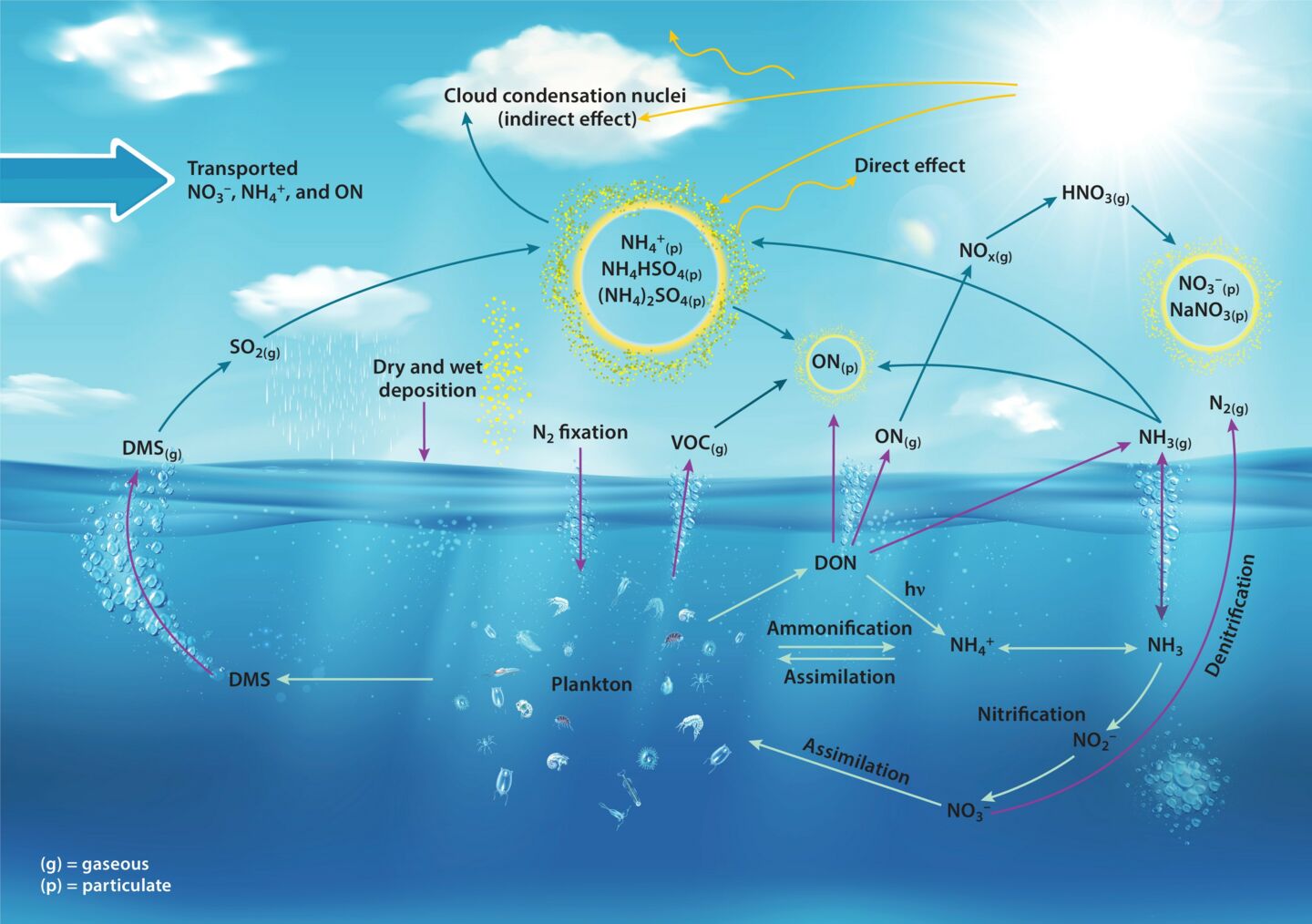
The nitrogen cycle is a crucial process that occurs in nature, playing a significant role in the sustainability of ecosystems. It involves the movement of nitrogen through different forms and states, ensuring that it is available for various organisms to use and recycle. Understanding the nitrogen cycle is essential for biologists, ecologists, and anyone interested in environmental science.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of the nitrogen cycle and uncover 12 intriguing facts about this vital process. From nitrogen fixation to nitrification, denitrification to nitrogen assimilation, these facts will shed light on the intricate mechanisms that nitrogen undergoes in order to support life on Earth.
So, let’s embark on a journey through the nitrogen cycle and discover some remarkable insights into this fundamental process that sustains the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.
Key Takeaways:
- Nitrogen cycle is essential for life on Earth, helping plants and animals grow. It involves bacteria, plants, and natural processes that keep our planet healthy and thriving.
- Excessive nitrogen can harm the environment, causing algal blooms and contributing to climate change. Managing the nitrogen cycle is crucial for protecting ecosystems and biodiversity.
Nitrogen is essential for life on Earth
The nitrogen cycle is a fundamental process that plays a crucial role in the sustenance of life on our planet. It involves the transformation of nitrogen into various forms that can be utilized by different organisms.
Nitrogen gas makes up the majority of the Earth’s atmosphere
Approximately 78% of Earth’s atmosphere is composed of nitrogen gas (N2). However, this form of nitrogen is not directly available for most organisms.
Nitrogen fixation is a key step in the nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixation is the process through which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into a usable form by certain bacteria, such as Rhizobium, which form a symbiotic relationship with leguminous plants.
Legumes play a vital role in nitrogen fixation
Plants like peas, beans, and clover have nodules on their roots where nitrogen-fixing bacteria reside. These bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, a critical nutrient for plant growth.
Denitrification returns nitrogen to the atmosphere
Denitrification is the process by which certain bacteria convert nitrates or nitrites back into atmospheric nitrogen. This completes the nitrogen cycle and helps maintain a balance of nitrogen in ecosystems.
Nitrogen is a component of DNA and proteins
Nitrogen is an essential element for the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins, which are the building blocks of life. Without an adequate supply of nitrogen, plants and animals cannot grow and function properly.
Fertilizer runoff can lead to harmful algal blooms
Excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers in agriculture can result in runoff into water bodies. This runoff can lead to the overgrowth of algae, depleting oxygen levels and causing harm to aquatic ecosystems.
The Haber-Bosch Process revolutionized nitrogen fixation
The Haber-Bosch Process, developed in the early 20th century, made it possible to artificially produce ammonia from atmospheric nitrogen on an industrial scale. This process greatly increased agricultural productivity.
Nitrogen cycle helps to maintain soil fertility
Through the nitrogen cycle, organic matter gets decomposed, releasing ammonia and other nitrogen compounds that enrich the soil. This natural process helps replenish nutrient levels and provide essential elements for plant growth.
Nitrogen cycle is closely linked to climate change
The excessive release of nitrogen compounds, such as nitrous oxide, into the atmosphere contributes to climate change and the depletion of the ozone layer. Managing nitrogen cycles is essential for mitigating these environmental impacts.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria have mutualistic relationships with plants
The bacteria involved in nitrogen fixation form symbiotic relationships with plants, providing them with usable nitrogen compounds while benefiting from the plants’ energy-rich carbon compounds.
Nitrogen cycle supports biodiversity
The availability of nitrogen in various forms within ecosystems supports the growth of diverse plant species, which, in turn, provide habitats and food sources for a wide range of animals.
As we have explored these 12 fascinating facts about nitrogen cycle, it becomes evident that this natural process is of utmost importance for the functioning of ecosystems and the survival of life on Earth.
Conclusion
The nitrogen cycle is a crucial process that plays a vital role in sustaining life on Earth. From the fixation of nitrogen to its conversion into various forms and its subsequent release back into the environment, this cycle ensures the availability of this essential element for all living organisms. Understanding the nitrogen cycle is fundamental for promoting sustainable agriculture practices, managing water quality, and mitigating environmental pollution.
With its intricate and interconnected processes, the nitrogen cycle showcases the delicate balance of nature and the resilience of ecosystems. By studying and conserving this cycle, we can strive towards preserving the health and wellbeing of our planet.
FAQs
1. What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is a natural process that involves the conversion of nitrogen in various forms, such as atmospheric nitrogen gas (N2), into compounds that can be utilized by living organisms.
2. Why is the nitrogen cycle important?
The nitrogen cycle is vital because it ensures the availability of nitrogen, which is an essential element for the growth and survival of organisms. It plays a critical role in maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting agricultural productivity.
3. What are the main steps of the nitrogen cycle?
The main steps of the nitrogen cycle include nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification. These processes contribute to the conversion of nitrogen into various forms within the environment.
4. How does nitrogen fixation occur?
Nitrogen fixation can happen through both biological and non-biological processes. Biological nitrogen fixation is carried out by certain bacteria and plants, while non-biological nitrogen fixation occurs through industrial processes.
5. How does human activity impact the nitrogen cycle?
Human activities such as industrial farming, fossil fuel combustion, and the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers have significantly disrupted the nitrogen cycle. These activities have led to an overabundance of reactive nitrogen in the environment, contributing to pollution and ecological imbalances.
Nitrogen's journey through ecosystems is truly remarkable, but many questions remain. How does denitrification return nitrogen gas to the atmosphere? What role do legumes and bacteria play in nitrogen fixation? Cyanobacteria's contributions to the nitrogen cycle are equally intriguing. Explore these topics further and gain a deeper understanding of this essential biogeochemical process.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


