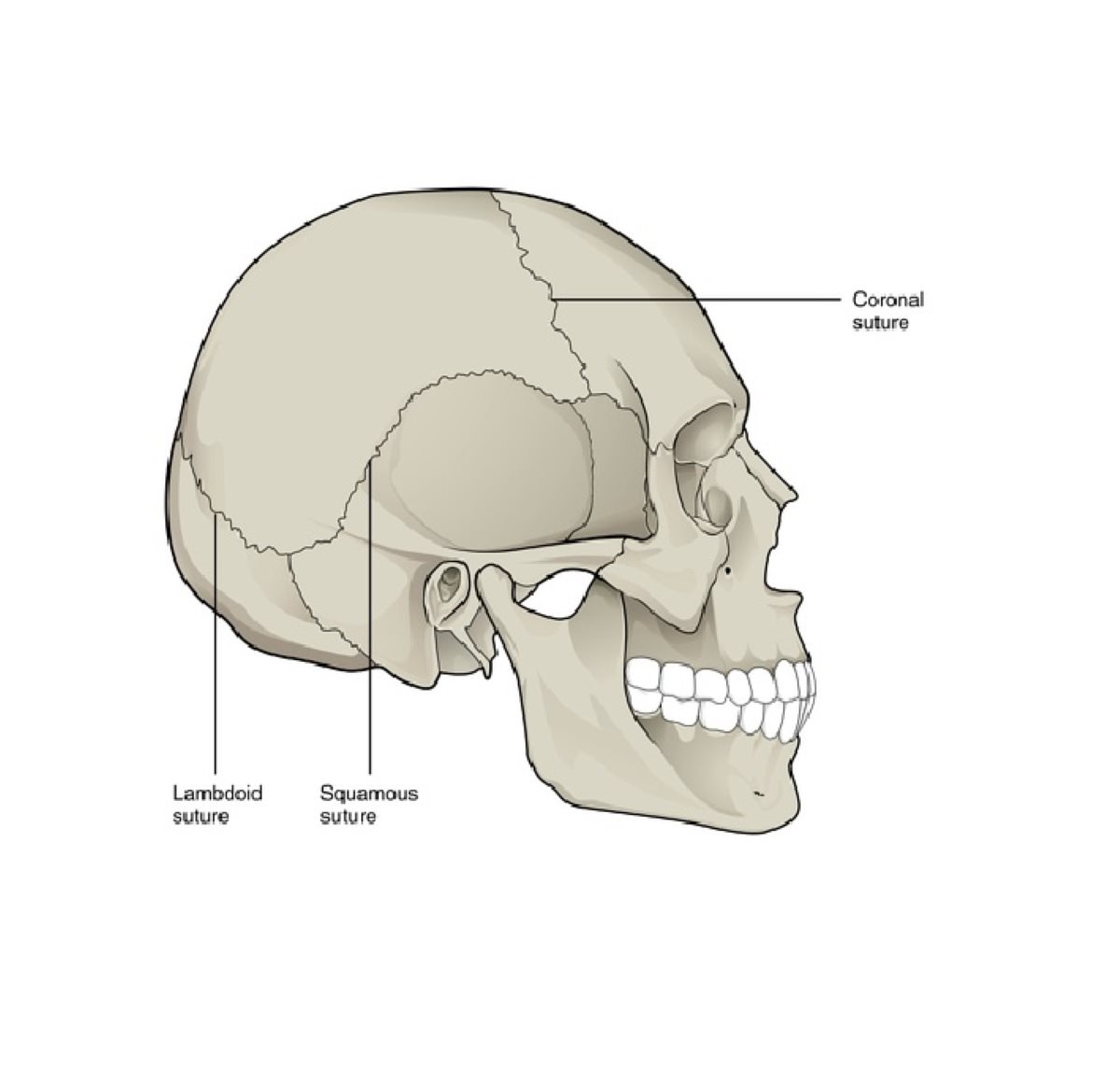
The human anatomy is a fascinating and complex subject, and one area that never fails to astound is the various sutures found in the skull. One such intriguing suture is the lambdoid suture. The lambdoid suture is located at the back of the skull, extending from the posterior fontanelle to the two parietal bones. It is named after the Greek letter “lambda” due to its resemblance to the said letter. This distinct suture plays a crucial role in the overall structure and stability of our skull.In this article, we will delve into the world of the lambdoid suture and explore 20 mind-blowing facts about it. From its developmental significance to its role in anatomical variations, we will uncover the fascinating aspects of this sutural junction. So, fasten your seat belts and get ready to embark on a journey through the intriguing world of the lambdoid suture!
Key Takeaways:
- The Lambdoid suture, shaped like the Greek letter lambda, connects the back of the skull and helps protect the brain. It fuses in childhood and is important for skull stability.
- Studying the Lambdoid suture can reveal information about age, sex, and ancestry from skeletal remains. It also plays a role in guiding medical procedures and protecting the brain.
The Lambdoid suture is one of the major cranial sutures.
This suture is located at the back of the skull, where the occipital bone meets the parietal bones.
The Lambdoid suture gets its name from its resemblance to the Greek letter lambda (?).
When viewed from above, the suture forms a shape that closely resembles the Greek letter lambda.
The Lambdoid suture is a fibrous joint that connects the occipital and parietal bones.
It allows for slight movement between the bones and plays a role in skull flexibility during childbirth.
The Lambdoid suture fuses together during early childhood.
By the age of 6 to 8 years old, the Lambdoid suture is typically fully fused and no longer allows for movement.
The Lambdoid suture is part of the complex network of cranial sutures.
These sutures provide strength and stability to the skull while also allowing for growth and expansion of the brain.
The Lambdoid suture can exhibit variations in its shape and size.
In some individuals, the suture may have irregularities or asymmetry, although this is usually not a cause for concern.
The Lambdoid suture is important for anthropologists and forensic scientists.
By studying the Lambdoid suture, experts can determine age, sex, and ancestral characteristics of skeletal remains.
The Lambdoid suture is susceptible to certain cranial abnormalities.
Conditions such as craniosynostosis, where the sutures fuse prematurely, can affect the growth and development of the skull.
The Lambdoid suture plays a role in brain protection.
Along with other cranial sutures, it helps to cushion and protect the brain from external forces.
The Lambdoid suture is present in both humans and many other mammals.
It is a fundamental feature of the skull structure across different species.
The Lambdoid suture contributes to the unique shape of the skull.
Its position and curvature play a part in determining an individual’s cranial morphology.
The Lambdoid suture can serve as a landmark for medical procedures.
Surgeons and medical professionals may use the suture’s location to guide the placement of implants or perform certain surgeries.
The Lambdoid suture marks the boundary between different bones of the skull.
It separates the occipital bone from the parietal bones and helps maintain the structural integrity of the skull.
The Lambdoid suture is less prone to stress and fractures compared to other sutures.
Its position at the back of the skull offers more protection and support.
The Lambdoid suture can ossify and become less flexible with age.
As part of the natural aging process, the suture gradually transforms into a bony junction.
The Lambdoid suture follows a specific pattern of growth and development during infancy.
It widens and expands to accommodate the rapid growth of the brain during early childhood.
The Lambdoid suture is connected to the sagittal suture.
These two sutures intersect each other at the midpoint of the top of the skull.
The Lambdoid suture can sometimes undergo premature closure.
This condition, known as lambdoid craniosynostosis, can lead to skull deformities and require surgical intervention.
The Lambdoid suture can be visualized using medical imaging techniques.
X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans can provide detailed images of the Lambdoid suture and help diagnose certain conditions.
The Lambdoid suture contributes to the overall stability and strength of the skull.
Its presence ensures that the different bones of the skull are securely connected and able to withstand various forces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the lambdoid suture is a crucial anatomical feature that plays a significant role in the development and structure of the human skull. This distinctive suture, located at the back of the skull, joins the parietal bones with the occipital bone. Understanding the lambdoid suture is essential for medical professionals, researchers, and anyone interested in human anatomy. The lambdoid suture serves as a vital landmark for identifying skull fractures, studying cranial growth patterns, and evaluating skeletal abnormalities. With its unique shape and function, the lambdoid suture exemplifies the remarkable complexity and interconnectedness of the human body. By delving into the fascinating facts about the lambdoid suture, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate wonders of the human anatomy.
FAQs
Q: What is the lambdoid suture?
A: The lambdoid suture is a fibrous joint that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone at the back of the skull.Q: What is the function of the lambdoid suture?
A: The lambdoid suture plays a crucial role in stabilizing the skull, protecting the brain, and allowing for growth and development during infancy and childhood.Q: How does the lambdoid suture develop?
A: The lambdoid suture begins to form during embryonic development as the different skull bones fuse together. It continues to develop and strengthen throughout childhood.Q: What happens if there is a problem with the lambdoid suture?
A: Abnormalities or abnormalities in the lambdoid suture can lead to skull deformities, such as craniosynostosis, which can affect brain development and require medical intervention.Q: Can the lambdoid suture change shape or size over time?
A: Yes, the lambdoid suture can undergo changes in shape and size during skull growth and development. However, once adulthood is reached, the suture generally fuses and remains stable.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
