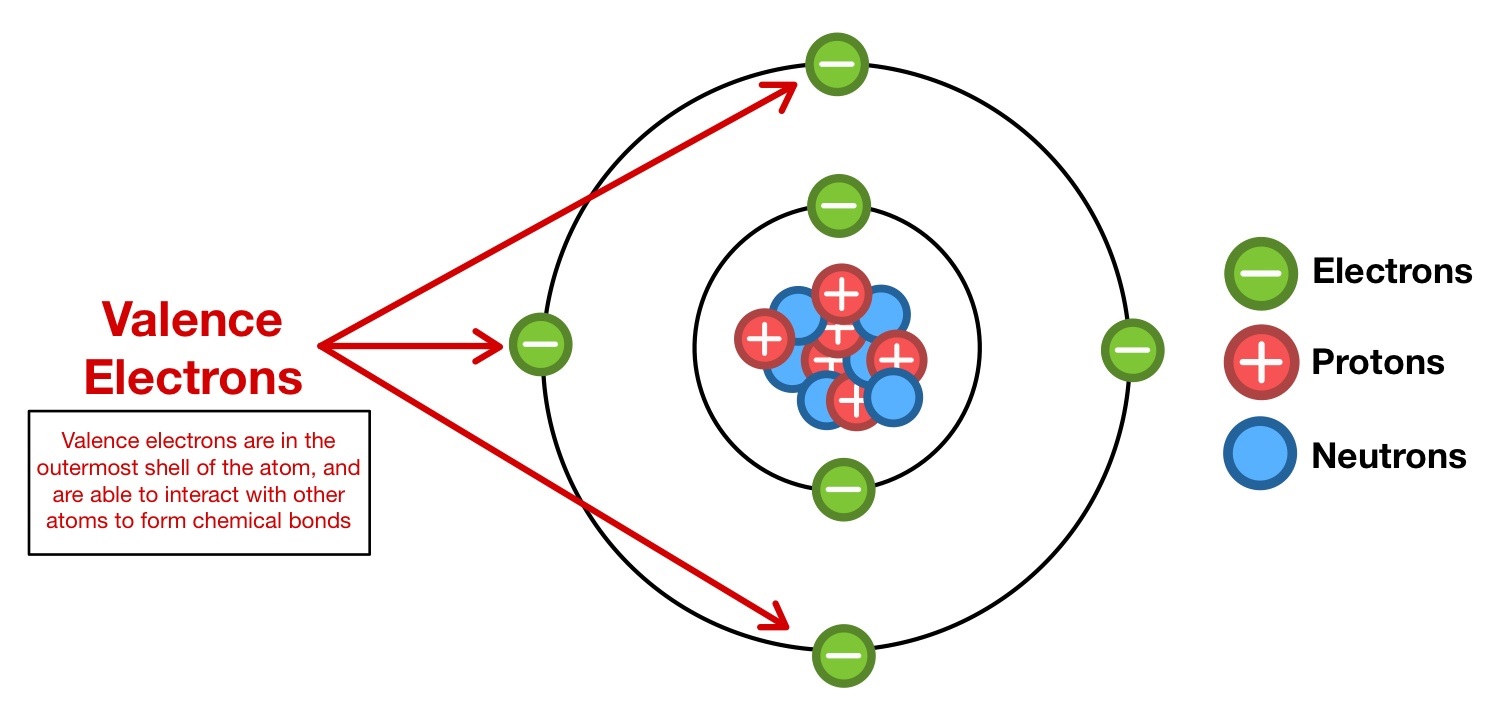
Valence electrons play a crucial role in chemistry as they determine the chemical properties and reactivity of elements. These electrons, which reside in the outermost energy levels of atoms, are responsible for the bonding and interactions between atoms. Understanding the behavior of valence electrons is fundamental in predicting the formation of molecules and compounds, as well as explaining chemical reactions.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of valence electrons and explore nine captivating facts about them. We will uncover their significance in the periodic table, their role in forming chemical bonds, and how they contribute to the unique properties of different elements. So, get ready to expand your knowledge of chemistry and discover the intriguing world of valence electrons!
Key Takeaways:
- Valence electrons determine how elements behave and bond with each other, shaping the properties of the world around us.
- The number and arrangement of valence electrons influence an element’s reactivity and its ability to form stable compounds.
Valence electrons play a crucial role in chemical bonding.
Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. They are involved in the formation of chemical bonds between atoms, which determines the reactivity and properties of elements.
Valence electrons determine an element’s placement in the periodic table.
The number of valence electrons in an atom determines its group and period in the periodic table. Elements with the same number of valence electrons exhibit similar chemical behavior.
Valence electrons can be identified using the periodic table.
The group number of an element in the periodic table represents the number of valence electrons it possesses. For example, elements in Group 1 have one valence electron, while elements in Group 18 have eight valence electrons.
The octet rule guides valence electron configuration.
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons. This rule helps to explain the formation of chemical bonds in many compounds.
Valence electrons are responsible for the conductivity of metals.
In metallic elements, valence electrons are delocalized and free to move throughout the metal lattice. These mobile valence electrons are responsible for the high electrical and thermal conductivity observed in metals.
Transition metals have varying numbers of valence electrons.
Unlike main group elements, transition metals have varying numbers of valence electrons due to the presence of d orbitals in their electron configuration. This property allows transition metals to exhibit multiple oxidation states.
Valence electrons determine the stability of ions.
When atoms gain or lose valence electrons, they form ions. The resulting number of valence electrons in the ion affects its stability. For example, ions strive to achieve a stable electron configuration by gaining or losing enough electrons to attain a full outer shell.
Valence electrons are involved in the formation of chemical compounds.
Chemical compounds are formed through the sharing or transfer of valence electrons between atoms. This process leads to the formation of stable compounds with lower energy compared to individual atoms.
The reactivity of elements is influenced by their valence electrons.
The number and arrangement of valence electrons impact an element’s reactivity. Elements with fewer valence electrons tend to be more reactive as they strive to achieve a full outer shell, while elements with a full outer shell are typically stable and less reactive.
Conclusion
Valence electrons are an essential concept in chemistry that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior and properties of elements. These electrons exist in the outermost energy level of an atom and determine its reactivity and bonding capabilities. Here are nine fascinating facts about valence electrons:
1. Valence electrons are involved in chemical bonding and determine an element’s ability to form compounds.
2. The number of valence electrons determines an element’s position in the periodic table and its group number.
3. Valence electrons are responsible for the formation of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.
4. The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons.
5. Transition metals have variable valence electrons and can exhibit multiple oxidation states.
6. The number of valence electrons affects an atom’s electronegativity and its tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
7. The Lewis dot structure is a useful representation to illustrate valence electrons in an atom or molecule.
8. Elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar valence electron configurations, leading to comparable chemical properties.
9. Valence electrons play a significant role in determining the physical and chemical properties of compounds, including their melting points, boiling points, and solubility.
FAQs
Q: What are valence electrons?
A: Valence electrons are electrons located in the outermost electron shell of an atom.
Q: How do valence electrons determine the reactivity of an element?
A: The number of valence electrons determines how easily an atom can gain, lose, or share electrons with other atoms, affecting its reactivity.
Q: How does the octet rule relate to valence electrons?
A: The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration with eight valence electrons.
Q: What is the significance of transition metals having variable valence electrons?
A: Variable valence electrons in transition metals allow them to exhibit multiple oxidation states and participate in various chemical reactions.
Q: How are valence electrons represented in the Lewis dot structure?
A: Valence electrons are depicted as dots or lines around the symbol of an element in the Lewis dot structure.
Q: What is the relationship between the number of valence electrons and an atom’s electronegativity?
A: The number of valence electrons can influence an atom’s electronegativity, which dictates its ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
Q: Why do elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar valence electron configurations?
A: Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which gives them similar chemical properties and reactivity patterns.
Q: What role do valence electrons play in determining compound properties?
A: Valence electrons play a significant role in determining the physical and chemical properties of compounds including melting points, boiling points, and solubility.
Valence electrons' captivating nature doesn't end here. Explore more intriguing facts about their behavior, configuration, and configuration/">how they're represented using Lewis dot structures. These fundamental particles hold the key to understanding chemical reactions, bonding, and the properties of elements. Delving deeper into valence electrons will enhance your appreciation for the fascinating world of chemistry and its impact on our daily lives. Continue your journey of discovery and unravel more mysteries surrounding these essential components of atoms.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
