The visceral peritoneum is a fascinating and crucial component of the human anatomy. Found within the abdominal cavity, this thin and delicate membrane plays a crucial role in protecting and supporting the organs within the abdominal region. Understanding the intricate details of the visceral peritoneum not only enhances our knowledge of human anatomy but also sheds light on the complexities of the human body.
In this article, we will delve deep into the world of the visceral peritoneum and explore 17 intriguing facts that will leave you awe-struck. From its unique structure to its vital functions, we will uncover the hidden secrets of this remarkable membrane. So, let’s embark on an enlightening journey and discover the wonders of the visceral peritoneum!
Key Takeaways:
- Visceral peritoneum is like a superhero cape for your organs, protecting and supporting them with its double-layered membrane and rich blood supply. It even secretes a special fluid to keep everything moving smoothly!
- Just like a team player, visceral peritoneum works with other membranes to maintain balance in the abdominal cavity, allowing for organ mobility and absorption of nutrients. It’s like the conductor of a symphony, ensuring everything works together harmoniously.
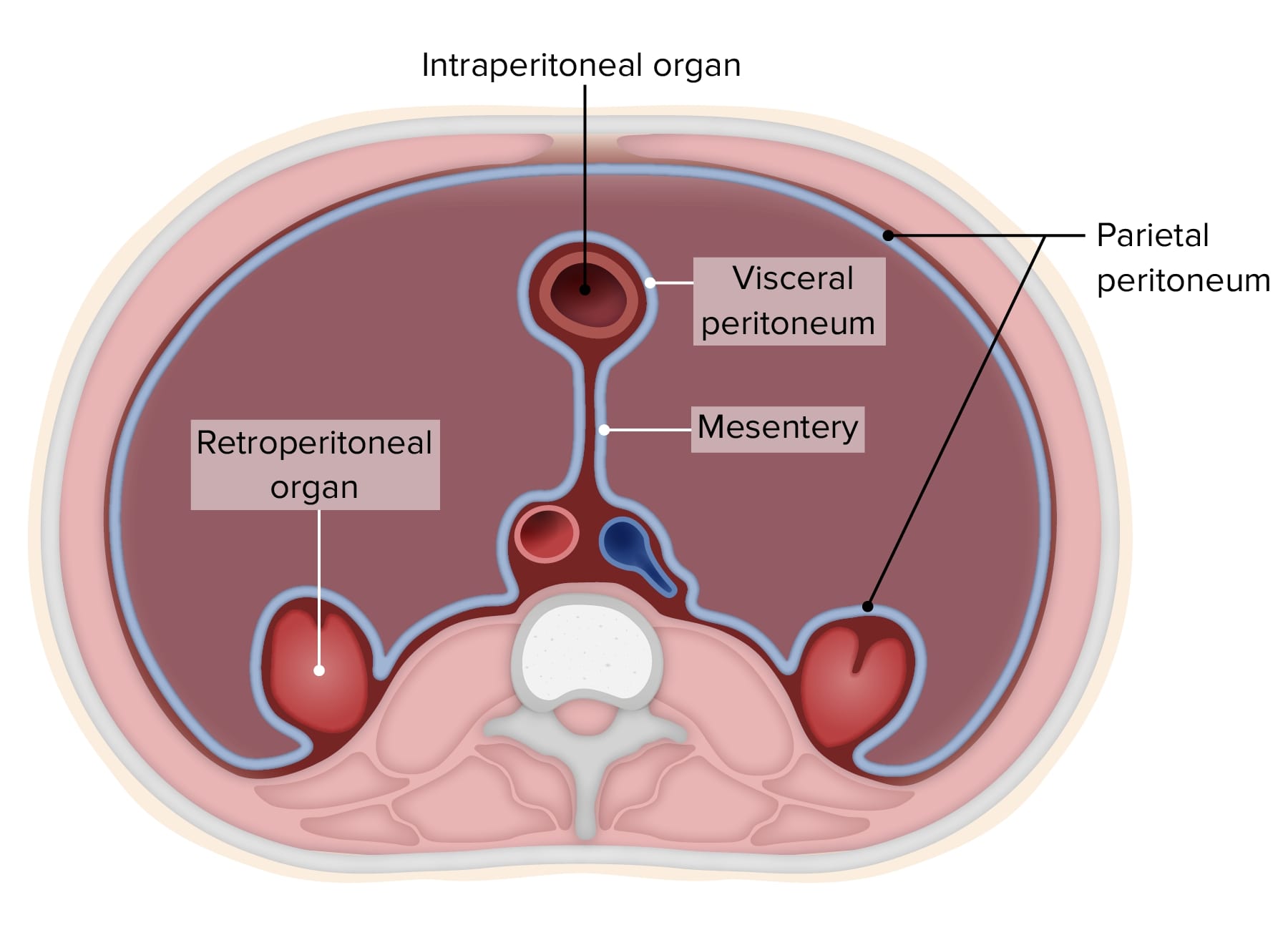
The Peritoneum is a Double-layered Membrane
Visceral peritoneum is one layer of the peritoneum, which is a double-layered membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers the organs within it.
It is Composed of Connective Tissue
Visceral peritoneum is primarily composed of connective tissue, consisting of collagen fibers that provide strength and support to the abdominal organs.
Visceral Peritoneum Covers the Organs
As the name suggests, visceral peritoneum covers the surface of the abdominal organs, including the liver, spleen, intestines, and stomach, providing a protective layer.
It Forms Mesenteries
Visceral peritoneum forms mesenteries, which are double folds of peritoneal membrane that suspend and anchor certain organs, such as the small intestine, within the abdominal cavity.
Peritoneal Fluid Lubricates the Organs
Visceral peritoneum secretes a serous fluid known as peritoneal fluid, which lubricates the surface of the abdominal organs, reducing friction and facilitating smooth movement.
It Allows for Organ Mobility
Visceral peritoneum enables the abdominal organs to have a certain degree of mobility and flexibility, allowing them to adjust and adapt to changes within the abdominal cavity.
Visceral Peritoneum is Innervated
Unlike the parietal peritoneum, which is highly innervated and sensitive to pain, visceral peritoneum is relatively insensitive to pain due to its minimal innervation.
It is Rich in Blood Supply
Visceral peritoneum receives a rich blood supply from various arteries, ensuring adequate oxygen and nutrient delivery to the abdominal organs.
Peritoneal Adhesions can Develop
Visceral peritoneum can develop adhesions, which are abnormal bands of scar tissue that can form between abdominal organs and the peritoneum, potentially causing discomfort or obstruction.
It Plays a Role in Absorption
Visceral peritoneum, particularly within the mesenteries, contains blood vessels and lymphatics that play a role in the absorption of nutrients from the intestines into the bloodstream.
It Interacts with Other Membranes
Visceral peritoneum interacts with other membranes, including the parietal peritoneum, allowing for coordinated movement and function of the abdominal organs.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma is a Potential Disease
Visceral peritoneum can be affected by a rare type of cancer called peritoneal mesothelioma, which originates from the mesothelial cells lining the peritoneum.
It Provides a Protective Barrier
Visceral peritoneum acts as a protective barrier, preventing the spread of infections or inflammation from one organ to another within the abdominal cavity.
It Has an Important Role in Embryonic Development
Visceral peritoneum participates in the formation and development of various organs during embryogenesis, playing a vital role in the growth and maturation of the abdominal cavity.
It Can Be Affected by Inflammation
Visceral peritoneum can become inflamed in conditions such as peritonitis, which may result from infections, trauma, or certain medical procedures.
Visceral Peritoneum Can Be Involved in Surgical Procedures
During surgical procedures, surgeons often manipulate the visceral peritoneum to access and treat underlying abdominal organs, ensuring optimal patient care.
It Plays a Role in Maintaining Abdominal Homeostasis
Visceral peritoneum contributes to maintaining the balance and stability of the abdominal cavity, helping to regulate temperature, fluid distribution, and overall homeostasis.
These 17 intriguing facts shed light on the significance and complexity of visceral peritoneum. Its role in protecting, supporting, and facilitating the functioning of abdominal organs makes it a crucial component of the human anatomy.
Conclusion
The visceral peritoneum is a fascinating component of the human anatomy. This thin, serous membrane plays a vital role in protecting and supporting our organs within the abdominal cavity. Throughout this article, we’ve explored 17 intriguing facts about the visceral peritoneum, uncovering its complex structure, functions, and unique characteristics.From its seamless coverage of organs to its involvement in abdominal infections, the visceral peritoneum serves as a crucial barrier, contributing to overall health and well-being. Its rich network of blood vessels and nerve endings enables it to interact with surrounding structures and play a role in sensory perception.As we continue to delve into the depths of human anatomy, understanding the intricacies of the visceral peritoneum reminds us of the incredible complexity and sophistication of our bodies. By gaining knowledge about this remarkable structure, we can deepen our appreciation for the wonders of the human form.
FAQs
1. What is the visceral peritoneum?
The visceral peritoneum is a serous membrane that covers the organs within the abdominal cavity, providing protection and support.
2. How is the visceral peritoneum different from the parietal peritoneum?
The visceral peritoneum covers organs, while the parietal peritoneum lines the abdominal cavity walls. They work together to create a protective barrier.
3. Can the visceral peritoneum become infected?
Yes, infections such as peritonitis can occur when the visceral peritoneum becomes inflamed due to injury or infection.
4. Does the visceral peritoneum have any sensory function?
Yes, the visceral peritoneum contains nerve endings, allowing it to contribute to sensory perception in the abdominal region.
5. How does the visceral peritoneum interact with blood vessels?
The visceral peritoneum has a rich network of blood vessels that supply nutrients to the organs it covers.
6. Can the visceral peritoneum be affected by diseases?
Yes, various diseases, including cancer, can affect the visceral peritoneum and require medical intervention.
The visceral peritoneum is just one fascinating aspect of the human body's intricate design. Delving deeper into the abdominal cavity, you'll find the greater omentum, a structure with its own set of mind-blowing facts. For those curious about the bigger picture, exploring the enigmatic world of anatomy reveals even more surprises. And if you're ready to be truly amazed, a journey through the marvels of the human body awaits, promising to leave you in awe of the incredible machine we inhabit.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
