Boron triiodide might sound like a mouthful, but this compound is more interesting than you might think. What is boron triiodide? It’s a chemical compound made up of one boron atom and three iodine atoms. This substance is known for its reactivity and usefulness in various chemical reactions. Why should you care? Well, boron triiodide plays a crucial role in organic synthesis, especially in the formation of carbon-iodine bonds. It’s also used in the semiconductor industry and has applications in research labs. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast or just curious, learning about boron triiodide can open up a world of fascinating facts. Ready to dive in? Let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Boron Triiodide, a pungent and reactive compound, has diverse uses from catalyzing chemical reactions to potential applications in pharmaceuticals. It requires careful handling and safety precautions due to its hazards.
- With a unique trigonal planar structure and covalent bonding, Boron Triiodide offers intriguing properties, including its color change under light and potential as a Lewis acid. Ongoing research explores its diverse applications.
What is Boron Triiodide?
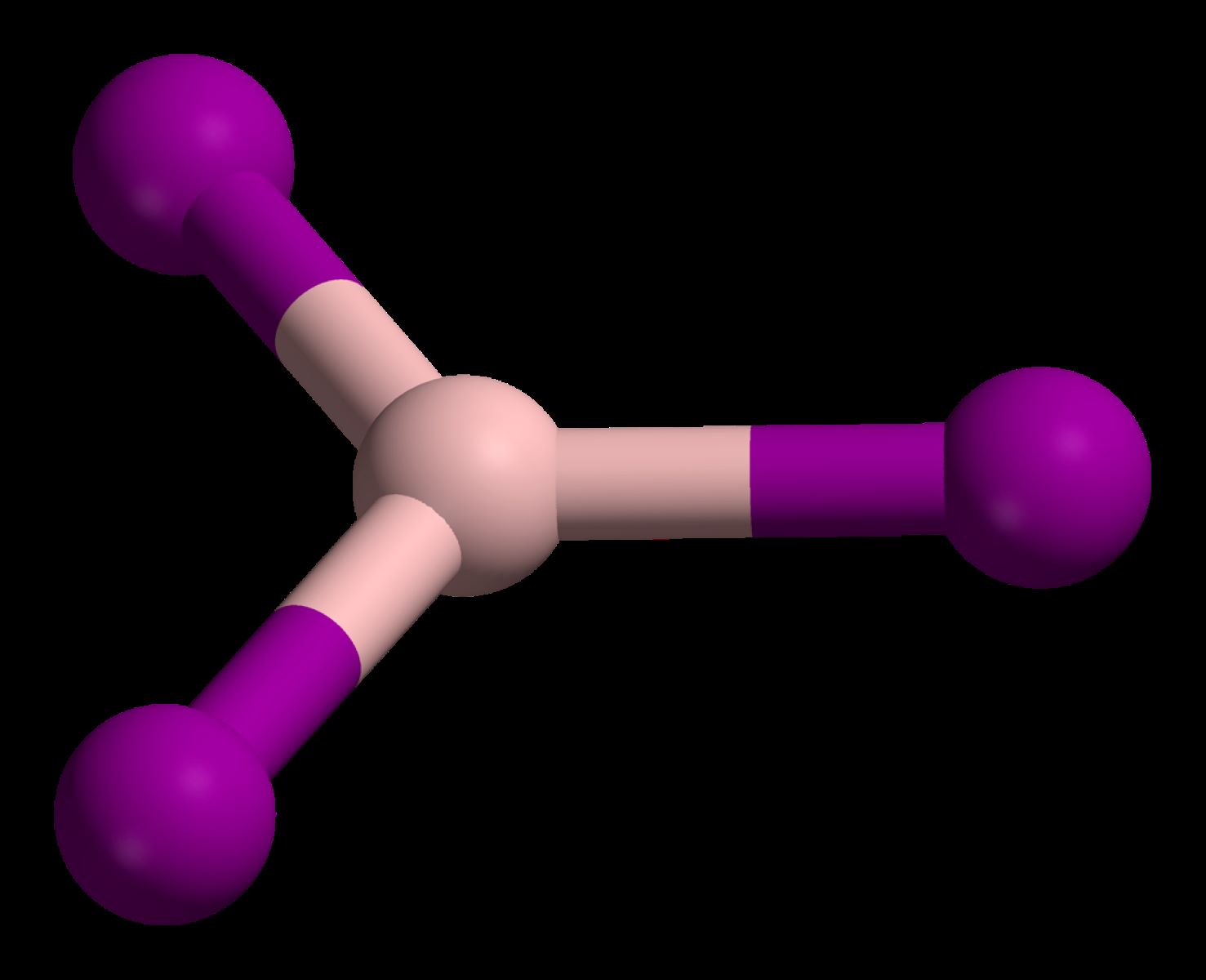
Boron Triiodide (BI3) is a chemical compound composed of one boron atom and three iodine atoms. This compound is known for its unique properties and applications in various fields, from chemistry to industry.
- Chemical Formula: The chemical formula for Boron Triiodide is BI3.
- Molecular Weight: It has a molecular weight of approximately 391.52 g/mol.
- Appearance: Boron Triiodide appears as a colorless to pale yellow crystalline solid.
- Odor: This compound has a pungent odor, which can be quite strong.
- Melting Point: BI3 has a melting point of about 49.9°C (121.8°F).
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of Boron Triiodide is around 210°C (410°F).
- Density: It has a density of 3.35 g/cm³ at room temperature.
- Solubility: BI3 is soluble in organic solvents like benzene and toluene but not in water.
- Reactivity: This compound is highly reactive, especially with water, forming hydrogen iodide and boric acid.
- Stability: Boron Triiodide is stable under normal conditions but decomposes in the presence of moisture.
Uses of Boron Triiodide
Boron Triiodide has several applications, particularly in the field of chemistry and materials science. Here are some of its notable uses:
- Catalyst: It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions.
- Chemical Intermediate: BI3 serves as an intermediate in the production of other boron-containing compounds.
- Doping Agent: In the semiconductor industry, it is used as a doping agent to modify the electrical properties of materials.
- Reagent: Boron Triiodide acts as a reagent in various chemical reactions, including the preparation of boron esters.
- Synthesis of Boron Nitride: It is used in the synthesis of boron nitride, a material with high thermal and chemical stability.
- Halogenation Reactions: BI3 is employed in halogenation reactions to introduce iodine atoms into organic molecules.
- Polymerization: It can initiate polymerization reactions in certain monomers.
- Gas-Phase Deposition: Used in gas-phase deposition techniques to create thin films of boron-containing materials.
- Laboratory Research: BI3 is utilized in research laboratories for various experimental purposes.
- Pharmaceuticals: It has potential applications in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of new drugs.
Safety and Handling of Boron Triiodide
Handling Boron Triiodide requires caution due to its reactive nature and potential hazards. Here are some safety considerations:
- Protective Equipment: Always wear appropriate protective equipment, including gloves and goggles, when handling BI3.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in the working area to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Storage: Store Boron Triiodide in a cool, dry place away from moisture and incompatible substances.
- First Aid: In case of contact with skin or eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical attention.
- Fire Hazard: BI3 is not flammable, but it can release toxic fumes when heated.
- Spill Cleanup: In case of a spill, use inert absorbent materials to clean up and dispose of properly.
- Disposal: Dispose of Boron Triiodide and its containers according to local regulations.
- Incompatibility: Avoid contact with water, alcohols, and strong bases, as these can cause violent reactions.
- Health Effects: Exposure to BI3 can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
- Emergency Procedures: Have emergency procedures in place for dealing with accidental exposure or spills.
Interesting Facts about Boron Triiodide
Beyond its practical uses and safety considerations, Boron Triiodide has some intriguing characteristics worth noting:
- Discovery: Boron Triiodide was first synthesized in the 19th century by reacting boron with iodine.
- Crystal Structure: It has a trigonal planar molecular geometry, with the boron atom at the center and iodine atoms at the corners.
- Bonding: The B-I bonds in BI3 are covalent, with each bond having a bond length of approximately 2.14 Å.
- Color Change: When exposed to light, Boron Triiodide can undergo a slight color change due to photodecomposition.
- Lewis Acid: BI3 acts as a Lewis acid, meaning it can accept electron pairs from other molecules.
- Hydrolysis: When hydrolyzed, it produces boric acid and hydrogen iodide, both of which have their own applications.
- Vapor Pressure: It has a relatively high vapor pressure at room temperature, making it volatile.
- Electron Configuration: The boron atom in BI3 has an electron configuration of [He] 2s2 2p1.
- Iodine Content: BI3 contains a high percentage of iodine by weight, making it useful in iodine chemistry.
- Research Potential: Ongoing research explores new applications and properties of Boron Triiodide in various scientific fields.
The Final Word on Boron Triiodide
Boron triiodide, a fascinating compound, plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions and industrial applications. Its unique properties, like high reactivity and ability to form stable complexes, make it indispensable in organic synthesis and semiconductor manufacturing. Understanding these facts about boron triiodide not only broadens your knowledge but also highlights its importance in scientific advancements.
Whether you're a chemistry enthusiast or just curious, knowing about boron triiodide can spark interest in the wonders of chemistry. From its molecular structure to its practical uses, this compound proves that even the smallest elements can have a significant impact. So, next time you hear about boron triiodide, you'll appreciate the science behind it and its contributions to technology and industry. Keep exploring, and who knows what other fascinating facts you'll uncover!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
