Welcome to the intriguing world of chemistry! In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic realm of Hess’s Law, a fundamental concept in thermochemistry. Hess’s Law, named after the Swiss scientist Germain Hess, allows us to calculate the heat of reaction for a chemical equation by combining known reactions. It is a powerful tool that helps us understand the principles of energy transfer in chemical reactions.
In this article, we will uncover 12 fascinating and lesser-known facts about Hess’s Law, shedding light on its significance and applications. So, whether you are a chemistry enthusiast or simply curious about the inner workings of chemical reactions, prepare to embark on a journey that will unravel the mysteries behind Hess’s Law.
Key Takeaways:
- Hess’s Law helps calculate heat changes in chemistry by using a cool trick called enthalpy. It’s like a math puzzle for chemists to solve energy mysteries in reactions.
- Hess’s Law is like a superhero power for chemists, helping them understand and predict energy changes in chemical reactions. It’s like having a secret formula to unlock the energy secrets of the universe!
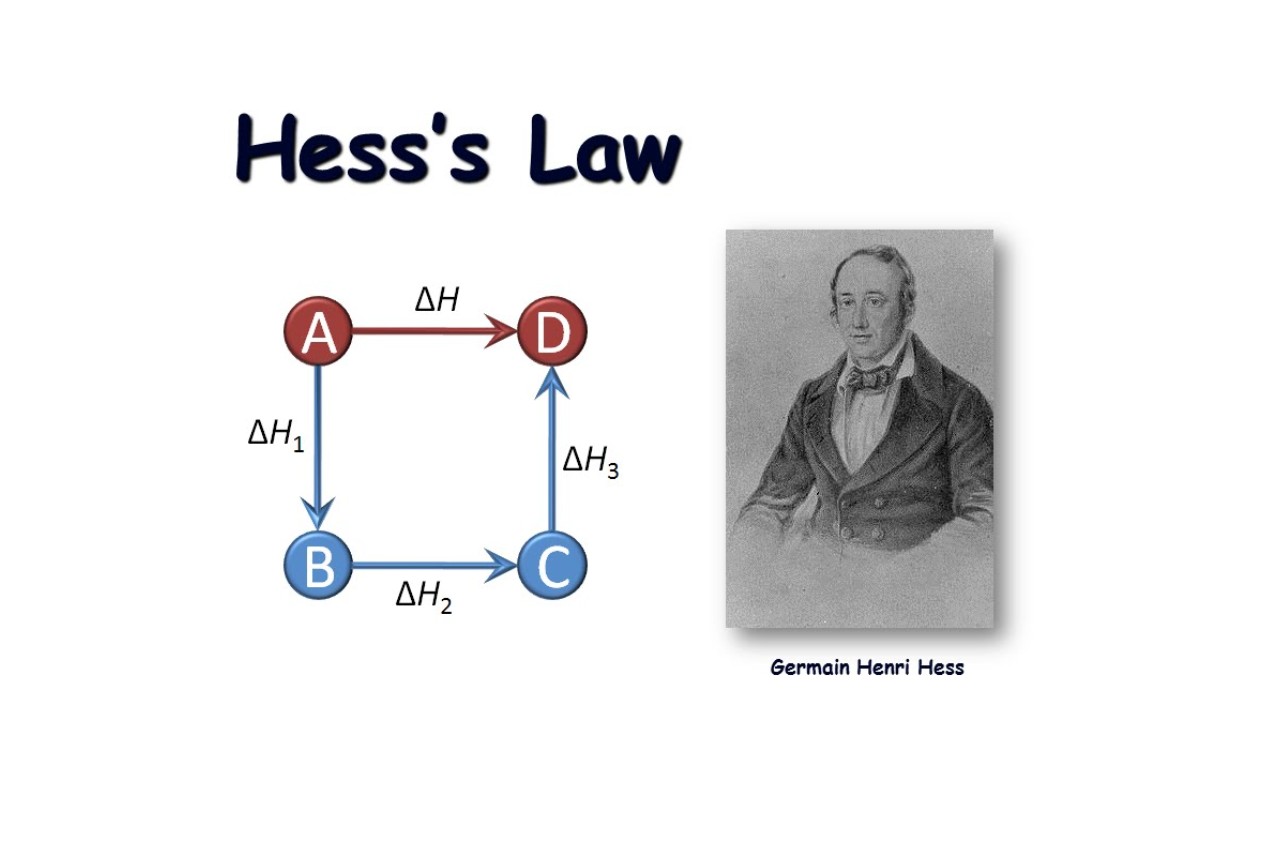
Hess’s Law is named after Germain Hess.
Hess’s Law, also known as the Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation, is named after the Swiss-Russian chemist Germain Hess. Hess proposed this thermodynamic principle in the mid-19th century.
Hess’s Law is based on the principle of energy conservation.
Hess’s Law is based on the fundamental principle of energy conservation, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed. This principle plays a crucial role in understanding the concept of heat changes in chemical reactions.
Hess’s Law allows for the calculation of enthalpy change.
One of the key applications of Hess’s Law is in calculating the enthalpy change (?H) of a chemical reaction. By considering a series of intermediate reactions and their corresponding enthalpy changes, the overall enthalpy change for the desired reaction can be determined.
Hess’s Law relies on the concept of enthalpy of formation.
Enthalpy of formation is a measure of the heat released or absorbed when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. Hess’s Law relies on the concept of enthalpy of formation to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction.
Hess’s Law is independent of the reaction pathway.
One fascinating aspect of Hess’s Law is that it is independent of the reaction pathway. This means that the overall enthalpy change of a reaction remains the same regardless of the route taken or the intermediates involved, as long as the initial and final conditions are the same.
Hess’s Law can be used to determine unknown enthalpy changes.
Hess’s Law provides a powerful tool for determining unknown enthalpy changes of reactions. By combining known reactions and their enthalpy changes, the enthalpy change of an unknown reaction can be determined through algebraic manipulation.
Hess’s Law is applicable to both physical and chemical processes.
While commonly used in chemical reactions, Hess’s Law is applicable to a wide range of processes, including physical changes such as phase transitions and dissolution. It allows for the determination of the overall enthalpy change in these processes.
Hess’s Law is based on extensive research and experimentation.
Hess’s Law was developed based on extensive research and experimentation conducted by Germain Hess and other scientists. Their investigations into the heat changes of various reactions laid the foundation for this important thermodynamic principle.
Hess’s Law can be applied to calculate lattice energy.
Lattice energy is the energy released when gaseous ions combine to form an ionic solid. By using Hess’s Law, the lattice energy of an ionic compound can be calculated by considering the formation of the compound from its constituent elements.
Hess’s Law is consistent with the first law of thermodynamics.
Hess’s Law is consistent with the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy is conserved in any physical or chemical process. The application of Hess’s Law in calculating enthalpy changes aligns with the energy conservation principle.
Hess’s Law is widely used in the field of thermochemistry.
Thermochemistry, a branch of physical chemistry, heavily relies on Hess’s Law for analyzing and predicting energy changes in chemical reactions. It provides a systematic approach for determining enthalpy changes and understanding the underlying thermodynamic principles.
Hess’s Law has practical applications in industries.
Hess’s Law finds practical applications in various industries, such as energy production and pharmaceutical manufacturing. It allows for the optimization of processes, efficient energy utilization, and the design of new chemical reactions.
Conclusion
Hess’s Law is a fundamental principle in chemistry that allows scientists to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction by using the enthalpy changes of other reactions. This law provides a powerful tool for understanding and predicting the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions.
Throughout this article, we have explored 12 enigmatic facts about Hess’s Law, shedding light on its significance and applications. From its origins to its practical uses in determining standard enthalpy of formation and reaction, Hess’s Law continues to play a crucial role in the field of chemistry.
By understanding and utilizing Hess’s Law, chemists can make more accurate predictions about the energy changes that accompany chemical reactions. This knowledge allows for the development of efficient processes and the creation of new materials that can positively impact various industries.
As we delve deeper into the world of chemistry, it is fascinating to uncover the mysteries and intricacies of laws like Hess’s Law, which contribute to our understanding of the fundamental principles governing chemical reactions.
FAQs
1. What is Hess’s Law?
Hess’s Law is a principle in chemistry that states that the overall enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is independent of the pathway taken from the reactants to the products.
2. How is Hess’s Law used?
Hess’s Law is used to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction by combining the enthalpy changes of other reactions. This allows chemists to determine the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions.
3. Why is Hess’s Law important?
Hess’s Law is important because it provides a method for determining the enthalpy change of a reaction even when direct measurements are not possible. It allows scientists to understand and predict the energy changes that occur during chemical reactions.
4. Can Hess’s Law be applied to all reactions?
Yes, Hess’s Law can be applied to all reactions as long as the reaction is fundamentally the same, meaning the reactants and products are the same.
5. Are there any limitations to using Hess’s Law?
One limitation of using Hess’s Law is that it assumes that the reaction is taking place under standard conditions. Additionally, if the reaction involves a change in phase, like a solid turning into a gas, additional calculations may be required.
Hess's Law unveils chemistry's enigmatic energy changes, but don't stop exploring now! Dive deeper into fascinating chemistry facts that will blow your mind. Enthalpy's extraordinary nature awaits your discovery, promising to reshape your understanding of chemical reactions. Moreover, prepare to be amazed by energy conservation's surprising principles that underpin our universe's fundamental workings. Keep feeding your curiosity and unraveling science's captivating mysteries!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
