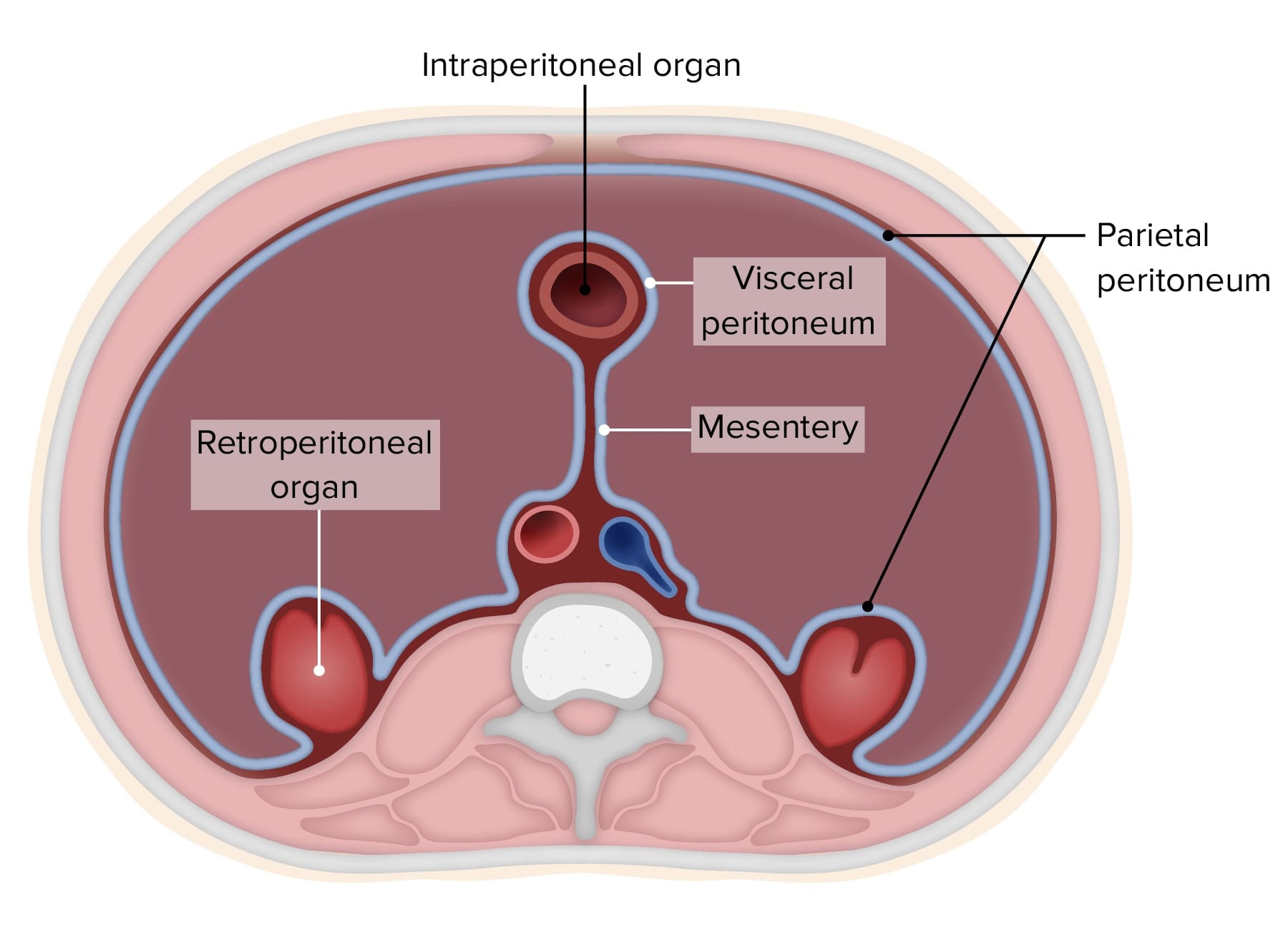
The Parietal peritoneum is an integral part of the human anatomy, playing a crucial role in the functioning of our digestive system. This fascinating membrane lines the abdominal cavity, providing a protective covering for the organs within. It is a double-layered structure that not only supports and cushions the organs but also facilitates their movement and prevents friction. Understanding the Parietal peritoneum is essential for medical professionals, but it can also offer intriguing insights for anyone interested in learning about the human body. In this article, we will delve into 12 fascinating facts about the Parietal peritoneum, shedding light on its anatomy, functions, and significance. So, get ready to explore the marvelous intricacies of this essential component of our abdominal region.
Key Takeaways:
- The parietal peritoneum is like a bodyguard for your organs, keeping them safe and in place within your abdomen. It also helps you feel pain and touch sensations, like a built-in alarm system!
- Just like a superhero, the parietal peritoneum produces a special fluid to keep your organs moving smoothly and plays a crucial role in digestion. It’s like a hidden helper in your belly, working hard to keep you healthy!
The Parietal Peritoneum: A Protective Membrane
The parietal peritoneum is a thin, serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It provides protection to the internal organs and helps to keep them in place.
Dual Layer Structure
The parietal peritoneum is made up of two layers – the outer parietal layer which lines the abdominal wall, and the inner visceral layer which covers the organs within the abdominal cavity.
Sensory Innervation
The parietal peritoneum is densely innervated with sensory fibers, which allows for the perception of pain and touch sensations. This helps in localizing abdominal discomfort or pain.
Mesenteries and Omenta
The parietal peritoneum forms various folds and double layers known as mesenteries and omenta. These structures provide support and attachment for organs such as the intestines.
Produces Peritoneal Fluid
The parietal peritoneum secretes a lubricating fluid called peritoneal fluid. This fluid reduces friction between organs and allows them to move smoothly during daily activities.
Connection with the Thoracic Cavity
The parietal peritoneum is continuous with the diaphragm, the muscular partition that separates the abdominal and thoracic cavities. This connection is important for coordinated breathing and movement.
Provides Blood Supply
The parietal peritoneum receives its blood supply from branches of the abdominal aorta, providing essential nutrients and oxygenation to maintain its function and integrity.
Role in Inflammation
The parietal peritoneum plays a crucial role in inflammatory conditions such as peritonitis. Inflammation of this membrane can cause severe abdominal pain and requires immediate medical attention.
Surgical Importance
The parietal peritoneum is a key consideration in abdominal surgeries. Surgeons ensure the proper closure of incisions in this membrane to prevent postoperative complications.
Diagnostic Tool in Imaging
The parietal peritoneum can be visualized through imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI. This aids in the diagnosis of various abdominal disorders and helps guide medical interventions.
Development and Formation
The parietal peritoneum develops from the mesoderm layer during embryonic development. It forms a protective layer around the abdominal organs as they develop and differentiate.
Important Role in Digestion
The parietal peritoneum plays a vital role in the digestion process by providing support and protection to abdominal organs involved in digestion, including the stomach, liver, and intestines.
Conclusion
The parietal peritoneum is a crucial part of the human anatomy that plays a significant role in protecting and supporting our internal organs. Understanding its functions and characteristics can help us appreciate the complexity and intricacy of the human body.Throughout this article, we have explored 12 fascinating facts about the parietal peritoneum. From its location within the abdominal cavity to its role in preventing infection and its unique blood supply, this tissue layer serves essential purposes.It is important to note that while the parietal peritoneum is an integral part of our anatomy, it can also be susceptible to certain medical conditions or trauma. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle and seek medical attention if any concerns or issues arise.By increasing our knowledge of the parietal peritoneum, we can enhance our appreciation for the incredible complexity and functionality of the human body. So, the next time you hear about this fascinating tissue layer, you’ll have a deeper understanding of its role in our overall well-being.
FAQs
Q: What is the parietal peritoneum?
The parietal peritoneum is a thin membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal cavity. It serves as a protective barrier and helps support the abdominal organs.
Q: How is the parietal peritoneum different from the visceral peritoneum?
While the parietal peritoneum lines the walls of the abdominal cavity, the visceral peritoneum covers the organs within the cavity. They work together to provide protection and support to the abdominal organs.
Q: What are some common medical conditions associated with the parietal peritoneum?
Some common medical conditions related to the parietal peritoneum include peritonitis, hernias, and adhesions. These conditions can cause pain and discomfort and often require medical treatment.
Q: How does the parietal peritoneum contribute to infection prevention?
The parietal peritoneum releases a fluid called peritoneal fluid, which contains immune cells that can help fight off infection. It also acts as a physical barrier, preventing bacteria from entering the abdominal cavity.
Q: Can the parietal peritoneum regenerate after injury?
Yes, the parietal peritoneum has the ability to regenerate after injury. However, the extent of regeneration depends on the severity and nature of the injury. Proper medical care and treatment are crucial for optimal healing.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
