Polyprotic acids are compounds that have multiple ionizable hydrogen atoms, meaning they can donate more than one proton in a chemical reaction. These acids play a crucial role in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and environmental sciences. Understanding the properties and behavior of polyprotic acids is essential for carrying out accurate calculations and predicting their effects in different contexts.
In this article, we will explore 19 fascinating facts about polyprotic acids. From their definition and classification to their uses and real-life applications, you will discover the intricacies of these compounds that make them both interesting and important. So, let’s dive into the world of polyprotic acids and unravel the mysteries that surround them.
Key Takeaways:
- Polyprotic acids, like phosphoric acid in soda, can donate multiple protons, affecting taste and industrial processes. They’re found in everyday products and play a role in acid-base balance in the body.
- Polyprotic acids, such as citric acid in fruits, have multiple dissociation steps and are used in acid-base titrations and buffer solutions. They contribute to the acidity of rainwater and have various industrial applications.
What is Polyprotic Acid?
Polyprotic acid is a type of acid that can donate more than one proton or hydrogen ion per molecule. It belongs to a class of acids known as polybasic acids and is characterized by its ability to dissociate multiple times in water.
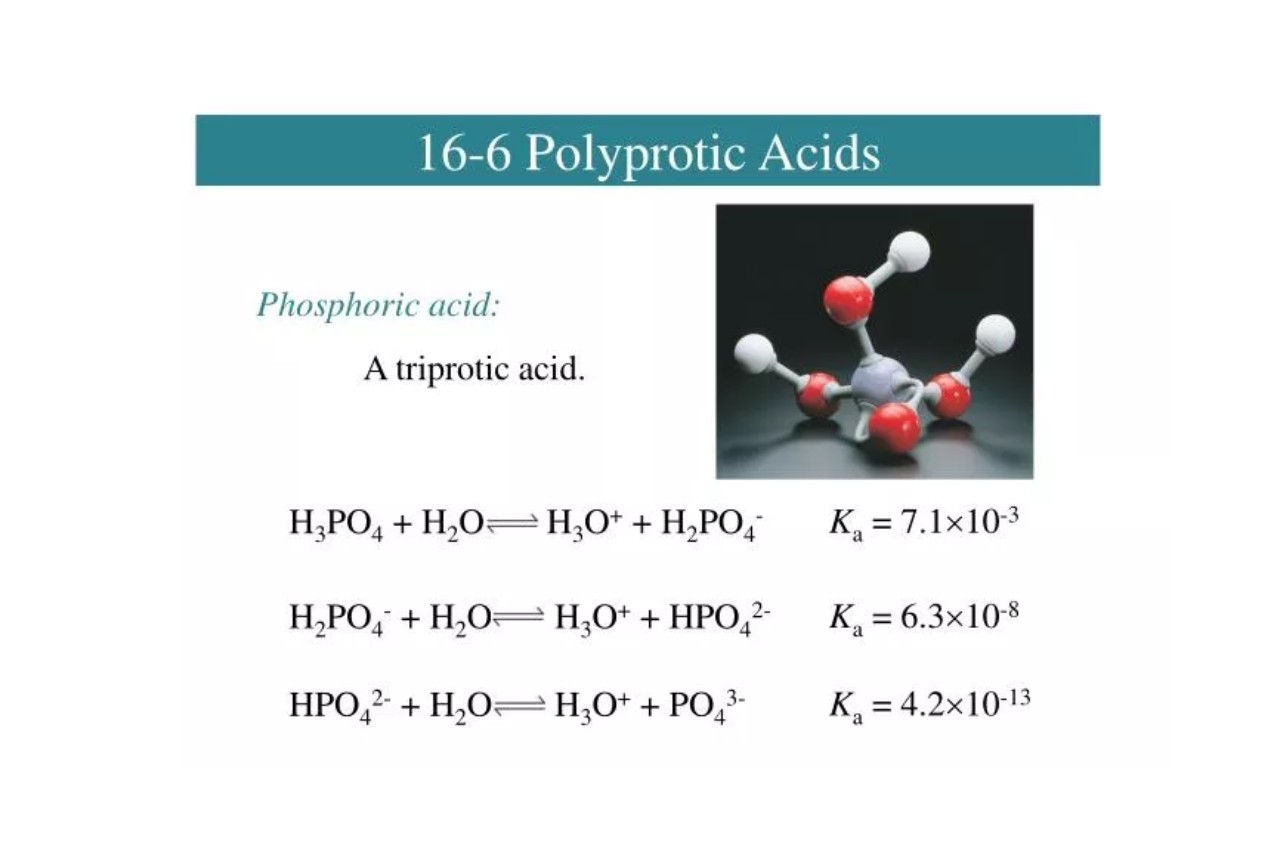
Polyprotic Acid Example
An example of a polyprotic acid is phosphoric acid (H3PO4), which can lose up to three protons during its dissociation process.
Acid Dissociation Constants
Polyprotic acids have multiple acid dissociation constants (Ka values), with each step representing the dissociation of one proton. These constants determine the strength of the acid at each dissociation stage.
Ionization of Polyprotic Acids
As polyprotic acids dissociate, they form corresponding hydrogen ions (H+) and negatively charged ions called polyprotic acid anions.
Multiple Equilibrium Reactions
The dissociation of polyprotic acids involves multiple equilibrium reactions, each with its own equilibrium constant. This adds complexity to the acid-base behavior of polyprotic acids.
Amphiprotic Nature
Polyprotic acids are amphiprotic, meaning they can act as both acids and bases. They can donate protons to other species as well as accept protons from them.
Acid Strength of Polyprotic Acids
The acid strength of each dissociation step in polyprotic acids decreases as more protons are lost. This is due to the decreasing concentration and increasing stability of the resulting polyprotic acid anions.
Phosphoric Acid Uses
Phosphoric acid, a common polyprotic acid, has various applications. It is used in the production of fertilizers, detergents, and food and beverage products.
Citric Acid as a Polyprotic Acid
Citric acid, another example of a polyprotic acid, is found in citrus fruits and is widely used as a flavoring agent in food and beverages.
Carbonic Acid in Carbonated Beverages
Carbonic acid, a weak polyprotic acid, is responsible for the refreshing fizz in carbonated beverages. It is formed when carbon dioxide dissolves in water.
Weak vs. Strong Polyprotic Acids
Some polyprotic acids, such as carbonic acid, are weak acids, while others, like sulfuric acid, are strong acids. The strength of a polyprotic acid is determined by its ability to completely dissociate in water.
Polyprotic Acids in Biochemistry
Polyprotic acids play vital roles in biological systems. For example, amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, contain multiple ionizable groups and can act as polyprotic acids.
Acid-Base Titration
Polyprotic acids are commonly used in acid-base titrations to determine unknown concentrations of acids or bases. The titration curve shows the stepwise neutralization of the acid as each proton is lost.
Buffer Solutions
Buffer solutions often utilize polyprotic acids and their corresponding conjugate bases to resist changes in pH. The multiple dissociation steps of polyprotic acids help maintain a stable pH range.
Acid Rain and Polyprotic Acids
The formation of acid rain is influenced by the presence of polyprotic acids, such as sulfuric acid. These acids contribute to the acidity of rainwater, which can have detrimental effects on the environment.
Acid-Base Balance in the Body
The human body regulates acid-base balance through various physiological mechanisms. Polyprotic acids, like carbonic acid, play a role in maintaining the pH of bodily fluids.
Common Polyprotic Acids
Apart from phosphoric acid, citric acid, and carbonic acid, other commonly encountered polyprotic acids include oxalic acid, maleic acid, and sulfuric acid.
Impact on Industrial Processes
Polyprotic acids have wide-ranging effects on industrial processes. They are used in metal cleaning, water treatment, pharmaceutical synthesis, and many other applications.
Acid-Base Reactions in Everyday Life
Polyprotic acids and their reactions are prevalent in everyday life. From the sour taste of lemon juice (citric acid) to the acidity of vinegar (acetic acid), we encounter the effects of polyprotic acids regularly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, polyprotic acids are a fascinating topic in chemistry with a range of unique properties and applications. Understanding the behavior of polyprotic acids can provide valuable insights into chemical reactions and equilibrium. From the concept of multiple ionizable hydrogen atoms to the importance of acid dissociation constants, polyprotic acids offer a complex and intriguing field of study.By exploring the equilibrium reactions of polyprotic acids, scientists are able to unlock a deeper understanding of chemical systems. This knowledge has practical applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, environmental sciences, and materials science. Studying polyprotic acids also contributes to our understanding of acid-base chemistry and the pH scale.Overall, the study of polyprotic acids offers a fascinating glimpse into the intricacies of chemical reactions and their applications in various fields. Its complexity and importance make it an essential area of study for any chemistry enthusiast.
FAQs
Q: What is a polyprotic acid?
A: A polyprotic acid is an acid that can donate more than one proton (hydrogen ion) in an aqueous solution. It has multiple ionizable hydrogen atoms, each with its own acid dissociation constant.
Q: What are some examples of polyprotic acids?
A: Examples of polyprotic acids include sulfuric acid (H2SO4), phosphoric acid (H3PO4), and carbonic acid (H2CO3).
Q: How do polyprotic acids differ from monoprotic acids?
A: Polyprotic acids can donate more than one proton, while monoprotic acids can only donate one proton. Polyprotic acids have multiple ionizable hydrogen atoms, which dictates their ability to donate multiple protons.
Q: What is the significance of acid dissociation constants in polyprotic acids?
A: Acid dissociation constants (Ka values) describe the extent to which an acid dissociates in a solution. In the case of polyprotic acids, multiple Ka values are associated with each ionizable hydrogen atom, representing the different stages of dissociation.
Q: How are polyprotic acids used in everyday life?
A: Polyprotic acids have various practical applications, such as in the production of fertilizers, cleaning agents, and pharmaceutical drugs. They are also important in environmental sciences for understanding acid rain and in the food industry for controlling pH levels.
Unraveling polyprotic acids' fascinating properties is just the beginning of your chemistry journey. Dive deeper into the world of chemical reactions and equilibrium by exploring buffer solutions, which maintain stable pH levels in various applications. Master the art of titration, a precise method for determining the concentration of an unknown solution. Grasp the fundamental concepts of acid-base reactions through the lens of the Bronsted-Lowry theory, which defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
