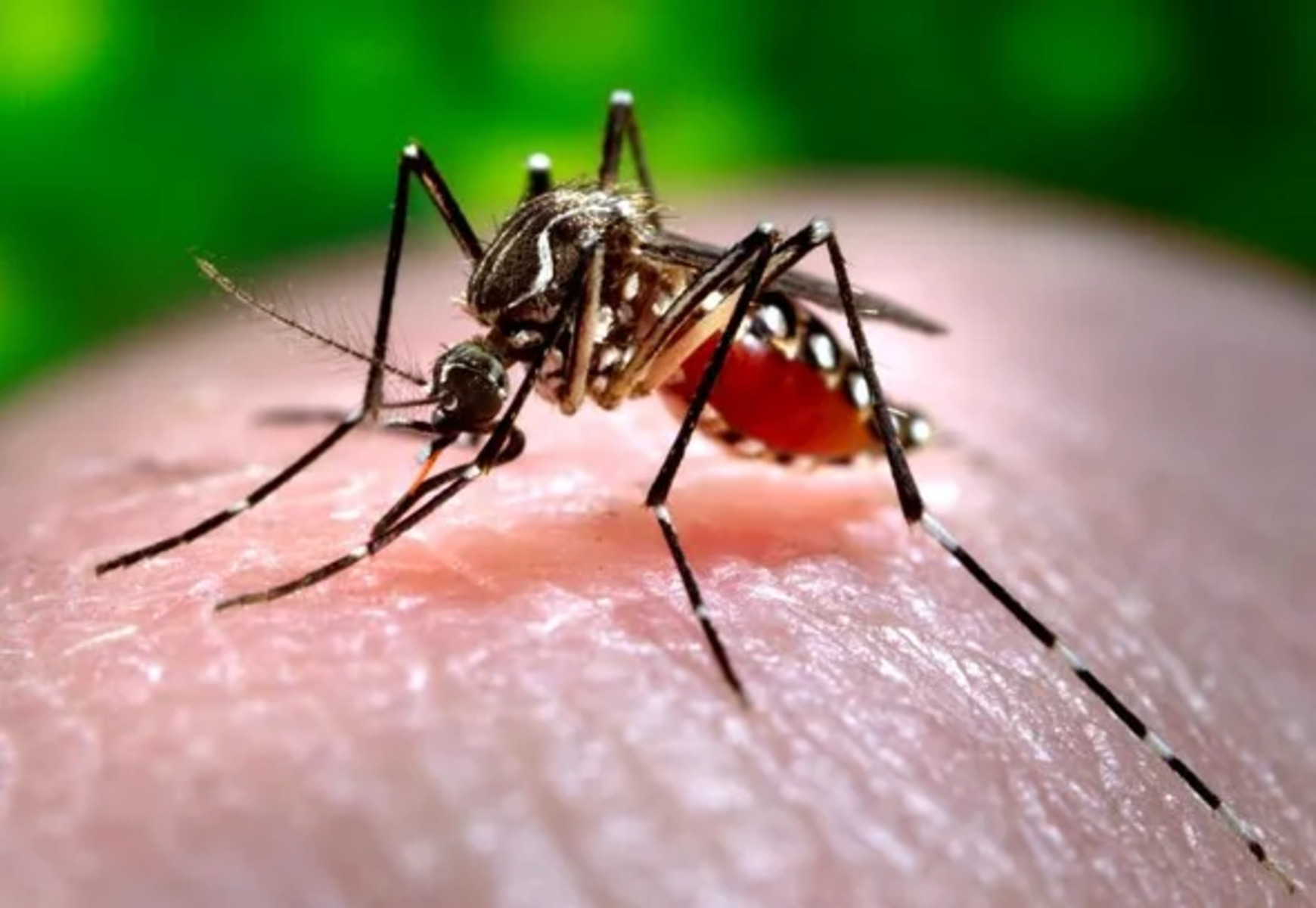
Vector-borne diseases are a significant threat to human health, with millions of people affected worldwide each year. These diseases, such as malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and Lyme disease, are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected vectors, such as mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, and sandflies. They are known for their ability to spread rapidly and cause widespread outbreaks.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of vector-borne diseases and explore 16 mind-blowing facts that will shed light on the complexities and impact of these diseases. From the astonishing transmission methods to the staggering global burden, these facts will highlight the urgent need for prevention, control, and research in the field of vector-borne diseases.
Key Takeaways:
- Vector-borne diseases are transmitted by pesky creatures like mosquitoes and ticks, putting over half the world’s population at risk. Prevention and public awareness are key to combating these diseases.
- Climate change is expanding the geographic range of disease-carrying vectors, making prevention and control efforts crucial in safeguarding public health.
Vector-borne diseases are transmitted by vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas.
These pesky creatures serve as carriers for pathogens, transmitting diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, Lyme disease, and more.
Over half of the world’s population is at risk of vector-borne diseases.
According to the World Health Organization, more than 3.9 billion people in at least 128 countries are susceptible to these diseases.
Mosquitoes are the deadliest animals on Earth.
While they might seem harmless, mosquitoes are responsible for millions of deaths each year due to malaria, dengue fever, and other diseases they transmit.
Climate change is contributing to the spread of vector-borne diseases.
Warmer temperatures and changing rainfall patterns create favorable conditions for vectors, allowing them to expand their habitats and increase disease transmission.
Vector-borne diseases can have severe consequences.
These diseases can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild flu-like symptoms to severe complications that can be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
Prevention is key in controlling vector-borne diseases.
Simple measures such as using mosquito nets, wearing protective clothing, eliminating breeding sites, and using insect repellents can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Travelers can unknowingly introduce vector-borne diseases to new areas.
People who travel to regions with high disease prevalence can bring the pathogens back with them, potentially leading to local outbreaks in their home countries.
Vector control programs play a crucial role in disease prevention.
Efforts to control vectors through insecticide use, mosquito population surveillance, and community education help to reduce the spread of these diseases.
Vector-borne diseases affect both developed and developing countries.
While these diseases are more prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, they can also affect countries with temperate climates.
Climate change is expanding the geographic range of some vectors.
As temperatures rise, mosquitoes and ticks are able to survive and thrive in areas where they were previously unable to, increasing the risk of disease transmission.
Poverty and limited access to healthcare contribute to the burden of vector-borne diseases.
Communities with inadequate resources are often more vulnerable to these diseases, as they may lack proper sanitation, housing, and healthcare services.
Vaccines and effective treatments exist for some vector-borne diseases.
While there is no universal vaccine for all vector-borne diseases, vaccines and treatments are available for specific ones, such as yellow fever and Japanese encephalitis.
Vector-borne diseases can have long-term health implications.
Some individuals who have recovered from vector-borne diseases may experience lingering health issues, such as chronic fatigue, joint pain, or neurological complications.
Climate change mitigation can help reduce the impact of vector-borne diseases.
Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to changing climates can help minimize the expansion of vector populations and the spread of diseases.
Vector-borne diseases disproportionately affect children and the elderly.
Young children and older adults are often more susceptible to the severe effects of these diseases, due to weakened immune systems and other underlying health conditions.
Public awareness and education are crucial in combating vector-borne diseases.
Informing the public about the risks, transmission modes, and preventive measures can empower individuals and communities to take necessary actions to protect themselves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vector-borne diseases are a serious global health concern. They are transmitted by various vectors such as mosquitoes, ticks, and fleas, and can lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Understanding the facts about these diseases is crucial for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.The 16 mind-blowing facts about vector-borne diseases highlighted in this article shed light on the magnitude of the problem. From the staggering number of people affected each year to the impact on global economies, these facts serve as a reminder of the importance of taking proactive measures to combat these diseases.By implementing vector control strategies, promoting public awareness, and investing in research and development, we can work towards reducing the burden of vector-borne diseases and safeguarding the health and well-being of communities worldwide.
FAQs
1. What are vector-borne diseases?
Vector-borne diseases are infectious diseases that are transmitted to humans or animals through a vector, such as mosquitoes, ticks, or fleas.
2. What are some common examples of vector-borne diseases?
Common examples of vector-borne diseases include malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, Lyme disease, and Chikungunya.
3. How do vector-borne diseases spread?
Vector-borne diseases spread when a vector, such as a mosquito, picks up the infectious agent from an infected human or animal and then transmits it to a susceptible individual during a subsequent feeding.
4. What are the symptoms of vector-borne diseases?
The symptoms of vector-borne diseases vary depending on the specific disease but can include fever, headache, body aches, rash, fatigue, and in severe cases, organ failure or death.
5. How can we prevent vector-borne diseases?
Prevention measures include using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, eliminating stagnant water sources, using bed nets, and getting vaccinated if available.
6. Are vector-borne diseases treatable?
Yes, many vector-borne diseases are treatable. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for a successful outcome.
7. Are vector-borne diseases only a problem in tropical regions?
No, vector-borne diseases can occur in both tropical and temperate regions. The distribution of these diseases is influenced by various factors, including climate, habitat, and human behavior.
8. How significant is the global impact of vector-borne diseases?
Vector-borne diseases have a significant global impact, with billions of people at risk and millions of cases reported annually. They also impose a substantial burden on healthcare systems and economies.
9. Is there ongoing research to combat vector-borne diseases?
Yes, there is ongoing research to develop new prevention methods, diagnostics, and treatments for vector-borne diseases. This research aims to improve control strategies and reduce the impact of these diseases.
10. How can individuals contribute to the prevention of vector-borne diseases?
Individuals can contribute to prevention efforts by practicing personal protective measures, supporting vector control programs, and promoting awareness in their communities.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
