, and solar cells.
Germanium, the “Hidden” Element
Germanium is often referred to as the “hidden” element due to its limited occurrence in the Earth’s crust. It possesses excellent optical and electrical properties, making it valuable in the production of infrared optics and semiconductor devices.
Arsenic, the Notorious Poison
Arsenic is infamous for its toxic nature, but it also has practical applications. It is used in the manufacturing of insecticides, wood preservatives, and certain medical drugs, highlighting its dual nature and versatility.
The Mysterious Antimony
Antimony has a long history of use in various industries, including cosmetics, paint production, and flame retardants. Its complex chemical properties continue to intrigue scientists, making it a subject of ongoing research.
Tellurium, the Rare Element
Tellurium is a relatively rare metalloid found in small amounts in the Earth’s crust. It is used in the production of alloys, as well as in applications such as solar panels and thermoelectric devices due to its unique electrical conductivity.
Polonium, the Radioactive Metalloid
Polonium is a highly radioactive metalloid with limited natural occurrence. Due to its radioactive nature, it finds application in various fields, including nuclear physics research and in some thermonuclear batteries.
Metalloids in Nature
Metalloids can be found in various natural environments, ranging from minerals and ores to the Earth’s crust. Their presence in the natural world contributes to the overall balance and diversity of our planet.
Metalloids in Everyday Life
Metalloids play a significant role in our daily lives, often without us realizing it. They can be found in items such as glass, ceramics, and even in the medicine we take, contributing to numerous technological advancements.
Metalloids and Environmental Impact
Due to their versatility and use in various industries, metalloids can have environmental implications. It is important to handle and dispose of them responsibly to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human health.
Metalloids and Scientific Discoveries
Metalloids have played a vital role in numerous scientific advancements and discoveries. They have contributed to breakthroughs in fields such as materials science, nanotechnology, and renewable energy research.
Metalloids in Space
Metalloids also have a presence beyond Earth. Scientists have detected their existence in meteorites and other celestial bodies, shedding light on the composition and evolution of the universe.
Metalloids and Human Health
While some metalloids can be toxic, they also have implications in medicine. Compounds containing metalloids are used in treatments for certain diseases, demonstrating their potential in the field of healthcare.
The Future of Metalloids
As scientific research continues to progress, our understanding of metalloids and their potential applications grows. The unique properties of metalloids make them a focus of ongoing studies, ensuring their relevance in future technological advancements.
In conclusion, these 17 captivating facts about metalloids highlight their significance in various industries, their connection to our everyday lives, and their potential to shape the future. The distinct characteristics of metalloids make them a fascinating subject for scientific exploration and innovation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, metalloids are a fascinating group of elements that possess both metallic and non-metallic properties. They play a crucial role in various fields such as electronics, industry, and medicine. From their unique physical and chemical characteristics to their applications in everyday life, metalloids continue to intrigue scientists and researchers worldwide.
FAQs
1. What are metalloids?
Metalloids are elements that exhibit properties of both metals and non-metals. They possess characteristics such as semi-conductivity, variability in their atomic structure, and intermediate electrical and thermal conductivity.
2. How many metalloids are there?
There are six recognized metalloids: boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and tellurium (Te). These elements are located along the “staircase” line of the periodic table, separating the metals from the non-metals.
3. What are the uses of metalloids?
Metalloids have diverse applications across various industries. For example, silicon is widely used in electronics and solar panels, arsenic has applications in medicine, and boron is used in the production of heat-resistant glasses and ceramics.
4. Can metalloids conduct electricity?
Yes, metalloids can conduct electricity, but their conductivity is intermediate between that of metals and non-metals. They can become better conductors by adding impurities or by altering their structure, which makes them useful in the field of electronics.
5. Are metalloids naturally occurring?
Yes, metalloids are naturally occurring elements and can be found in the Earth’s crust. They are commonly found in minerals and ores, and their extraction and purification are essential for various industrial processes.
Metalloids may be the unsung heroes of the periodic table, but their fascinating properties and applications make them worthy of exploration. From boron's lightweight strength to silicon's technological prowess, these elements bridge the gap between metals and nonmetals in captivating ways. Arsenic's notorious reputation as a poison belies its usefulness in semiconductors, while tellurium's rarity hasn't stopped it from making its mark in solar panels and thermoelectric devices. As you've discovered the wonders of metalloids, why not delve deeper into the mysteries of germanium, another metalloid with its own set of amazing properties and uses?
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
