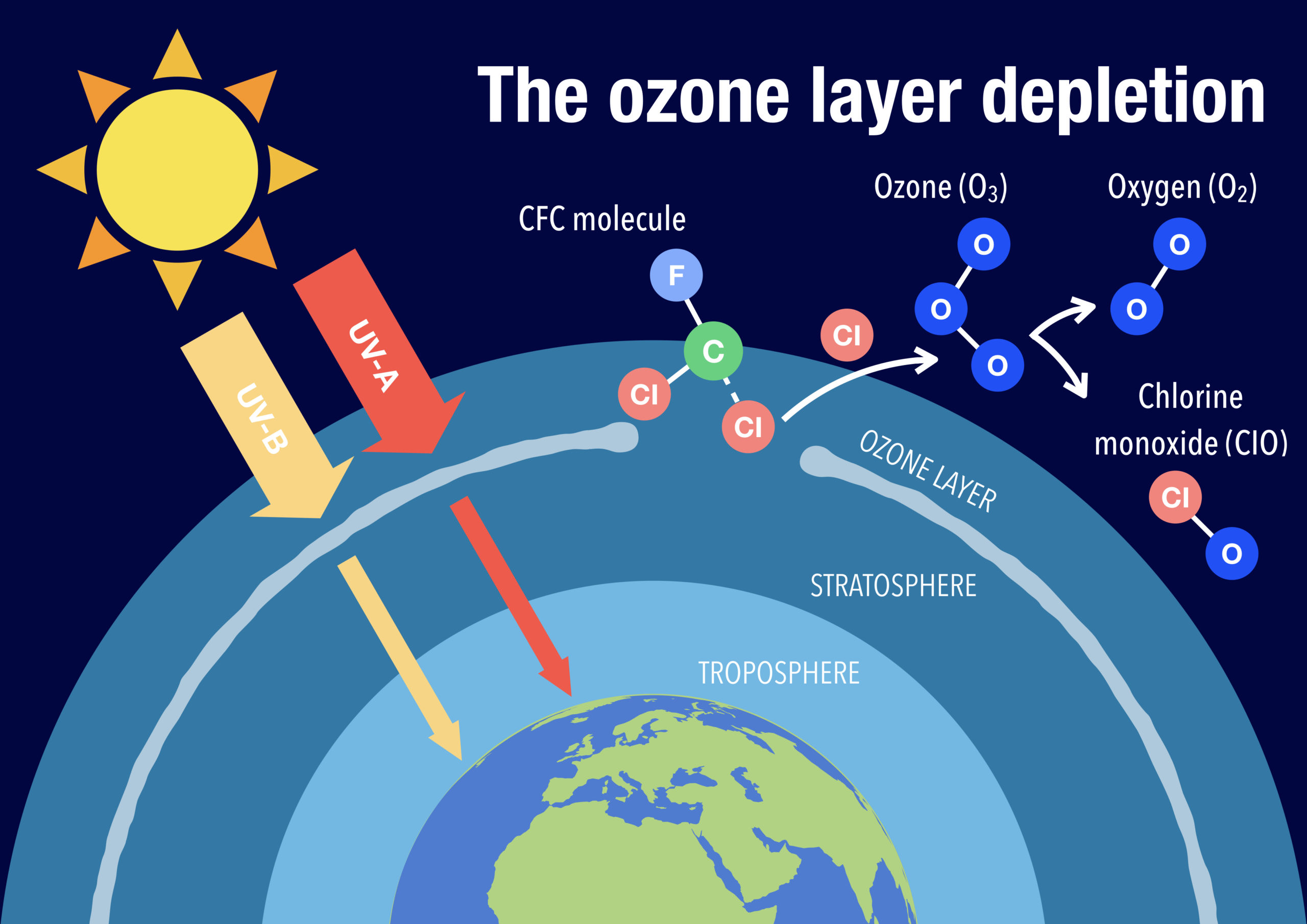
The ozone layer, a fragile shield of gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, is essential for our survival. It plays a crucial role in protecting us from the harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted by the sun. Unfortunately, over the years, this protective layer has been significantly depleted, posing serious threats to human health and the environment.
In this article, we will delve into the extraordinary facts surrounding ozone layer depletion. From the causes and consequences to the efforts made for its preservation, we will explore the fascinating world of ozone layer science and shed light on its importance.
Join us on this informative journey as we uncover 15 extraordinary facts about ozone layer depletion, helping you gain a deeper understanding of the challenges humanity faces and the steps we can take to safeguard our planet for future generations.
Key Takeaways:
- The ozone layer shields us from harmful UV radiation, but human activities are causing its depletion, leading to health risks and ecosystem disruptions.
- International efforts like the Montreal Protocol have helped reduce ozone-depleting substances, but we still need to monitor and address this global concern for the long-term health of our planet.
The Ozone Layer Shield
The ozone layer acts as a shield, protecting life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted by the sun. It absorbs most of the sun’s UV-B rays and prevents them from reaching the surface.
The Discovery of the Ozone Hole
In 1985, scientists first discovered a massive hole in the ozone layer above Antarctica. This shocking revelation caught the world’s attention and sparked international efforts to address the issue.
Human-made Ozone Depleting Substances
Ozone depletion is primarily caused by human-made substances, collectively known as ozone-depleting substances (ODS). These include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), and halons, commonly found in refrigerants, air conditioning systems, and aerosol propellants.
Impact on Human Health
Excessive exposure to UV radiation due to ozone layer depletion increases the risk of skin cancer, cataracts, suppressed immune system, and other health problems.
Harmful Effects on Ecosystems
Ozone depletion negatively impacts ecosystems, potentially affecting plant growth, marine life, and the overall balance of ecosystems. Some species are more vulnerable to UV radiation than others, leading to disruptions in food chains and biodiversity loss.
The Ozone Hole Expansion and Contraction
The Antarctic ozone hole expands and contracts seasonally, with its peak size occurring during the southern hemisphere spring. This cyclical phenomenon is influenced by temperature, wind patterns, and chemical reactions involving ODS.
International Efforts: The Montreal Protocol
The Montreal Protocol, adopted in 1987, is an international treaty designed to phase out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances. It has been a remarkable success, with almost universal ratification and significant reductions in ODS usage.
Recovery of the Ozone Layer
Thanks to the global efforts to reduce ODS usage, the ozone layer is showing signs of recovery. However, complete restoration is expected to take several decades.
The Role of Volcanic Eruptions
Although human activities are the primary driver of ozone depletion, volcanic eruptions also release gases that can contribute to the depletion process. However, their impact is relatively minimal compared to ODS.
Ozone Depletion in Polar Regions
Ozone depletion is most severe in the polar regions, particularly over Antarctica, where the ozone hole has been a recurring phenomenon. This is due to different atmospheric conditions and the accumulation of ODS in those areas.
The Link to Climate Change
Ozone depletion and climate change are interconnected, but they are distinct environmental issues. While both involve the Earth’s atmosphere, they have different causes and impacts.
Stratospheric Ozone vs. Ground-Level Ozone
Stratospheric ozone, found in the upper atmosphere, protects us from UV radiation. On the other hand, ground-level ozone, a component of air pollution, is harmful to human health and the environment.
The Importance of Ozone Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of ozone levels is crucial in evaluating the progress made in ozone layer protection and identifying areas that need further attention. Satellite-based ozone monitoring provides valuable data for scientists and policymakers.
Ozone Depletion and Agriculture
Ozone depletion can impact agriculture by reducing crop yields and affecting plant health. Certain crops, such as soybeans and peanuts, are more susceptible to UV radiation damage.
Long-Term Effects of Ozone Depletion
The long-term effects of ozone depletion are still being studied. It is important to continue monitoring and addressing this issue to safeguard the health of our planet and future generations.
These 15 extraordinary facts about ozone layer depletion underline the importance of taking immediate action to protect our ozone layer. By reducing the use of ozone-depleting substances and implementing sustainable practices, we can contribute to the preservation of this vital shield that protects life on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the depletion of the ozone layer is a serious concern that continues to affect our planet and its inhabitants. It is crucial for us to understand the causes and consequences of ozone layer depletion in order to take necessary actions to protect and restore it. From the harmful effects of UV radiation to the impact on climate change, ozone layer depletion poses significant risks to our environment and human health.Fortunately, international efforts such as the Montreal Protocol have made significant progress in reducing the use of ozone-depleting substances and promoting the adoption of safer alternatives. However, it is important to remain vigilant and continue our efforts to further protect and heal the ozone layer.By raising awareness, adopting sustainable practices, and supporting initiatives that aim to reduce harmful emissions, we can all contribute to the preservation of the ozone layer and the overall well-being of our planet. Let us work together to safeguard this vital shield that protects us from the sun’s harmful UV rays and ensures a sustainable future for generations to come.
FAQs
Q: What is the main cause of ozone layer depletion?
A: The main cause of ozone layer depletion is the release of certain chemical compounds, known as ozone-depleting substances, into the atmosphere. These substances include chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), and halons, which are commonly used in refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and fire extinguishers.
Q: How does ozone layer depletion affect the environment?
A: Ozone layer depletion allows an increased amount of ultraviolet (UV) radiation to reach the Earth’s surface. This can have detrimental effects on both the environment and living organisms. It can lead to increased rates of skin cancer, cataracts, and other health issues in humans. It can also harm marine ecosystems, damage crops, and affect the overall balance of ecosystems.
Q: What is the Montreal Protocol, and why is it important?
A: The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty that aims to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances. It has been successful in reducing the use of these substances and has played a crucial role in preventing further depletion of the ozone layer. It is important because it demonstrates the effectiveness of international cooperation in addressing global environmental challenges.
Q: Can the ozone layer recover?
A: With the implementation of the Montreal Protocol and the reduction in the use of ozone-depleting substances, there have been signs of recovery in the ozone layer. However, complete recovery is a slow process that requires long-term commitment and continued efforts to limit the release of harmful substances into the atmosphere.
Q: How can individuals contribute to protecting the ozone layer?
A: Individuals can contribute to protecting the ozone layer by reducing their use of products that contain ozone-depleting substances, such as aerosol sprays and certain types of refrigerants. Additionally, adopting energy-efficient practices and supporting policies and initiatives that promote sustainability can also help reduce our impact on the ozone layer.
Ozone layer depletion is a serious issue that affects us all, but it's not the only environmental concern we face. Global warming is another pressing matter, causing temperatures to rise and altering ecosystems worldwide. UV radiation from the sun can also lead to skin cancer, making it crucial to protect ourselves and stay informed. Explore more fascinating facts about these topics and discover how you can make a difference in preserving our planet for future generations.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


