Quinones are fascinating organic compounds that play crucial roles in various biological and chemical processes. Found in everything from plants to bacteria, these compounds are essential for life as we know it. Quinones are involved in cellular respiration, photosynthesis, and even the production of certain antibiotics. Their unique chemical structure allows them to participate in electron transfer reactions, making them vital for energy production in cells. Beyond biology, quinones are also used in industrial applications, such as dyes and pigments. Understanding these versatile molecules can provide insights into both natural processes and technological advancements. Ready to dive into 50 intriguing facts about quinones? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Quinone, a colorful and versatile compound, is crucial for energy production, biological processes, and industrial applications. It's found in nature, used in everyday products, and even has potential health benefits.
- From vibrant dyes to energy storage, quinone's impact on our world is far-reaching. Its historical significance, biological importance, and potential future uses make it a fascinating and essential compound in our lives.
What is Quinone?
Quinone is a fascinating chemical compound with a variety of uses and properties. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this versatile substance.
-
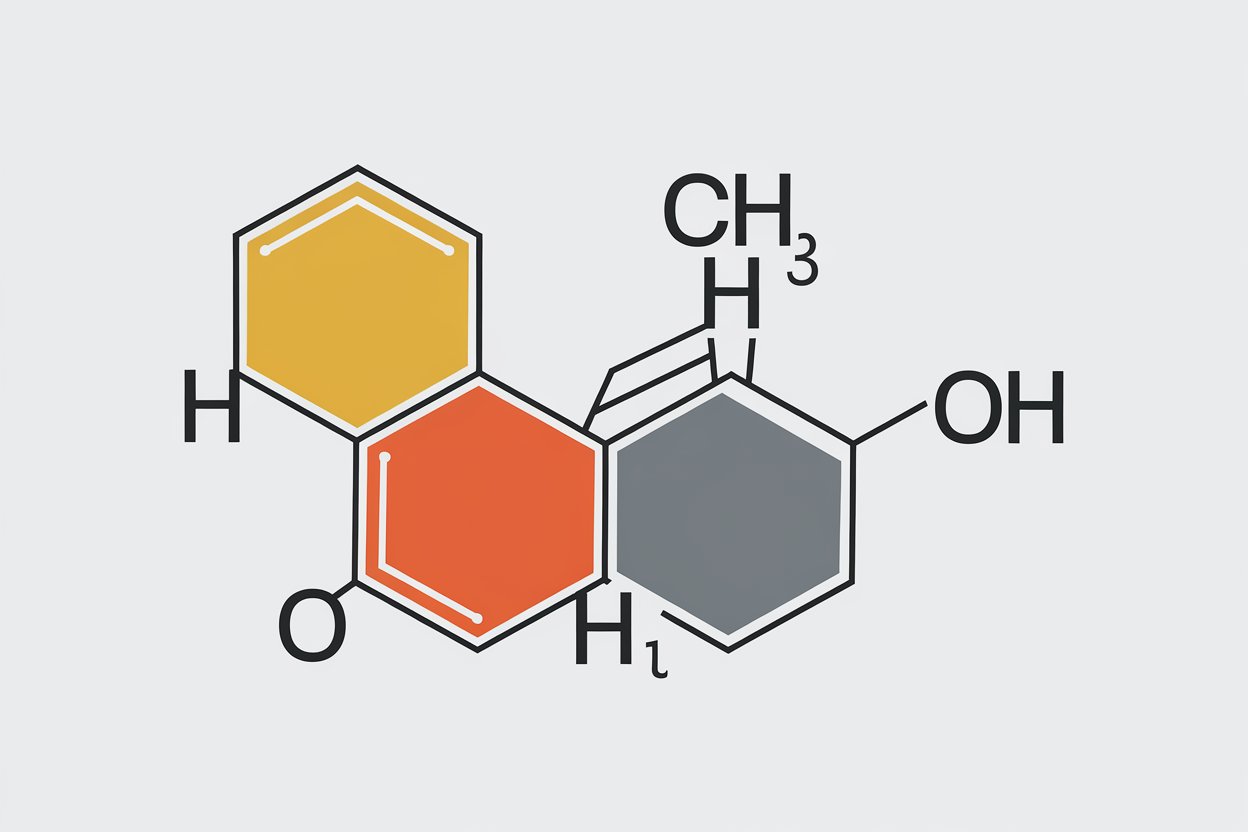
Quinones are a class of organic compounds characterized by a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure.
-
They are typically yellow, orange, or red in color due to their conjugated double bonds.
-
Quinones are found in nature, particularly in plants, fungi, and bacteria.
-
They play a crucial role in the electron transport chain, which is vital for cellular respiration.
Historical Background of Quinone
Understanding the history of quinone can provide insight into its importance and development over time.
-
The term "quinone" was first coined by German chemist Friedrich Wöhler in 1838.
-
Quinone was initially derived from the oxidation of quinic acid, a compound found in cinchona bark.
-
Early uses of quinone included its application as a dye due to its vibrant colors.
-
The discovery of quinone paved the way for the development of synthetic dyes and pigments.
Chemical Properties of Quinone
Quinone's chemical properties make it unique and useful in various applications.
-
Quinones are highly reactive due to their conjugated double bonds.
-
They can undergo redox reactions, making them important in biological systems.
-
Quinones can act as electron acceptors in biochemical processes.
-
They are soluble in organic solvents but have limited solubility in water.
Biological Significance of Quinone
Quinones play a vital role in many biological processes, making them essential for life.
-
Ubiquinone, also known as coenzyme Q10, is a type of quinone crucial for cellular energy production.
-
Vitamin K, another quinone, is essential for blood clotting.
-
Quinones are involved in the synthesis of ATP, the energy currency of cells.
-
They help protect cells from oxidative damage by acting as antioxidants.
Industrial Uses of Quinone
Quinone's unique properties make it valuable in various industrial applications.
-
Quinones are used in the production of dyes and pigments.
-
They serve as intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals.
-
Quinones are employed in the rubber industry as vulcanizing agents.
-
They are used in the manufacture of photographic chemicals.
Environmental Impact of Quinone
Quinone's presence and use can have significant environmental implications.
-
Quinones can be toxic to aquatic life if released into water bodies.
-
They can undergo photodegradation, breaking down under sunlight.
-
Some quinones are used in pesticides, impacting soil and water quality.
-
Biodegradation of quinones by microorganisms can help mitigate their environmental impact.
Health Implications of Quinone
Quinone's interaction with biological systems can have both beneficial and harmful effects on health.
-
Coenzyme Q10 supplements are used to boost energy and support heart health.
-
Excessive exposure to quinones can cause skin irritation and respiratory issues.
-
Some quinones have been studied for their potential anticancer properties.
-
Quinones can cause oxidative stress if not properly regulated in the body.
Quinone in Research and Development
Ongoing research continues to uncover new applications and properties of quinone.
-
Scientists are exploring quinones as potential treatments for neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Research is being conducted on quinone-based materials for energy storage.
-
Quinones are being studied for their role in photosynthesis and artificial photosynthesis.
-
New synthetic methods are being developed to produce quinones more efficiently.
Fun Facts about Quinone
Here are some quirky and lesser-known facts about quinone that might surprise you.
-
The bright yellow color of turmeric comes from a quinone called curcumin.
-
Quinones are responsible for the color change in autumn leaves.
-
Some quinones have a distinct, pungent odor.
-
The red color of certain lichens is due to quinone compounds.
Quinone in Popular Culture
Quinone has even made its way into popular culture in unexpected ways.
-
The vibrant colors of quinone dyes have been used in traditional textiles.
-
Quinone-based pigments are used in some artist paints.
-
Historical documents and artworks have been preserved using quinone-based chemicals.
-
Quinone's role in photosynthesis has been featured in educational documentaries.
Future Prospects of Quinone
The future holds exciting possibilities for the application and understanding of quinone.
-
Advances in nanotechnology could lead to new quinone-based materials.
-
Quinones may play a role in developing sustainable energy solutions.
-
Ongoing research could uncover new medicinal uses for quinones.
-
Environmental studies may find ways to mitigate the impact of quinone pollution.
Quinone in Everyday Life
Quinone might be more present in your daily life than you realize.
-
Some skincare products contain quinones for their antioxidant properties.
-
Quinone derivatives are used in hair dyes.
-
Certain food preservatives contain quinone compounds.
-
Quinones are found in some household cleaning products.
-
The ink in some pens and markers contains quinone-based dyes.
-
Quinones are used in the production of certain types of plastics.
The Final Word on Quinones
Quinones are fascinating compounds with a wide range of applications. From their role in biological processes to their use in industrial applications, these molecules are incredibly versatile. They play a crucial part in photosynthesis, respiration, and even medicinal chemistry. Their ability to undergo redox reactions makes them valuable in energy storage and electronic devices.
Understanding quinones can lead to advancements in healthcare, environmental science, and technology. Researchers continue to explore their potential, uncovering new uses and benefits. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or just curious, knowing about quinones can enrich your understanding of the natural world and its complexities.
So, next time you hear about quinones, you'll know they're more than just a chemical term—they're key players in many aspects of life and industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
