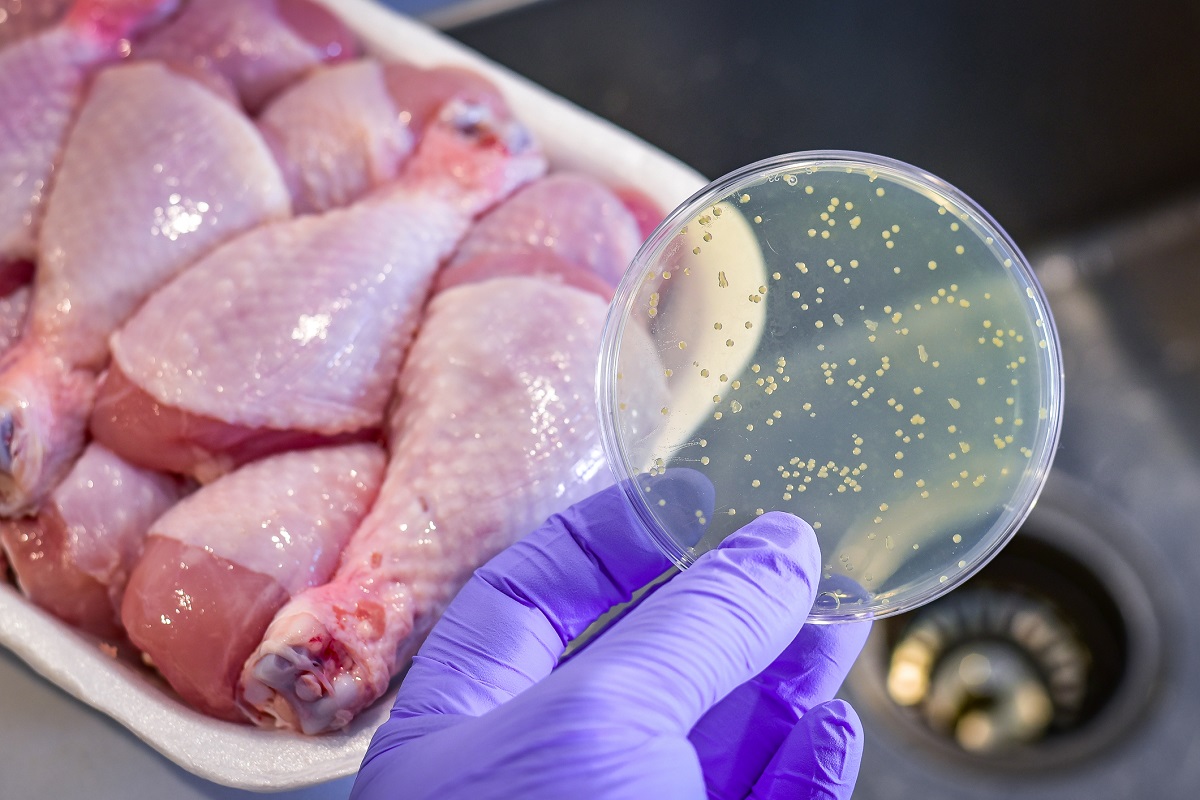
Foodborne illnesses are a major concern worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. These illnesses, also known as food poisoning, are caused by consuming contaminated food or drinks. They can range from mild discomfort to severe illness and even death in extreme cases. With the increasing globalization of food production and distribution, it is more important than ever to understand the risks and take necessary precautions to prevent foodborne illnesses.
In this article, we will explore 18 astounding facts about foodborne illnesses that will not only educate you but also highlight the importance of food safety. From common causes and symptoms to surprising sources and prevention strategies, this information will empower you to make informed decisions when it comes to your food choices and handling practices.
Key Takeaways:
- Foodborne illnesses affect millions yearly, mostly from bacteria in undercooked meats and unwashed produce. Proper hygiene and cooking can prevent these illnesses and their severe complications.
- Contaminated water, poor food storage, and vulnerable populations increase the risk of foodborne illnesses. Collaboration and awareness are crucial in preventing outbreaks globally.
Foodborne illnesses affect millions of people each year.
Foodborne illnesses, also known as food poisoning, is a significant public health concern worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), roughly 600 million people fall ill each year due to consuming contaminated food.
Bacteria are the most common cause of foodborne illnesses.
Bacterial contamination is responsible for the majority of foodborne illnesses. Pathogens such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter can lead to severe gastrointestinal symptoms when ingested.
Poor food hygiene practices contribute to the spread of foodborne illnesses.
Inadequate handwashing, improper storage of food, and cross-contamination are common causes of foodborne illnesses. It is crucial to follow proper food handling procedures to minimize the risk of contamination.
Raw and undercooked meats are a common source of foodborne illnesses.
Consuming raw or undercooked meats, including poultry, beef, and pork, can expose individuals to harmful bacteria and parasites. Thorough cooking helps eliminate these pathogens and reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Fruits and vegetables can also be sources of foodborne illnesses.
While fruits and vegetables are generally healthy, they can harbor bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli if not properly washed or contaminated during the growing or handling process.
Foodborne illnesses can cause severe complications.
Some foodborne pathogens can lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as young children, pregnant women, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of foodborne illnesses can vary.
Common symptoms of foodborne illnesses include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and dehydration. The onset and severity of symptoms may vary depending on the pathogen and individual factors.
Foodborne illnesses can be prevented through proper food safety practices.
Practicing good food safety habits such as washing hands regularly, cooking food thoroughly, storing food at appropriate temperatures, and avoiding cross-contamination can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Contaminated water can also lead to foodborne illnesses.
Improperly treated water or water contaminated with fecal matter can introduce pathogens into the food chain, leading to foodborne illnesses. It is essential to consume safe and clean water for food preparation and drinking.
Foodborne illnesses have economic implications.
Foodborne outbreaks can have significant economic consequences, including medical costs, hospitalizations, loss of productivity, and damage to the food industry due to recalls and loss of consumer trust.
Proper food storage is essential in preventing foodborne illnesses.
Storing food at the correct temperature, separating raw and cooked foods, and avoiding cross-contamination are crucial in preventing the growth of bacteria and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Some foodborne illnesses have long-term health effects.
Certain types of foodborne illnesses, such as those caused by parasites or specific strains of bacteria, can have long-term health effects, including kidney failure, chronic arthritis, and even neurological disorders.
Children and the elderly are more susceptible to foodborne illnesses.
Due to their weaker immune systems, children and older adults are at higher risk of developing severe complications from foodborne illnesses. Extra precautions must be taken when handling and preparing food for these vulnerable populations.
Foodborne illnesses can be more severe during pregnancy.
Pregnant women are at increased risk of developing serious complications from foodborne illnesses, which can also be harmful to the fetus. It is important for expectant mothers to practice strict food safety measures.
Contaminated food can cause outbreaks in large groups of people.
Inadequately processed or prepared food in settings like restaurants, schools, or catered events can cause outbreaks of foodborne illnesses, affecting a large number of people simultaneously.
Some foodborne illnesses are preventable through vaccinations.
Vaccinations against certain pathogens, such as hepatitis A and typhoid fever, can help prevent foodborne illnesses associated with these specific bacteria or viruses.
Proper cleaning of food preparation surfaces is crucial.
Cross-contamination can occur when food preparation surfaces aren’t adequately cleaned, leading to the spread of bacteria and increasing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Foodborne illnesses are a global challenge.
Foodborne illnesses affect people worldwide, regardless of geographical location or economic status. Collaborative efforts and global awareness are essential in combating and preventing these illnesses.
Conclusion
Foodborne illnesses pose a significant threat to public health, and being aware of the facts surrounding these diseases is crucial. From the staggering number of annual cases to the various ways they can be contracted, it is clear that preventing foodborne illnesses should be a top priority for individuals, communities, and governmental bodies alike. By understanding the risks associated with improper food handling, storage, and preparation, we can take proactive measures to reduce the occurrence of these illnesses.It is important to remember that ensuring food safety is a collective effort. By following proper hygiene practices, cooking food thoroughly, and purchasing from reputable sources, we can significantly minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses. Moreover, staying informed about food recalls, practicing safe handling techniques, and educating ourselves and others can go a long way in preventing the spread of these infections.Let us all strive for a safer food environment and work towards a future where foodborne illnesses are no longer a widespread concern.
FAQs
Q: What are foodborne illnesses?
A: Foodborne illnesses, also known as food poisoning or foodborne infections, are illnesses caused by consuming contaminated food or beverages.
Q: What are the most common causes of foodborne illnesses?
A: The most common causes of foodborne illnesses are bacteria (such as Salmonella and E. coli), viruses (such as norovirus), parasites (such as Toxoplasma), and toxins produced by harmful microorganisms.
Q: What are the symptoms of foodborne illnesses?
A: Symptoms can vary depending on the type of pathogen involved but commonly include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and fatigue.
Q: How can foodborne illnesses be prevented?
A: Foodborne illnesses can be prevented by following proper food handling and storage practices, cooking food to the appropriate temperatures, practicing good personal hygiene, and avoiding cross-contamination.
Q: Who is most at risk for foodborne illnesses?
A: Young children, pregnant women, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to severe cases of foodborne illnesses.
Q: Can foodborne illnesses be treated?
A: Most cases of foodborne illnesses resolve on their own without specific treatment. However, in severe cases, medical attention and supportive care may be required.
Foodborne illnesses pose significant health risks, but you can protect yourself by staying informed. Learning about specific bacteria like Clostridium perfringens, understanding the role of food scientists in ensuring food safety, and using tools like instant read thermometers can help you avoid these dangerous conditions. Take control of your health and explore more fascinating facts about food safety today!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
