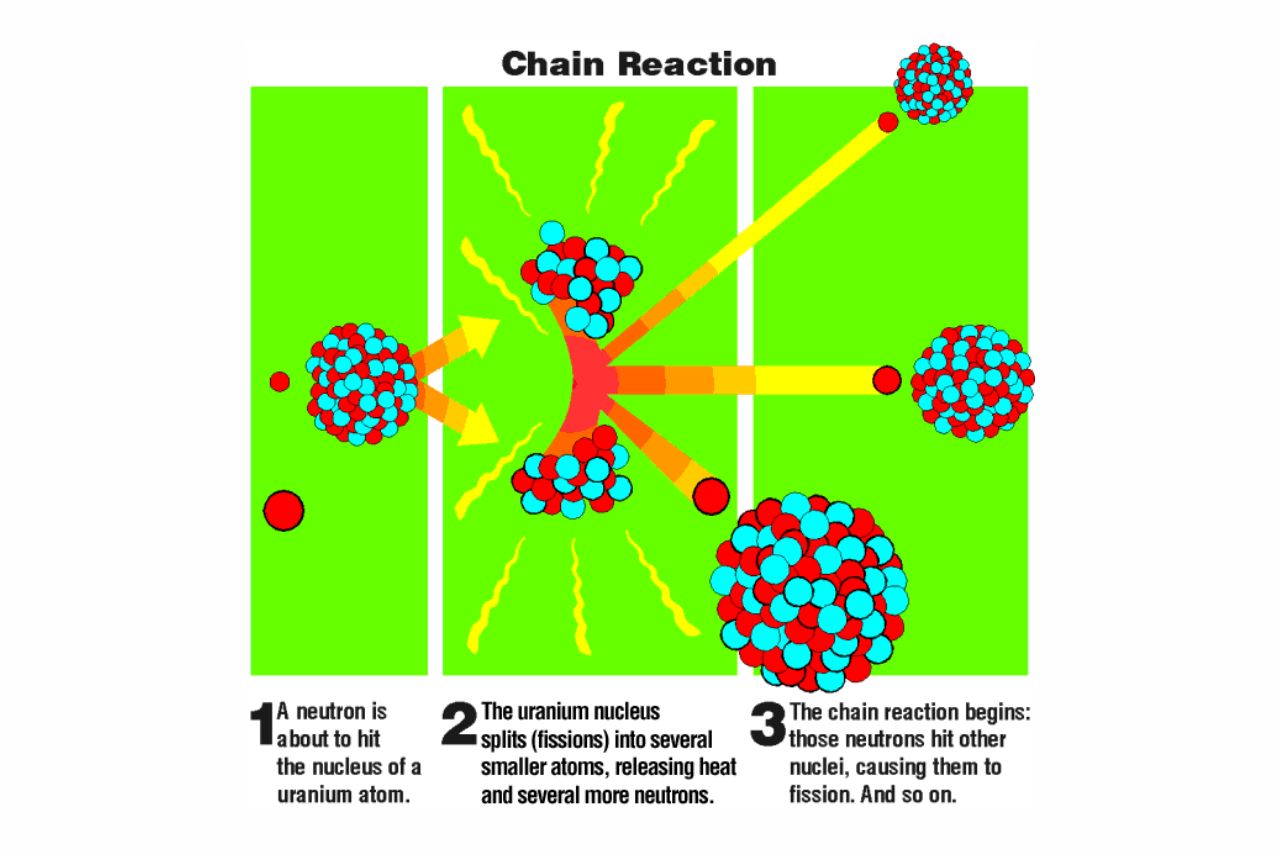
Chain reactions are fascinating phenomena that occur in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and even social dynamics. It is a process where a series of events or actions leads to a continuous and self-sustaining reaction. In the world of chemistry, chain reactions play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of substances and reactions.
In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of chain reactions and explore 16 fascinating facts that will leave you in awe. From the explosive power of a nuclear chain reaction to the delicate balance required for a biochemical reaction, chain reactions encompass a wide range of fascinating phenomena.
So, brace yourself for a journey into the captivating realm of chain reactions and prepare to be amazed by the intricacies and wonders that occur when a series of events sets off a chain of unstoppable reactions.
Key Takeaways:
- Chain reactions, discovered in 1933, have revolutionized physics, chemistry, and nuclear energy. They power nuclear plants, drive biological processes, and even inspire metaphors in sociology and psychology.
- Neutrons play a key role in mediating chain reactions, which have potential future applications in medicine, energy, and materials science. Understanding their complexities is crucial for safe and efficient use.
The Discovery of Chain Reaction
Chain reaction, a process where a nuclear or chemical reaction sets off a series of similar reactions, was first discovered by Hungarian scientist Leo Szilard in This groundbreaking concept would go on to revolutionize the fields of physics, chemistry, and nuclear energy.
Enrico Fermi’s Controlled Nuclear Chain Reaction
In 1942, Italian physicist Enrico Fermi achieved the world’s first controlled nuclear chain reaction. This milestone experiment took place at the University of Chicago as part of the top-secret Manhattan Project, laying the foundation for the development of atomic bombs.
Nuclear Power Generation
The process of controlled nuclear chain reaction is harnessed in nuclear power plants to generate electricity. The heat produced by the reaction is used to create steam, which drives turbines and produces electricity without the emission of greenhouse gases.
Fission and Fusion Chain Reactions
Chain reactions can occur through two main mechanisms: fission and fusion. In fission chain reactions, heavy atomic nuclei split into smaller fragments, releasing a large amount of energy. Fusion chain reactions, on the other hand, involve the combining or fusing of light atomic nuclei to create heavier elements.
Importance in Nuclear Weapons
Chain reactions play a critical role in the functioning of nuclear weapons. By initiating an uncontrolled chain reaction, an atomic bomb can release an immense amount of energy in a very short period, causing catastrophic destruction.
Chemical Chain Reactions
Chain reactions are not limited to nuclear reactions. They also occur in chemical reactions, where the products of one reaction can initiate subsequent reactions. Examples include the combustion of fuel, polymerization reactions, and the oxidation of organic compounds.
Chain Reaction in Biological Systems
In biological systems, chain reactions are involved in various processes. One notable example is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) used in DNA amplification, a crucial technique in molecular biology and genetic research.
Self-Sustaining Reactions
Chain reactions have the ability to become self-sustaining, meaning once initiated, they can continue without external intervention. This property is utilized in many industrial processes, such as the production of synthetic materials and the generation of power.
Nuclear Chain Reaction Safety Measures
Strict safety measures and control systems are implemented in nuclear reactors to prevent uncontrolled chain reactions and ensure the safe generation of nuclear power. These include control rods, which absorb neutrons to regulate the rate of the chain reaction.
Chain Reaction as a Metaphor
The concept of chain reaction has also been metaphorically extended to describe a series of events in which each one triggers the next. This analogy is often used in fields such as sociology, economics, and psychology to explain the ripple effect of actions and their consequences.
The “Domino Effect”
The phrase “domino effect” is a common term used to describe a chain reaction where one event sets off a series of similar events. This concept originates from the observation of how falling dominoes topple one after another due to their interconnectedness.
Chain Reaction in Popular Culture
The concept of chain reaction has been depicted in various forms of media, including movies, TV shows, and video games. It often serves as a plot device, creating suspense and driving the narrative forward.
Nuclear Chain Reaction Regulations
The safe management and regulation of nuclear chain reactions are governed by strict international treaties and national regulations. These measures aim to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons and ensure the safe use of nuclear technology.
Neutron-Mediated Chain Reactions
In many chain reactions, neutrons are the key particles that mediate the process. They initiate and propagate the reaction by colliding with and causing the fission or fusion of atomic nuclei.
Potential Future Applications
Researchers are exploring potential future applications of chain reactions in areas such as medicine, energy generation, and materials science. These advancements have the potential to revolutionize these fields and contribute to scientific progress.
Complexity of Chain Reactions
Chain reactions can exhibit complex behaviors, as they involve a multitude of factors and variables. Understanding and managing these complexities are essential for the safe and efficient application of chain reactions in various fields.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chain reactions are fascinating phenomena that have immense significance in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and nuclear science. Understanding the science behind chain reactions is crucial for applications such as energy production, chemical synthesis, and even the detonation of explosives.
From the initial triggering event to the self-sustaining propagation, chain reactions involve intricate processes that involve the release and transfer of energy or particles. These reactions can occur in a controlled manner, as seen in nuclear reactors, or unleash devastating destruction, as demonstrated by nuclear bombs.
By harnessing the power of chain reactions, scientists and engineers have made significant advancements in areas such as clean energy generation, medical treatments, and material synthesis. Moreover, the study of chain reactions continues to unveil new insights into the fundamental principles of chemistry and physics.
In summary, chain reactions not only captivate our curiosity but also play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the universe and improving various aspects of our lives.
FAQs
Q: What is a chain reaction?
A: A chain reaction is a sequence of events where the output of one reaction becomes the trigger for the next reaction in a self-sustaining manner.
Q: What causes a chain reaction to occur?
A: Chain reactions occur when there is an initial trigger event that releases energy or particles, which then initiates subsequent reactions.
Q: How do chain reactions relate to nuclear power?
A: Chain reactions are central to nuclear power generation. In a nuclear reactor, controlled chain reactions sustain the release of energy from nuclear fission processes.
Q: Are chain reactions always destructive?
A: No, chain reactions can have both constructive and destructive applications depending on the context in which they occur. For example, chain reactions play a vital role in chemical synthesis and energy production.
Q: Can chain reactions be stopped once initiated?
A: Yes, chain reactions can be controlled and stopped through various methods, such as using moderators or absorbing materials to limit the availability of the reactants.
Q: Are all chain reactions spontaneous?
A: No, some chain reactions require an external trigger, whereas others may occur spontaneously under the right conditions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
