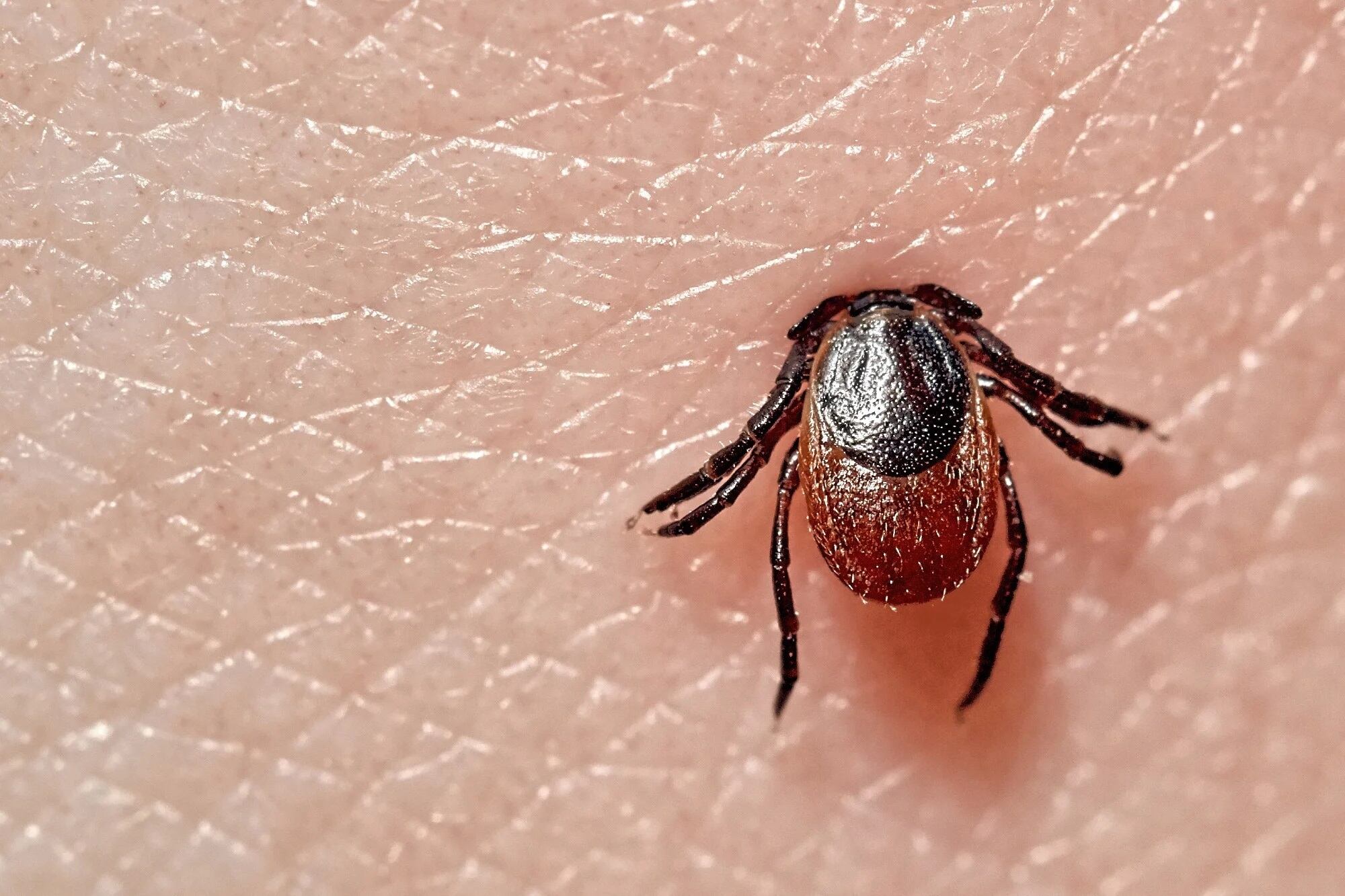
Lyme disease is a prevalent but often misunderstood illness that is transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks. This condition, named after the town of Lyme, Connecticut, where it was first identified in 1975, can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe complications if left untreated. Despite its serious nature, there are several fascinating and lesser-known aspects of Lyme disease that are worth exploring. In this article, we'll delve into 18 intriguing facts about Lyme disease, shedding light on various aspects of its history, symptoms, diagnosis, and prevention. So, let's embark on a journey to uncover some surprising insights about this complex and enigmatic illness.
Key Takeaways:
- Lyme Disease is named after the town of Lyme, Connecticut, and is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi transmitted through tick bites. Early recognition and treatment are crucial for a positive outcome.
- Preventing tick bites and early detection are key to reducing the risk of Lyme Disease. Pets can also be at risk, and ongoing research is focused on developing a vaccine.
Lyme Disease is named after the town of Lyme, Connecticut.
The disease was first identified in 1975 when a cluster of children in Lyme, Connecticut, experienced unusual arthritic symptoms. This led to the discovery of the disease, which was named after the town where the cases were identified.
Lyme Disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi.
Borrelia burgdorferi is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks. These ticks are commonly found in wooded and grassy areas, and when they bite, they can transmit the bacterium into the human bloodstream, leading to Lyme Disease.
The characteristic bullseye rash is a common early symptom of Lyme Disease.
One of the early signs of Lyme Disease is a distinctive rash that resembles a bullseye, with a red outer ring surrounding a clear area and then a red center. This rash, known as erythema migrans, typically appears within 3-30 days of a tick bite and is an indicator of infection.
Lyme Disease can affect the heart, joints, and nervous system.
If left untreated, Lyme Disease can spread to different parts of the body, leading to a range of symptoms. These can include heart palpitations, joint pain and swelling, and neurological problems such as nerve pain and inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
Not all individuals with Lyme Disease develop the bullseye rash.
While the bullseye rash is a well-known symptom of Lyme Disease, not everyone who is infected will develop this distinctive rash. This makes it important for individuals to be aware of other potential symptoms of the disease, such as fever, fatigue, and muscle aches.
There are three stages of Lyme Disease.
Lyme Disease progresses through three stages: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated. Each stage is associated with specific symptoms and complications, with the early localized stage typically characterized by the bullseye rash and flu-like symptoms.
Lyme Disease is often misdiagnosed due to its diverse symptoms.
Given the wide range of symptoms that can occur in different stages of the disease, Lyme Disease is frequently misdiagnosed as conditions such as chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, and various psychiatric illnesses. This can lead to delays in receiving appropriate treatment.
Tick bites are more likely to transmit Lyme Disease if the tick is attached for more than 36 hours.
Studies have shown that the longer a tick remains attached to the skin, the higher the risk of transmitting Lyme Disease. Early and prompt removal of ticks can significantly reduce the likelihood of infection.
Lyme Disease is diagnosed based on symptoms, physical findings, and the possibility of exposure to infected ticks.
Physicians often rely on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and a thorough patient history to diagnose Lyme Disease. Laboratory testing may also be used to confirm the diagnosis, particularly in cases where the characteristic rash is absent.
Lyme Disease can be effectively treated with antibiotics.
Early detection and treatment of Lyme Disease are crucial for a full recovery. Antibiotics such as doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime axetil are commonly prescribed to combat the infection, with most patients responding well to treatment.
There is a debate about the existence of chronic Lyme Disease.
Some individuals continue to experience symptoms such as fatigue, muscle aches, and joint pain even after receiving standard Lyme Disease treatment. This has led to ongoing debate within the medical community about the existence and treatment of chronic Lyme Disease.
Preventing tick bites is key to reducing the risk of Lyme Disease.
Measures such as using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities, and promptly removing attached ticks can help minimize the risk of contracting Lyme Disease.
Lyme Disease is most prevalent in the Northeastern and Midwestern United States.
While Lyme Disease can be found in many areas across the United States, it is most commonly reported in the Northeastern and Midwestern regions, where the blacklegged ticks that transmit the disease are prevalent.
Untreated Lyme Disease can lead to long-term complications.
If Lyme Disease is not promptly treated, it can lead to persistent symptoms, including arthritis, cognitive defects, and nerve damage. These long-term complications highlight the importance of early detection and appropriate medical care.
There is ongoing research to develop a Lyme Disease vaccine.
Efforts are underway to develop a vaccine to prevent Lyme Disease. While a Lyme Disease vaccine was previously available, it was withdrawn from the market. However, research continues to explore the potential for an effective vaccine against the disease.
Pets, particularly dogs, can also contract Lyme Disease.
Just like humans, pets can be at risk of Lyme Disease if they are bitten by an infected tick. This makes it important for pet owners to take preventive measures and seek veterinary care if their pets show signs of infection.
Lyme Disease can have a significant impact on daily life.
For individuals living with chronic Lyme Disease, the condition can have a profound impact on their daily activities and overall well-being. This underscores the importance of ongoing support and research to address the complexities of the disease.
Early recognition and treatment of Lyme Disease are essential for a positive outcome.
With increased awareness, preventive measures, and prompt medical intervention, the prognosis for individuals with Lyme Disease can be favorable. Early recognition and treatment play a crucial role in preventing the progression of the disease and minimizing potential complications.
FAQs
What is Lyme disease?
Lyme disease is an infectious illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks.
What are the common symptoms of Lyme disease?
The early signs of Lyme disease may include a distinctive skin rash called erythema migrans, along with flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, body aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
Lyme disease is diagnosed based on symptoms, physical findings (such as the characteristic rash), and the possibility of exposure to infected ticks. Laboratory testing can be helpful if used correctly and performed with validated methods.
Can Lyme disease be prevented?
Preventive measures include using insect repellent, removing ticks promptly, landscaping to create tick-safe zones, and employing tick control products.
Is Lyme disease treatable?
Lyme disease is treatable with antibiotics. Most cases of Lyme disease can be successfully treated with a few weeks of antibiotics.
Conclusion
Lyme disease is a complex and serious illness that requires prompt attention and proper understanding. By being aware of the symptoms, prevention methods, and available treatments, individuals can protect themselves and their loved ones from the potential risks associated with Lyme disease. It's important to stay informed and seek medical assistance if any symptoms or concerns arise.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
