Halogenation is a fascinating chemical process that involves the addition of a halogen element, such as chlorine, fluorine, bromine, or iodine, to a compound. This reaction is widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and materials science. Halogenation plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of countless products, ranging from medications to plastics and pesticides.
In this article, we will delve into 15 astonishing facts about halogenation. You will discover the fundamental principles behind this chemical process, explore its applications in different fields, and uncover some intriguing examples of halogenated compounds. So, fasten your seatbelts, and get ready to be amazed by the remarkable world of halogenation!
Key Takeaways:
- Halogenation is a powerful chemical process that adds halogen elements to compounds, impacting everything from water treatment to pharmaceuticals. It’s like giving compounds a special superpower to fight off germs and fires!
- Halogenation has both amazing benefits and potential risks, from making medicines more effective to harming the environment. It’s like a superhero with incredible abilities, but also a responsibility to use them wisely.
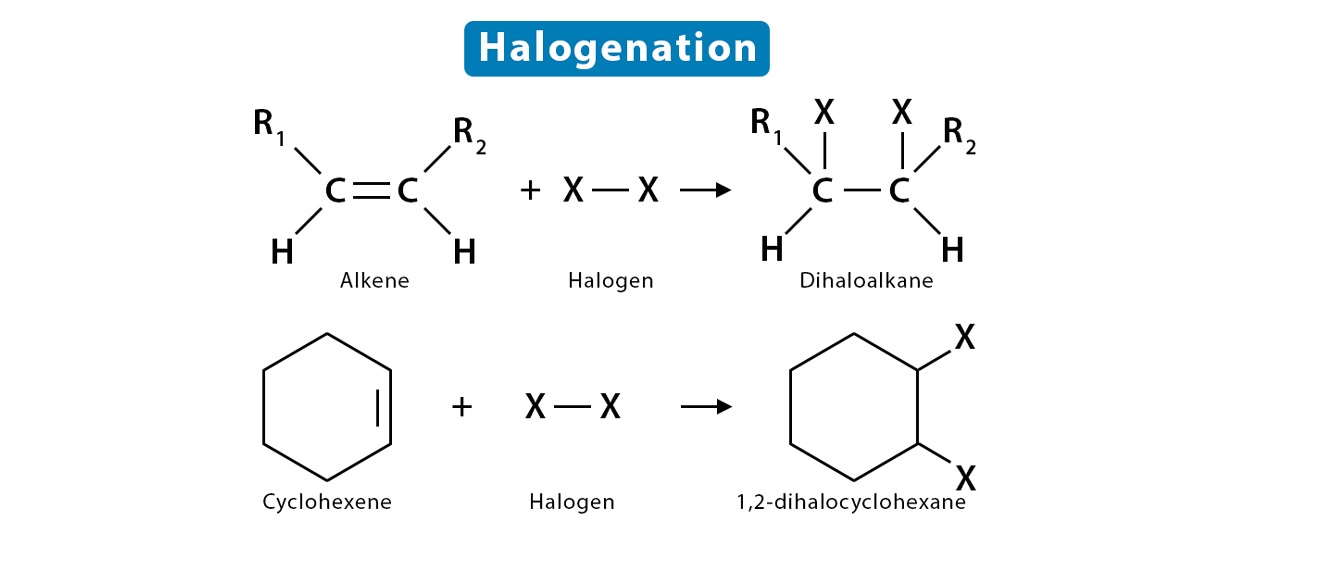
What is Halogenation?
Halogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the addition of a halogen element to a compound or substance. These halogen elements include chlorine, bromine, fluorine, iodine, and astatine. This process is widely used in various industries and has numerous applications.
Halogenation and Organic Chemistry
Halogenation plays a significant role in organic chemistry. It is used to introduce halogen atoms into organic molecules, resulting in the formation of halogenated compounds. These compounds have unique properties and find applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and other fields.
Importance of Halogenation
Halogenation is important because it can modify the properties of a substance, such as its reactivity, stability, and solubility. It can also enhance the effectiveness of certain chemical processes or reactions. Additionally, halogenated compounds are often used as intermediates in the synthesis of various chemical products.
Halogenation in Water Treatment
Halogenation, particularly the use of chlorine, is commonly employed in water treatment to disinfect water. Chlorine effectively destroys harmful microorganisms, making the water safe for consumption. This process is crucial in maintaining public health and preventing the spread of waterborne diseases.
Halogenation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry extensively uses halogenation to introduce halogen atoms into drug molecules. This modification can enhance the drug’s stability, bioavailability, and pharmacological activity. Halogenated drugs include antibiotics, anesthetics, and anti-inflammatory medications.
Halogenation in Flame Retardants
Halogenated compounds are widely used in flame retardants to reduce the flammability of materials. The addition of halogens helps inhibit or slow down the burning process, therefore increasing the fire resistance of products like textiles, plastics, and furniture.
Halogenation in Refrigeration
Refrigeration systems, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, use halogenated compounds as refrigerants. These compounds undergo phase changes between liquid and gas states to absorb heat from the surrounding environment. However, due to their environmental impact, efforts have been made to develop more eco-friendly alternatives.
Halogenation in Polymer Science
Halogenation is essential in the field of polymer science. It can modify the properties of polymers, such as their heat resistance, electrical conductivity, and chemical stability. Halogenated polymers are commonly used in electrical insulation, flame retardant materials, and industrial coatings.
Halogenation and Food Preservation
In the food industry, halogenation is utilized as a method of food preservation. Chlorine-based compounds, such as chlorine dioxide and hypochlorous acid, are used to disinfect food-processing surfaces and equipment, ensuring food safety and preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
Halogenation and Agriculture
Halogenation is applied in agriculture to control the growth of pests and pathogens. Halogenated pesticides, like methyl bromide and chloropicrin, have been widely used for soil sterilization and pest eradication. However, due to their environmental impact, their use has been restricted in many countries.
Halogenation in Dyeing and Bleaching
Halogenation is involved in the dyeing and bleaching processes in the textile industry. Halogenated bleaching agents, such as chlorine and chlorine dioxide, are used to remove colorants and impurities from textiles, resulting in brighter and cleaner fabrics.
Halogenation in the Petroleum Industry
The petroleum industry employs halogenation in refining processes. Halogen-assisted reactions are used to enhance the efficiency of cracking, isomerization, and other refining processes, leading to the production of various petroleum products.
Halogenation in Environmental Science
Halogenation is a topic of interest in environmental science due to the impact of halogenated compounds on ecosystems and human health. Researchers are studying the fate, transport, and effects of these compounds, as well as developing methods to safely remove them from the environment.
Halogenation and Ozone Depletion
Certain halogenated compounds, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons, contribute to ozone layer depletion. These substances have been phased out through international agreements like the Montreal Protocol, which aims to protect the ozone layer and reduce global warming potential.
Halogenation and Green Chemistry
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on developing sustainable and environmentally friendly chemical processes. Green chemistry aims to minimize waste, reduce hazardous substances, and optimize resource utilization. The application of halogenation in green chemistry focuses on finding alternative, cleaner methods to achieve the desired chemical transformations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, halogenation is a fascinating process that has numerous applications in chemistry. It involves the introduction of halogens into organic compounds, resulting in the formation of new substances with altered properties. From disinfecting water to synthesizing pharmaceuticals, halogenation plays a vital role in various industries.
Throughout this article, we explored 15 astonishing facts about halogenation. We learned about the different halogens commonly used in this process, such as chlorine, bromine, and iodine. We also delved into the mechanisms and reactions involved in halogenation and discovered its diverse applications in areas like food preservation, industrial chemistry, and material science.
Overall, halogenation is a powerful tool that chemists utilize to modify and enhance the properties of organic compounds. Its impact on various aspects of our daily lives cannot be understated.
FAQs
1. What is halogenation?
Halogenation is the process of introducing halogen atoms, such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine, into organic compounds.
2. What are the main halogens used in halogenation?
The main halogens used in halogenation are chlorine, bromine, and iodine.
3. What are some common applications of halogenation?
Halogenation is commonly used for disinfection of water, synthesis of pharmaceuticals, food preservation, and industrial chemistry.
4. How does halogenation work?
Halogenation typically involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom in an organic compound by a halogen atom, resulting in the formation of a halogenated product.
5. Are there any safety considerations when working with halogenation?
Yes, working with halogenation requires proper safety measures as halogens can be toxic, corrosive, and reactive. It is important to handle halogenation reactions in a well-ventilated area, wear appropriate protective equipment, and follow established safety protocols.
6. Can halogenation be reversible?
Depending on the specific reaction conditions, halogenation can be reversible. Some halogenated compounds can undergo dehalogenation reactions to regenerate the original organic compound.
7. Can halogenation be used in the synthesis of drugs?
Yes, halogenation is commonly used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals. Introducing halogen atoms into organic compounds can alter their properties, such as enhancing their stability, bioavailability, or targeting specific receptors.
8. Is halogenation an environmentally friendly process?
The environmental impact of halogenation depends on the specific halogen and reaction conditions used. Some halogens, such as chlorine, can have adverse effects on the environment when released in large quantities. However, advancements in green chemistry aim to minimize the environmental footprint of halogenation processes.
9. Are there any alternatives to halogenation?
Yes, there are alternative methods for modifying organic compounds that do not involve halogens. Some examples include oxidation, reduction, or substitution reactions using different chemical reagents.
10. Can halogenation reactions be controlled?
Yes, the selectivity and outcome of halogenation reactions can be controlled by adjusting reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvent, and the presence of catalysts. Chemists carefully optimize these variables to achieve desired products.
Halogenation's astonishing facts have piqued your curiosity, but there's more to explore! Delve into the captivating world of halogens, uncover interesting tidbits about astatine, or be amazed by unbelievable alkyl halide facts. Each topic offers a unique perspective on the fascinating chemistry of halogenated compounds. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply a science enthusiast, these articles will satisfy your thirst for knowledge and leave you wanting more. So, which captivating subject will you investigate next?
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


