Atmospheric chemistry, the study of chemical processes occurring in the Earth’s atmosphere, is a fascinating and complex field that plays a crucial role in understanding our planet’s climate, air quality, and the composition of our atmosphere. From the formation of ozone to the impact of pollutants on human health, atmospheric chemistry reveals the intricate interactions between the atmosphere and various compounds present in it.
In this article, we will explore 15 enigmatic facts about atmospheric chemistry that shed light on the fascinating world above us. From the role of greenhouse gases in climate change to the formation of smog and the chemistry behind the stunning colors of the auroras, these facts will deepen your understanding of the crucial role that chemistry plays in shaping our atmosphere and impacting our daily lives.
Key Takeaways:
- The ozone layer protects us from harmful UV radiation, and understanding atmospheric chemistry helps us preserve this vital shield for our health and the environment.
- Atmospheric chemistry influences air quality, climate change, and even the formation of phenomena like acid rain and polar stratospheric clouds. It’s like a hidden puzzle that affects our daily lives in surprising ways.
The Ozone Layer Shield
One of the most fascinating aspects of atmospheric chemistry is the protective role played by the ozone layer. This fragile shield located in the Earth’s stratosphere helps to filter out harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, averting its detrimental effects on living organisms.
The Greenhouse Effect
Atmospheric chemistry is integral to the understanding of the greenhouse effect. Certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide and methane, act as greenhouse gases, trapping heat and contributing to global warming.
Acid Rain Phenomenon
The occurrence of acid rain is a direct consequence of atmospheric chemistry. Pollutants released into the air, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, can undergo chemical reactions, resulting in the formation of acidic compounds that fall back to Earth as rain.
Atmospheric Aerosols
Did you know that aerosols, tiny solid or liquid particles suspended in the atmosphere, play a critical role in atmospheric chemistry? These aerosols can influence cloud formation, air quality, and even the global climate by reflecting or absorbing sunlight.
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
The phenomenon of stratospheric ozone depletion, primarily caused by human-made chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), remains one of the most enigmatic aspects of atmospheric chemistry. This depletion exposes the planet to increased UV radiation, posing risks to human health and ecosystems.
Air Pollution and Smog Formation
Understanding atmospheric chemistry is crucial for comprehending the causes and consequences of air pollution and smog formation. Emissions from vehicles, factories, and other sources undergo complex reactions in the atmosphere, leading to the creation of pollutants and the notorious haze known as smog.
Chemical Reactions in the Troposphere
The troposphere, the lowest layer of the Earth’s atmosphere, is where most chemical reactions occur. From the oxidation of pollutants to the formation of ground-level ozone, these reactions in the troposphere greatly impact air quality and our daily lives.
Ozone Hole over Antarctica
An intriguing phenomenon related to atmospheric chemistry is the formation of the ozone hole over Antarctica. This hole, identified in the 1980s, has raised concerns worldwide due to its impact on UV radiation levels and potential global atmospheric circulation patterns.
Atmospheric Aerosol-Cloud Interactions
Scientists are still working to unravel the complex interactions between atmospheric aerosols and clouds. These interactions can affect cloud properties, precipitation patterns, and even the Earth’s energy budget, making them a captivating subject within atmospheric chemistry.
Nitrogen Cycle and Atmospheric Chemistry
The nitrogen cycle, a vital process that converts nitrogen between various forms, is intimately linked to atmospheric chemistry. Nitrogen-based compounds can contribute to air pollution and the formation of secondary pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere.
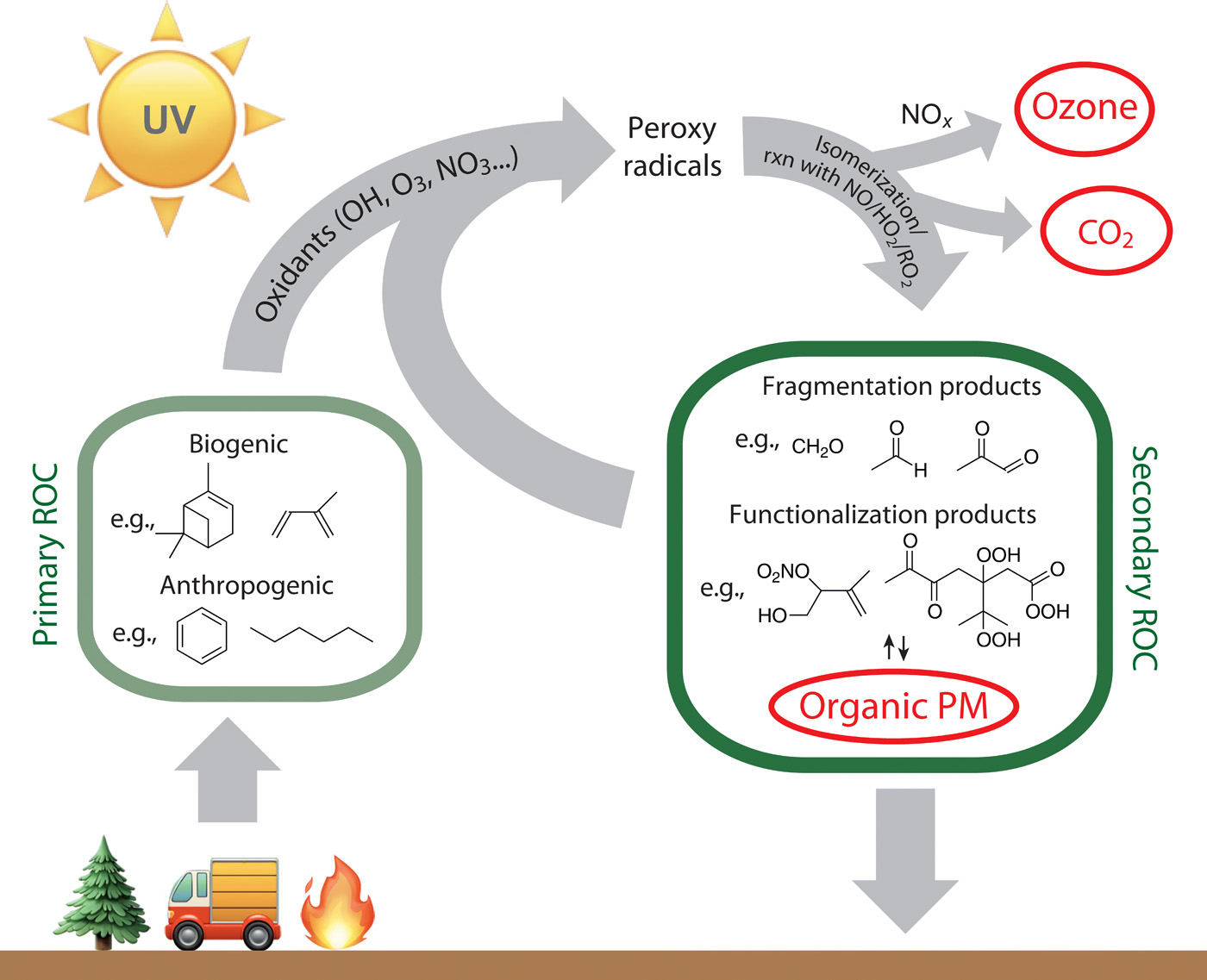
Volatile Organic Compounds
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are significant contributors to atmospheric chemistry. Released from sources like vegetation and human activities, these compounds can undergo chemical reactions in the atmosphere, leading to the formation of ozone and aerosols.
Ozone Formation in the Troposphere
While typically associated with the stratosphere, ozone also plays a role in atmospheric chemistry within the troposphere. Ozone formation occurs through complex reactions involving precursor pollutants, sunlight, and temperature conditions, contributing to air pollution concerns.
Polar Stratospheric Clouds
Polar stratospheric clouds, also known as nacreous clouds, hold a certain mystique in atmospheric chemistry. These iridescent clouds form in the polar regions during winter and play a critical role in the occurrence of chemical reactions leading to ozone depletion.
The Role of Trace Gases
Trace gases, present in minute concentrations in the atmosphere, can have a substantial impact on atmospheric chemistry. Examples include ozone, carbon monoxide, and volatile organic compounds, which can influence air quality, climate change, and the ozone layer.
Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Change
Finally, perhaps the most crucial enigma surrounding atmospheric chemistry is its relationship with climate change. Understanding the complex interactions between gases, aerosols, and radiation is essential for comprehending and mitigating the anthropogenic effects on our planet’s climate.
Conclusion
Atmospheric chemistry is a fascinating field that plays a crucial role in our understanding of the Earth’s atmosphere and its impact on climate change and human health. The enigmatic facts about atmospheric chemistry highlight the complexity and intricacy of the processes occurring in the atmosphere.
From the formation of ozone to the role of aerosols in regulating climate, atmospheric chemistry uncovers the secrets of the air we breathe. The interplay between natural and anthropogenic processes leads to a delicate balance that can be both awe-inspiring and concerning.
As we continue to study atmospheric chemistry, it is crucial to recognize its significance in addressing environmental challenges and shaping policy decisions. By understanding the complexities of atmospheric chemistry, we can work towards developing sustainable solutions and mitigating the impact of human activities on our atmosphere.
FAQs
Q: What is atmospheric chemistry?
A: Atmospheric chemistry is the study of the chemical composition, reactions, and processes occurring in the Earth’s atmosphere. It focuses on understanding how gases, aerosols, and pollutants interact and influence climate, air quality, and ecosystems.
Q: Why is atmospheric chemistry important?
A: Atmospheric chemistry is crucial for understanding and addressing environmental challenges such as climate change, air pollution, and ozone depletion. It helps us analyze the impacts of human activities on the atmosphere and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Q: What is the role of aerosols in atmospheric chemistry?
A: Aerosols are tiny particles suspended in the air, such as dust, soot, and pollutants. They play a significant role in atmospheric chemistry as they can act as cloud condensation nuclei, affect the formation of precipitation, and influence climate by scattering and absorbing sunlight.
Q: How does atmospheric chemistry contribute to climate change?
A: Atmospheric chemistry plays a vital role in climate change. The emissions of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, react in the atmosphere, leading to the greenhouse effect and global warming. Additionally, the formation of aerosols and their interaction with clouds can have both cooling and warming effects on the climate.
Q: How do human activities impact atmospheric chemistry?
A: Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, industrial processes, and deforestation, release pollutants and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These emissions can alter the chemical composition of the atmosphere, leading to air pollution, ozone depletion, and climate change.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
