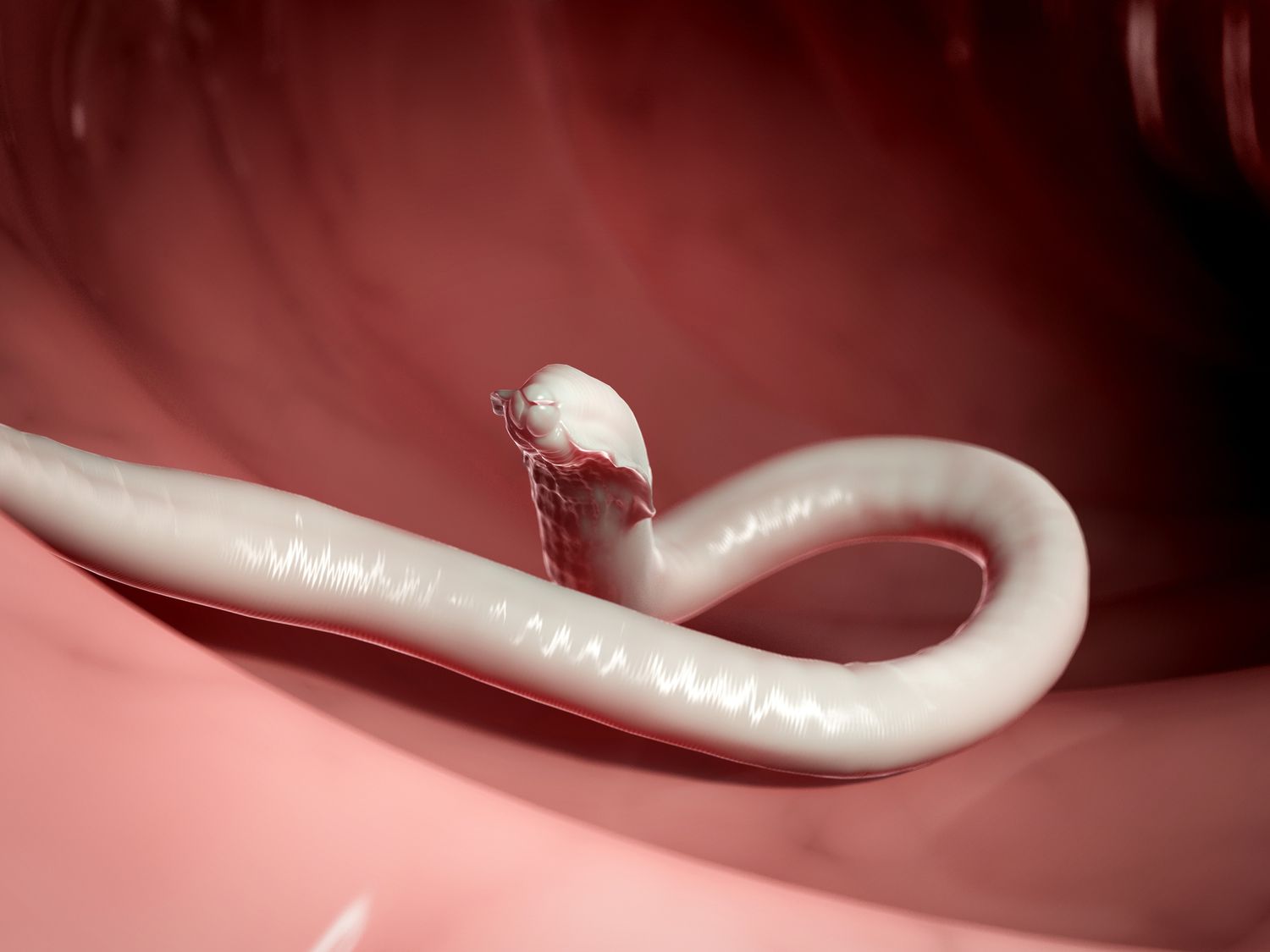
Helminth parasites are fascinating organisms that have the ability to colonize and survive within the bodies of their hosts. These parasites belong to the phylum Helminthes, which includes various types such as roundworms, flatworms, and tapeworms. While the thought of being infested with parasites may seem repulsive, helminths play an intricate role in the ecosystem and have unique adaptations that enable them to thrive in different environments.
In this article, we will delve into the astonishing world of helminth parasites and explore 19 intriguing facts about these creatures. From their diverse life cycles to their remarkable survival strategies, there is much to uncover about these often overlooked organisms. So, brace yourself as we embark on a journey into the captivating realm of helminth parasites!
Key Takeaways:
- Helminth parasites are diverse, complex organisms that can cause diseases in humans and animals. Proper hygiene, sanitation, and medical treatment are essential for preventing and managing these infections.
- Helminth parasites have been around for millions of years and play a crucial role in ecosystems. They can manipulate their hosts and have zoonotic potential, highlighting the need for understanding and managing these fascinating organisms.
Helminth parasites are multicellular organisms
Helminth parasites are a diverse group of multicellular organisms that include various species of worms. These parasites can infect humans and animals, causing a wide range of diseases.
There are different types of helminth parasites
Helminth parasites can be classified into two main groups: roundworms (nematodes) and flatworms (cestodes and trematodes). Each group has its unique characteristics and life cycles.
Helminth parasites have complex life cycles
Helminth parasites undergo complex life cycles involving multiple hosts. The stages of their life cycle can vary, including eggs, larvae, and adult worms. These parasites often require specific environmental conditions to complete their life cycles.
Helminth parasites can cause a variety of diseases
Helminth infections can lead to a variety of diseases in both humans and animals. Some common helminth-induced diseases include hookworm infections, schistosomiasis, ascariasis, and tapeworm infections. These diseases can present with various symptoms depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Helminth parasites have complex reproductive strategies
Helminth parasites employ diverse reproductive strategies to ensure their survival and transmission. Some parasites can reproduce sexually, while others can reproduce asexually through the production of eggs or larvae.
Helminth parasites can manipulate their hosts
Helminth parasites have the ability to manipulate the behavior and physiology of their hosts to enhance their own survival and reproduction. They can alter the immune response, modify the host’s feeding behavior, or induce specific changes in the host’s reproductive system.
Helminth infections can be endemic in certain regions
Helminth infections are often endemic in tropical and subtropical regions, where environmental conditions favor the survival and transmission of these parasites. Poor sanitation, inadequate access to clean water, and close contact with infected individuals or animals contribute to the spread of helminth infections.
Helminth parasites can have zoonotic potential
Some helminth parasites have zoonotic potential, meaning they can be transmitted between animals and humans. Examples include the pork tapeworm (Taenia solium) and the dog tapeworm (Echinococcus granulosus), which can cause serious health problems in humans if ingested.
Helminth infections can be transmitted through contaminated food and water
Helminth infections are commonly transmitted through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. Fecal contamination of soil or water sources can lead to the presence of helminth eggs or larvae, which can then infect individuals who consume contaminated substances.
Helminth infections can be prevented through proper hygiene and sanitation
Proper hygiene and sanitation practices, such as washing hands before meals, drinking clean water, and cooking food thoroughly, can help prevent helminth infections. Good sanitation infrastructure and access to clean water sources are crucial in reducing the transmission of these parasites.
Helminth parasites can be treated with anthelmintic drugs
Anthelmintic drugs are medications specifically designed to treat helminth infections. These drugs target the parasites and either kill them or inhibit their growth and reproduction. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of helminth infections.
Helminth infections can have long-term effects on human health
Chronic helminth infections can have long-term effects on human health, particularly in children. These infections can lead to malnutrition, impaired growth and development, anemia, and reduced cognitive function. Treating and preventing helminth infections is crucial for maintaining good overall health.
Helminth parasites have been used in medical research
Helminth parasites, particularly certain species of worms, have been used in medical research to study the immune system and develop new treatments for autoimmune diseases. These parasites have shown potential in modulating the immune response and reducing inflammation.
Helminth infections can be asymptomatic
Not all helminth infections manifest with noticeable symptoms. Some individuals may harbor helminth parasites without experiencing any symptoms or health issues. However, even asymptomatic infections can pose a risk of transmission to others.
Helminth parasites have existed for millions of years
Helminth parasites have a long evolutionary history and have been found in fossil records dating back millions of years. They have adapted to various environments, hosts, and ecological niches throughout their evolution.
Helminth parasites can alter the host’s immune response
Helminth parasites have evolved mechanisms to dampen the host’s immune response, allowing them to establish persistent infections. This ability to modulate the immune system has implications for understanding and potentially treating immune-related disorders.
Helminth infections can be diagnosed through laboratory tests
Laboratory tests, such as stool examinations and blood tests, can help diagnose helminth infections. These tests can detect the presence of parasite eggs, larvae, or specific antibodies in the patient’s sample.
Helminth parasites can adapt to drug treatments
Some helminth parasites have developed resistance to common anthelmintic drugs, making treatment more challenging. This highlights the need for ongoing research and the development of new treatment strategies to combat helminth infections.
Helminth parasites play a role in ecosystems
Helminth parasites are an integral part of ecosystems, as they interact with various hosts and contribute to the regulation of populations and the balance of ecosystems. Understanding the ecological roles of helminth parasites is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, helminth parasites are remarkable organisms that have coevolved with their hosts over millions of years. These parasites have developed fascinating mechanisms to survive and exploit their hosts, resulting in complex and intricate life cycles. From their ability to manipulate the behavior of their hosts to their intricate reproductive strategies, helminth parasites continue to captivate researchers and medical professionals alike. Understanding the biology and adaptations of these parasites is crucial for developing effective treatment and prevention strategies. As scientists uncover more astonishing facts about helminth parasites, we are constantly reminded of the wonders of the natural world and the intricate relationships that exist within it.
FAQs
1. What are helminth parasites?
Helminth parasites are multicellular organisms that belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms) and Nematoda (roundworms). They include various species such as tapeworms, flukes, and hookworms.
2. How do helminth parasites infect humans?
Helminth parasites can infect humans through contaminated water or food, contact with contaminated soil, or through vectors such as mosquitoes or snails. Some parasites can also be acquired through direct contact with infected animals.
3. What are the symptoms of helminth infections?
The symptoms of helminth infections can vary depending on the type of parasite. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, anemia, and fatigue. In severe cases, helminth infections can lead to organ damage and long-term health complications.
4. How are helminth infections diagnosed?
Helminth infections are diagnosed through various methods including stool examinations to detect parasite eggs, blood tests to detect specific antibodies, and imaging techniques such as ultrasound or endoscopy to visualize the parasites in the body.
5. Can helminth infections be treated?
Yes, helminth infections can be treated with anti-parasitic medications. The type and duration of treatment depend on the specific parasite involved. In some cases, multiple rounds of treatment may be required to ensure complete eradication of the parasites.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
