Point defects, also known as crystallographic defects, are imperfections or irregularities in the arrangement of atoms in a crystal lattice. These defects can occur due to various reasons, such as impurities, vacancies, or substitutions in the crystal structure. While they might be viewed as flaws, point defects play a crucial role in determining the properties and behavior of materials.
From influencing the electrical conductivity of semiconductors to enhancing the catalytic activity of materials, point defects have garnered significant attention in the field of chemistry. In this article, we will explore 12 mind-blowing facts about point defects, shedding light on their profound impact on the world of materials science and beyond.
Key Takeaways:
- Point defects are tiny imperfections in materials that can change their properties. They come in different types, like vacancies and interstitials, and can be used to make better solar cells and magnetic materials.
- Point defects are like tiny superheroes in the world of chemistry, influencing everything from material strength to solar energy conversion. By understanding and controlling these defects, scientists can create amazing new materials for the future.
Point Defects: Imperfections on the Atomic Scale
Point defects are atomic-scale imperfections that occur in crystalline solids. These defects can significantly influence the properties and behavior of materials.
Different Types of Point Defects
There are several types of point defects, including vacancies, interstitials, substitutional atoms, and impurity atoms. Each type has a unique effect on the material’s structure and properties.
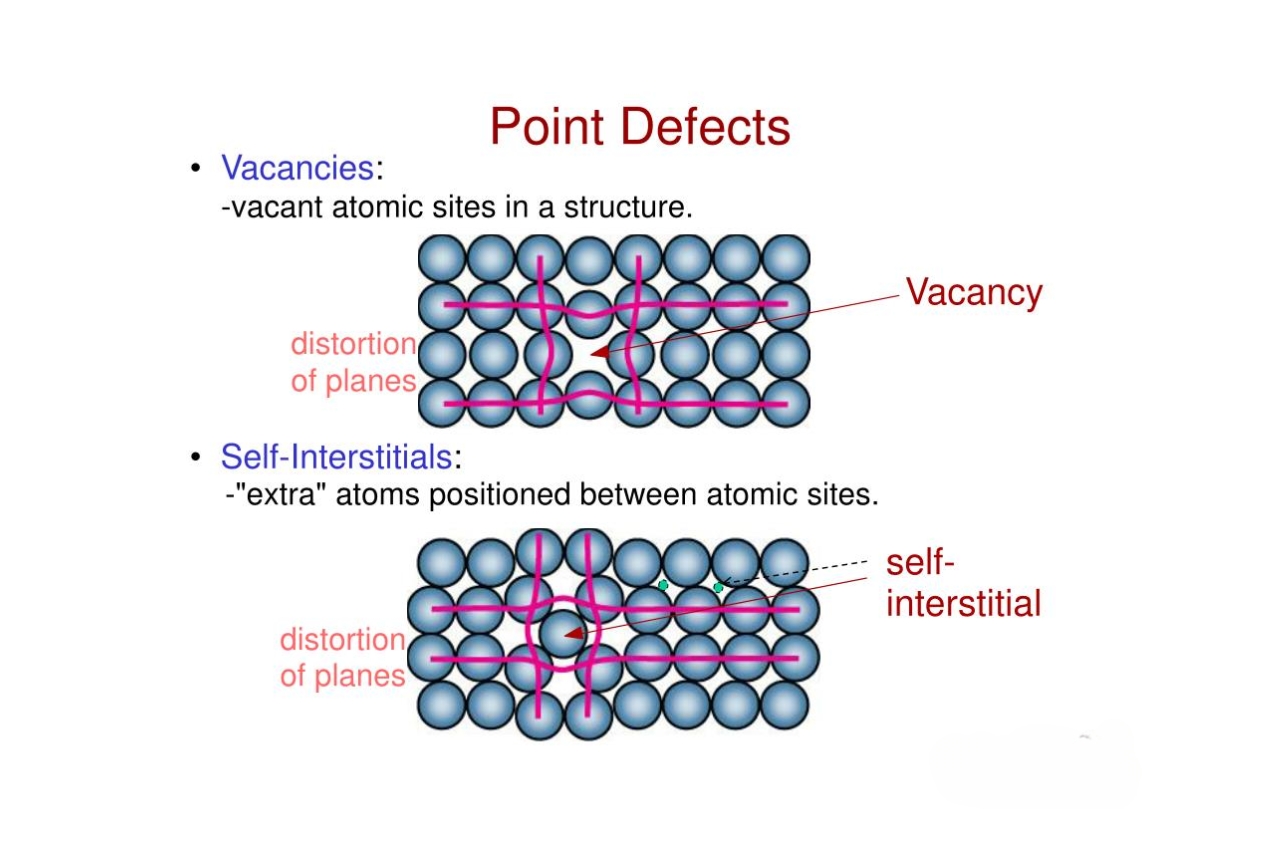
Vacancies: Missing Atoms in Crystal Lattice
Vacancies are point defects that arise when an atom is missing from its proper position in the crystal lattice. These vacancies affect the density and conductivity of the material.
Interstitials: Extra Atoms Squeezed into Crystal Structure
Interstitials occur when an extra atom is trapped in the interstitial spaces between the regular lattice atoms. These defects can alter the mechanical strength and diffusion properties of the material.
Substitutional Atoms: Foreign Atoms Taking the Place of Regular Atoms
Substitutional point defects occur when foreign atoms replace or substitute regular lattice atoms. These substitutions can introduce different chemical properties into the material.
Impurity Atoms: Unwanted Foreign Atoms Present in the Material
Impurity atoms are unwanted foreign atoms that are present in a material. These defects can affect the electrical conductivity, optical properties, and even the color of the material.
Point Defects Influence Material Properties
Point defects can significantly impact the mechanical, electrical, thermal, and optical properties of materials. Controlling these defects can lead to the development of new materials with enhanced characteristics.
Point Defects in Semiconductor Devices
In semiconductor devices, point defects play a crucial role in determining the device’s performance. The intentional introduction of specific defects can modulate conductivity and other semiconductor properties.
Point Defects and Catalysis
Point defects are critical in catalysis, where they can provide active sites for chemical reactions to occur. Understanding and controlling these defects can lead to improved catalytic performance.
Point Defects and Solar Energy Conversion
Solar cells utilize point defects to enhance their efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. Defect engineering techniques are employed to optimize charge transport and reduce energy losses.
Point Defects in Magnetic Materials
The presence of point defects can affect the magnetic properties of materials. Manipulating these defects enables the development of advanced magnetic materials for various applications.
Point Defects and Nanotechnology
Point defects play a crucial role in nanotechnology, where they can be utilized to engineer materials with desired properties at the atomic scale. This opens up possibilities for advancements in fields such as electronics, medicine, and energy.
These 12 mind-blowing facts about point defects demonstrate the significance of these atomic-scale imperfections in materials science and engineering. From their influence on material properties to their applications in various technologies, point defects continue to spark innovation and exploration in the field of chemistry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, point defects are fascinating and integral to the world of chemistry. These minuscule imperfections in crystal structures have a profound impact on the properties and behavior of materials. From enhancing conductivity to contributing to the vibrant colors of gems, point defects shape the world around us in remarkable ways.Understanding point defects not only deepens our knowledge of materials but also opens up new avenues for technological advancements. By harnessing the power of point defects, scientists and engineers can develop improved electronic devices, efficient catalytic systems, and innovative energy storage solutions.As we continue to explore the intricate world of point defects, the possibilities for discovery and innovation are boundless. These 12 mind-blowing facts about point defects serve as a glimpse into the vast potential that lies within these tiny imperfections. So, the next time you marvel at the brilliance of a gem or use a cutting-edge electronic device, remember that point defects are the hidden heroes shaping our modern world.
FAQs
1. What are point defects?
Point defects are atomic or molecular level imperfections in crystal structures that result from missing or extra atoms, or the substitution of atoms.
2. What is the significance of point defects in materials?
Point defects alter the properties and behavior of materials, influencing factors such as conductivity, color, and mechanical strength.
3. How do point defects affect electrical conductivity?
Point defects can introduce additional charge carriers in a material, thereby increasing its conductivity.
4. Are point defects always undesirable?
No, point defects can have both positive and negative effects depending on the specific application. For example, point defects are essential in semiconductors for their electronic properties.
5. Can point defects be intentionally created?
Yes, point defects can be deliberately introduced through processes such as doping or ion implantation to alter the properties of materials for specific purposes.
6. What is the role of point defects in catalysis?
Point defects can act as active sites for chemical reactions, enhancing catalytic activity and improving the efficiency of various chemical processes.
7. Do point defects influence the color of materials?
Yes, certain point defects can absorb or reflect specific wavelengths of light, leading to the distinct coloration of materials such as gemstones.
8. Can point defects affect the mechanical strength of a material?
Point defects can influence the mechanical properties of materials, including hardness, toughness, and brittleness.
9. Are all point defects permanent?
No, some point defects can be thermally or chemically annealed, meaning they can be reversed under certain conditions.
10. Are point defects only found in crystalline materials?
Point defects are predominantly associated with crystalline materials, but they can also occur in amorphous materials to a lesser extent.
11. Can point defects play a role in energy storage?
Yes, point defects can impact the performance of energy storage devices such as batteries and fuel cells by influencing ion diffusion, charge transfer, and overall efficiency.
12. Are point defects studied extensively in research?
Yes, point defects are actively researched to unlock their potential in various fields of science and engineering, including materials science, solid-state physics, and nanotechnology.
Point defects may be tiny, but their impact is immense. From influencing material properties to revolutionizing nanotechnology, these atomic-scale imperfections hold countless secrets waiting to be uncovered. If you found these facts about point defects captivating, just wait until you explore the intriguing world of Schottky defects. Prepare to have your mind blown once again as you delve into the depths of crystal structures and their fascinating imperfections.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
