Polymerization is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the world of chemistry. It involves the joining together of small molecules called monomers to form long chains known as polymers. This process has a wide range of applications and has contributed significantly to advancements in various fields, including materials science, pharmaceuticals, and industrial manufacturing.
In this article, we will explore 17 enigmatic facts about polymerization. From the discovery of synthetic polymers to the mechanisms behind different polymerization reactions, we will delve into the intriguing world of polymer chemistry. So, buckle up and get ready to unravel the mysteries behind this fundamental process that has revolutionized the way we develop and utilize materials in our everyday lives.
Key Takeaways:
- Polymerization is a cool chemical reaction where small molecules join together to form long chains. It’s used to make things like plastics, fabrics, and even medicine!
- There are different types of polymerization, and it’s used in many industries. Scientists are always working to make it better and find new ways to use it.
Polymerization: What is it?
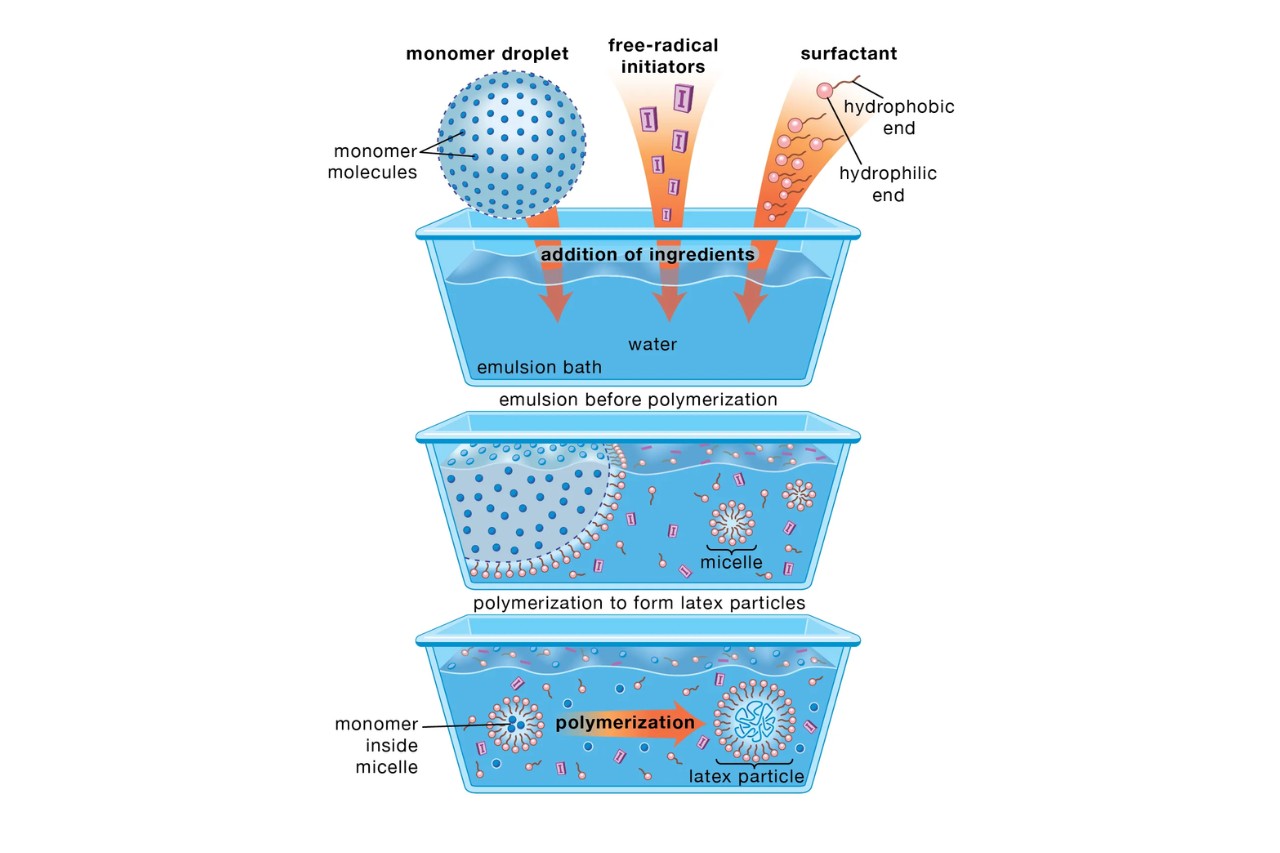
Polymerization is a chemical reaction in which small molecules, called monomers, combine to form long chains, known as polymers. This process is catalyzed by heat, pressure, or chemicals known as initiators.
Chain Reaction
Polymerization follows a chain reaction mechanism, where the formation of one polymer chain leads to the initiation of another, resulting in a continuous growth of the polymer structures.
Types of Polymerization
There are two primary types of polymerization: addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization involves the combination of monomers without the generation of byproducts, while condensation polymerization produces small molecules, such as water, as byproducts.
Cross-Linking
In some cases, polymerization can lead to the formation of cross-linked polymers, where the polymer chains are interconnected. This cross-linking enhances the mechanical properties of the resulting polymer, making it more durable.
Industrial Applications
Polymerization is widely used in various industries. It is employed in the production of plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, as well as in the synthesis of synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester.
Radical Polymerization
Radical polymerization is a type of addition polymerization that occurs through the initiation, propagation, and termination of free radicals. It is the most common method for producing polymers.
Step-Growth Polymerization
In contrast to addition polymerization, step-growth polymerization involves the reaction between functional groups present in the monomers, leading to the formation of high molecular weight polymers.
Biopolymers
Polymerization also occurs naturally in living organisms, leading to the formation of biopolymers. Examples include proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates, which are essential for life.
Copolymerization
Copolymerization involves the polymerization of two or more different monomers. This process allows for the synthesis of polymers with unique properties and characteristics.
Living Polymerization
Living polymerization techniques enable precise control over the molecular weight and structure of polymers. This method is often used in the production of specialty polymers for specific applications.
Polymerization in Medicine
Polymerization plays a vital role in the pharmaceutical industry. It is utilized in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering, and the development of biodegradable polymers for surgical implants.
Polyethylene: The Most Produced Polymer
Polyethylene, a versatile polymer with various applications, is the most widely produced polymer globally. It is used in packaging materials, bottles, and even in medical devices.
Polymerization Kinetics
Studying the kinetics of polymerization is crucial for understanding the reaction rate, mechanisms, and controlling the properties of the resulting polymers.
Industrial Polymerization Processes
Industrial polymerization processes are optimized to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure consistent polymer quality for large-scale production.
Polymerization Catalysts
Catalysts play a vital role in promoting polymerization reactions. Common catalysts include transition metals, organic compounds, and enzymes in biological systems.
Polymerization Monitoring
Monitoring polymerization reactions is essential to ensure the desired polymer properties and prevent side reactions. Techniques such as spectroscopy and chromatography are used for real-time analysis.
Future of Polymerization
The field of polymerization continues to advance, with ongoing research focused on sustainable polymers, efficient catalysts, and new polymerization techniques to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
These 17 enigmatic facts about polymerization only scratch the surface of this complex and versatile process. As scientists and engineers continue to explore its intricacies, we can expect new breakthroughs and innovations in the world of polymers.
Conclusion
Polymerization is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. From the creation of plastics to the synthesis of complex materials, it has revolutionized various industries. Throughout this article, we have explored 17 enigmatic facts about polymerization.We learned about the different types of polymerization reactions, such as addition and condensation, and the key factors that influence the process. We explored the significance of catalysts and initiators in kickstarting polymerization reactions and generating high-quality polymers.Additionally, we delved into the world of polymerization kinetics and the various polymerization techniques employed by scientists and engineers. We discussed the importance of molecular weight and distribution in determining the properties of polymers.Overall, polymerization is a versatile and intricate process that continues to drive innovation in fields ranging from materials science to biotechnology. By understanding its principles and applications, we can harness its power to create new and exciting materials that shape our future.
FAQs
1. What is polymerization?
Polymerization is a chemical reaction in which small molecules known as monomers join together to form large, complex structures called polymers.
2. What are the different types of polymerization?
The two main types of polymerization are addition polymerization and condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization involves the sequential addition of monomers, while condensation polymerization results in the elimination of small molecules, such as water, during polymer formation.
3. What role do catalysts play in polymerization?
Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. In polymerization, catalysts help facilitate the bonding of monomers and ensure the desired polymer structure is achieved.
4. How does molecular weight affect the properties of polymers?
Molecular weight influences various properties of polymers, such as strength, flexibility, and melting point. Higher molecular weight generally leads to stronger and more rigid polymers.
5. What are some applications of polymerization?
Polymerization has countless applications across different industries. It is used in the production of plastics, synthetic fibers, coatings, adhesives, and biomedical materials, just to name a few.
6. How does polymerization contribute to sustainability?
Polymerization allows for the recycling and repurposing of waste polymers, reducing the reliance on virgin materials. It also enables the development of biodegradable polymers, reducing environmental impact.
7. Can polymerization reactions be reversed?
In some cases, polymers can be depolymerized, breaking down the large polymer chains into smaller monomers. However, this process is not always straightforward and depends on the specific polymer and conditions.
8. Are all polymers synthetic?
No, not all polymers are synthetic. There are also naturally occurring polymers, such as proteins, cellulose, and DNA, which play vital roles in living organisms.
9. How long does the polymerization process usually take?
The duration of polymerization varies depending on several factors, including the type of polymerization, reaction conditions, and the desired properties of the final polymer. It can range from minutes to several hours.
10. Are there any safety considerations when working with polymerization reactions?
Yes, safety precautions must be followed when handling polymerization reactions, as some monomers and catalysts may be toxic or flammable. Proper ventilation, protective equipment, and adherence to handling protocols are necessary to ensure safety.
Polymerization's enigmatic nature leaves many curious about its depths. Copolymers, formed by combining different monomers, add another layer of intrigue to this fascinating process. Polymer chemistry itself is a vast field, holding countless secrets waiting to be uncovered. Exploring these related topics will satisfy your craving for knowledge and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the world of polymers.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
