Diborane is a fascinating chemical compound with the formula B2H6. Known for its unique structure and reactivity, it plays a crucial role in various industrial and scientific applications. What makes diborane so special? This compound is not just another boring molecule; it has a rich history and a set of properties that make it stand out. From its discovery in the early 20th century to its use in rocket fuel and organic synthesis, diborane has proven to be incredibly versatile. Why should you care about diborane? Understanding this compound can offer insights into the world of chemistry and its practical uses. Dive into these 40 facts to uncover the secrets of diborane!
Key Takeaways:
- Diborane is a unique and versatile chemical compound with applications in organic synthesis, rocket fuel, and semiconductor industry. Its reactivity and toxic nature require careful handling and disposal methods.
- Despite its sweet odor, diborane is highly toxic and flammable, posing environmental risks. Ongoing research aims to explore new applications and improve safety measures for this fascinating compound.
What is Diborane?
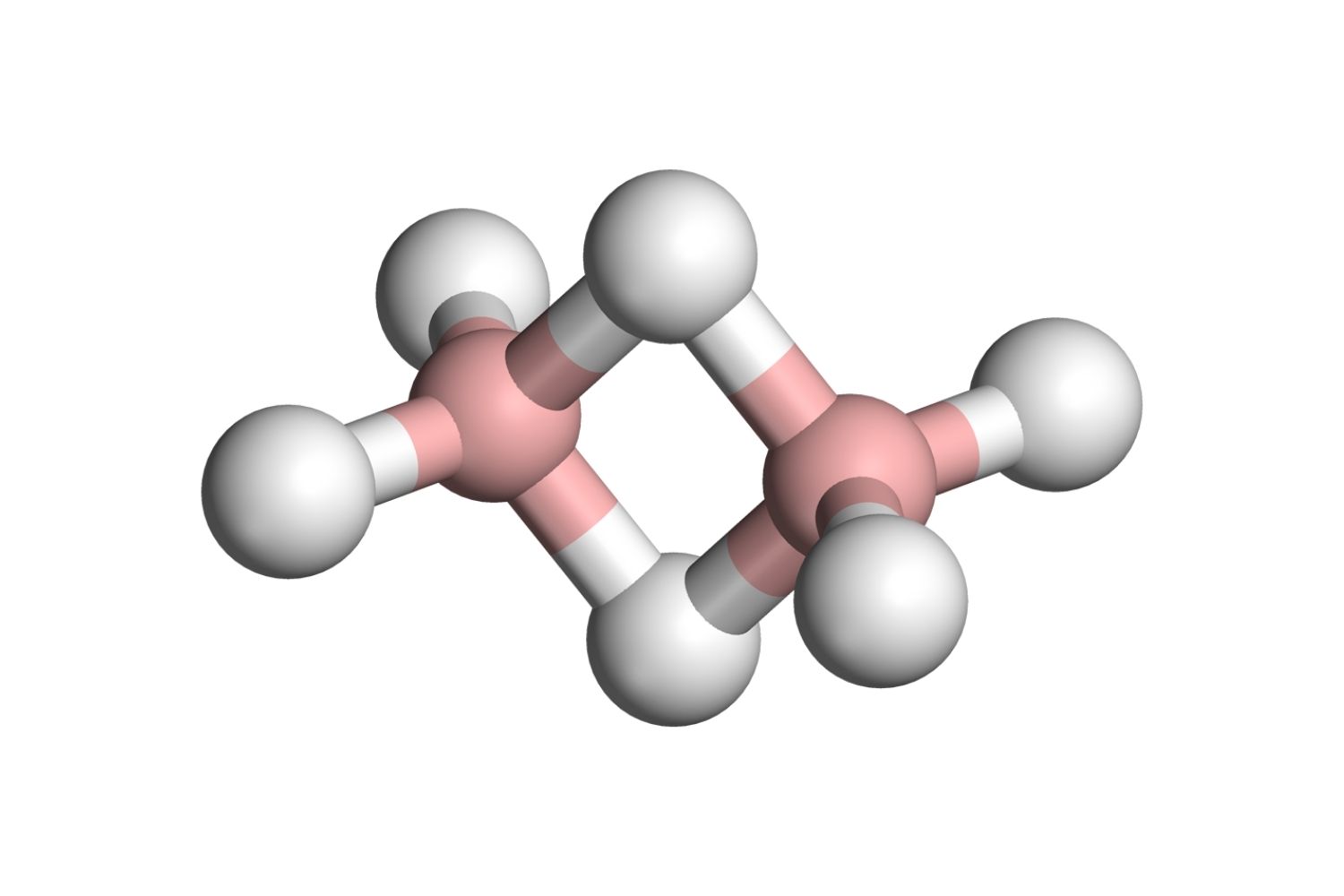
Diborane is a fascinating chemical compound with the formula B₂H₆. It is a colorless, highly flammable gas with a sweet odor. This compound has numerous applications in chemistry and industry, making it an interesting subject to explore.
- Diborane consists of two boron atoms and six hydrogen atoms.
- It is known for its electron-deficient bonding, which means it has fewer electrons than needed for conventional bonds.
- The molecule has a unique structure with two bridging hydrogen atoms.
- Diborane is highly reactive and can ignite spontaneously in air.
- It was first synthesized in 1912 by Alfred Stock.
Uses of Diborane
Diborane has a variety of uses, particularly in the field of organic synthesis and as a rocket fuel. Its unique properties make it valuable for several industrial applications.
- It is used as a reducing agent in organic chemistry.
- Diborane serves as a precursor for the production of other boron-containing compounds.
- It is employed in the semiconductor industry for doping silicon and germanium.
- Diborane is used in the synthesis of boranes, which are important in hydroboration reactions.
- It has been explored as a potential rocket fuel due to its high energy content.
Safety and Handling
Due to its highly reactive nature, diborane must be handled with extreme care. Understanding its safety protocols is crucial for anyone working with this compound.
- Diborane is highly toxic and can cause severe respiratory issues.
- It should be stored in tightly sealed containers to prevent leaks.
- Proper ventilation is necessary when working with diborane to avoid inhalation.
- Protective gear, including gloves and goggles, is essential when handling diborane.
- In case of exposure, immediate medical attention is required.
Chemical Reactions Involving Diborane
Diborane participates in a variety of chemical reactions, making it a versatile reagent in the laboratory. Its reactivity is a key feature that chemists exploit in different processes.
- Diborane reacts with water to form boric acid and hydrogen gas.
- It can undergo hydroboration reactions with alkenes to form organoboranes.
- Diborane reacts with ammonia to produce borazine, also known as "inorganic benzene."
- It can be used to reduce metal oxides to their respective metals.
- Diborane reacts with halogens to form boron trihalides.
Historical Significance
The discovery and study of diborane have contributed significantly to the field of chemistry. Its unique properties have led to advancements in understanding chemical bonding and reactivity.
- Alfred Stock's work on diborane laid the foundation for modern boron chemistry.
- The study of diborane helped in the development of the concept of three-center two-electron bonds.
- Diborane's unique bonding structure challenged traditional views of chemical bonding.
- Research on diborane has led to the discovery of other boron hydrides.
- The compound has been used as a model system for studying electron-deficient compounds.
Environmental Impact
While diborane has many useful applications, it also poses environmental risks. Understanding its impact on the environment is important for developing safe handling and disposal methods.
- Diborane can contribute to air pollution if released into the atmosphere.
- It is highly flammable and can cause fires or explosions if not handled properly.
- Diborane can react with moisture in the air to form toxic byproducts.
- Proper disposal methods are necessary to prevent environmental contamination.
- Research is ongoing to develop safer alternatives to diborane for industrial applications.
Fun Facts About Diborane
Beyond its scientific and industrial significance, diborane has some interesting and lesser-known facts that make it a captivating subject.
- Diborane has a sweet, almost pleasant odor, despite being highly toxic.
- It is one of the simplest boron hydrides, yet it has a complex bonding structure.
- Diborane can form explosive mixtures with air, even at low concentrations.
- It has been used in the past as a fumigant for pest control.
- Diborane's unique properties have made it a subject of study in theoretical chemistry.
Future Prospects
The study and application of diborane continue to evolve. Researchers are exploring new ways to harness its properties for innovative uses.
- Advances in nanotechnology may lead to new applications for diborane.
- Researchers are investigating diborane's potential in hydrogen storage for fuel cells.
- New synthetic methods are being developed to produce diborane more efficiently.
- Diborane's reactivity is being explored for use in advanced materials science.
- Ongoing research aims to improve the safety and handling of diborane in industrial settings.
Diborane: A Fascinating Compound
Diborane, a compound of boron and hydrogen, holds a unique place in chemistry. Its structure and bonding have intrigued scientists for decades. This gas, with its distinctive smell, is highly reactive and used in various industries. From semiconductor manufacturing to rocket fuel, diborane's applications are vast.
Understanding its properties helps in handling it safely. Diborane is toxic and flammable, requiring careful storage and usage. Despite its dangers, its benefits in chemical synthesis and material science are undeniable.
Exploring diborane reveals the complexity and beauty of chemical compounds. Its unique characteristics make it a subject of ongoing research. Whether you're a student, scientist, or just curious, diborane offers a glimpse into the wonders of chemistry. Keep learning and stay curious about the world around you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
