Cellular respiration is a fundamental process that occurs within all living organisms. It is the set of metabolic reactions that convert nutrients, such as glucose, into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). While most people have a basic understanding of cellular respiration, there are several surprising and fascinating facts about this crucial process that may not be commonly known. In this article, we will explore ten intriguing facts about cellular respiration that will give you a deeper appreciation for the complexity and importance of this biological process. From the role of mitochondria to the different stages involved, these facts will shed light on the inner workings of cellular respiration and its significance in sustaining life.
Key Takeaways:
- Cellular respiration is the process that turns food into energy for all living things, even without oxygen. It’s like a power plant inside cells, keeping them running smoothly.
- Just like a well-oiled machine, cellular respiration has evolved over billions of years to efficiently produce energy and keep living organisms healthy. It’s a vital part of the circle of life!
Cellular respiration is essential for energy production in all living organisms.
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert glucose and other organic molecules into usable energy in the form of ATP. It is a fundamental process that occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Cellular respiration can occur in the absence of oxygen.
While the most efficient form of cellular respiration requires oxygen and is known as aerobic respiration, certain organisms can carry out anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen. This process, also known as fermentation, produces less ATP but allows cells to continue generating energy in oxygen-deprived environments.
Cellular respiration is a series of complex biochemical reactions.
Cellular respiration involves a series of interconnected biochemical reactions, including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. These reactions are carefully regulated to maximize the production of ATP while minimizing the generation of harmful byproducts.
The majority of ATP production occurs during the electron transport chain.
The electron transport chain is the final stage of cellular respiration, where most of the ATP is generated. Through a series of redox reactions, electrons are transferred along the chain, ultimately leading to the synthesis of ATP. This process is highly efficient and produces the majority of the cell’s energy.
Cellular respiration is not limited to glucose as a fuel source.
While glucose is the most common substrate for cellular respiration, other molecules can also serve as fuel sources. These include fatty acids from lipids and amino acids from proteins. Cells have the ability to break down these molecules and channel them into the cellular respiration pathway.
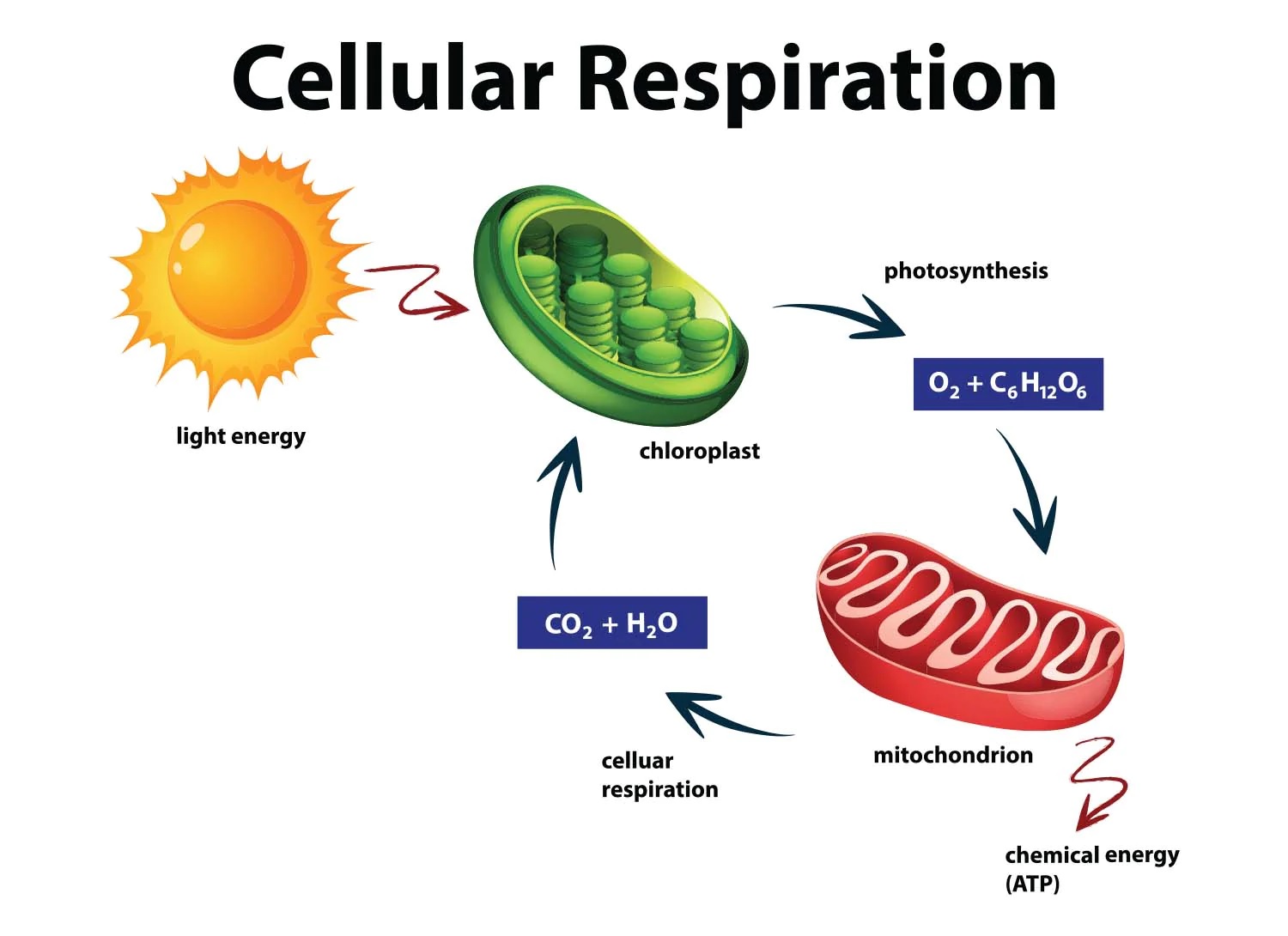
Cellular respiration is closely linked to photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected processes that sustain life on Earth. During photosynthesis, plants capture energy from sunlight and convert it into glucose. The glucose produced is then used by cells through the process of cellular respiration to generate ATP and sustain cell function.
Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
As glucose is broken down during cellular respiration, carbon dioxide is released as a byproduct. This carbon dioxide is carried by the bloodstream to the lungs, where it is exhaled. This is an essential part of the carbon cycle and contributes to maintaining the balance of carbon in the environment.
Certain chemicals and medications can affect cellular respiration.
Various substances can impact cellular respiration either by inhibiting or enhancing the process. For example, cyanide is a potent inhibitor of cellular respiration and can be deadly at high concentrations. On the other hand, certain medications like statins can improve cellular respiration and energy production in cells.
Cellular respiration plays a role in human health and disease.
Disruptions in cellular respiration can have significant implications for human health. Disorders such as mitochondrial diseases result from impaired cellular respiration and can lead to a wide range of symptoms and health complications. Understanding cellular respiration is crucial for advancing treatment options for such conditions.
Cellular respiration has evolved over billions of years.
Cellular respiration is an ancient metabolic pathway that has evolved over billions of years. It is believed to have originated in the earliest prokaryotic cells and has been refined and optimized over time. The efficiency and complexity of cellular respiration reflect its importance in sustaining life on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cellular respiration is a fascinating process that is essential for all living organisms. It plays a fundamental role in converting energy from food into a usable form, allowing cells to function and thrive. Throughout this article, we have explored 10 surprising facts about cellular respiration, shedding light on its complexity and importance.
We have learned about the different stages of cellular respiration, including glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. We have also discovered how cellular respiration is connected to other metabolic processes, such as photosynthesis and fermentation.
Furthermore, we have explored how cellular respiration is influenced by various factors, including temperature, pH levels, and the availability of oxygen. We have also discussed the significance of cellular respiration in maintaining overall health and how disruptions in this process can lead to various diseases.
Overall, cellular respiration is a captivating subject that continues to be studied and explored in the field of biology. By understanding its intricacies and the surprising facts surrounding it, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable processes that occur within our cells.
FAQs
Q: What is cellular respiration?
A: Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert energy from food into a usable form, typically ATP (adenosine triphosphate), to power various cellular activities.
Q: How is cellular respiration different from photosynthesis?
A: While cellular respiration is the process of breaking down food molecules to release energy, photosynthesis is the process by which plants and some other organisms convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen.
Q: How many stages are there in cellular respiration?
A: Cellular respiration consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle or TCA cycle), and the electron transport chain.
Q: Does cellular respiration only occur in humans and animals?
A: No, cellular respiration occurs in all living organisms, including plants, fungi, and bacteria.
Q: Can cellular respiration occur without oxygen?
A: Yes, cellular respiration can occur without oxygen through a process called anaerobic respiration or fermentation. However, this process produces less ATP compared to aerobic respiration.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
