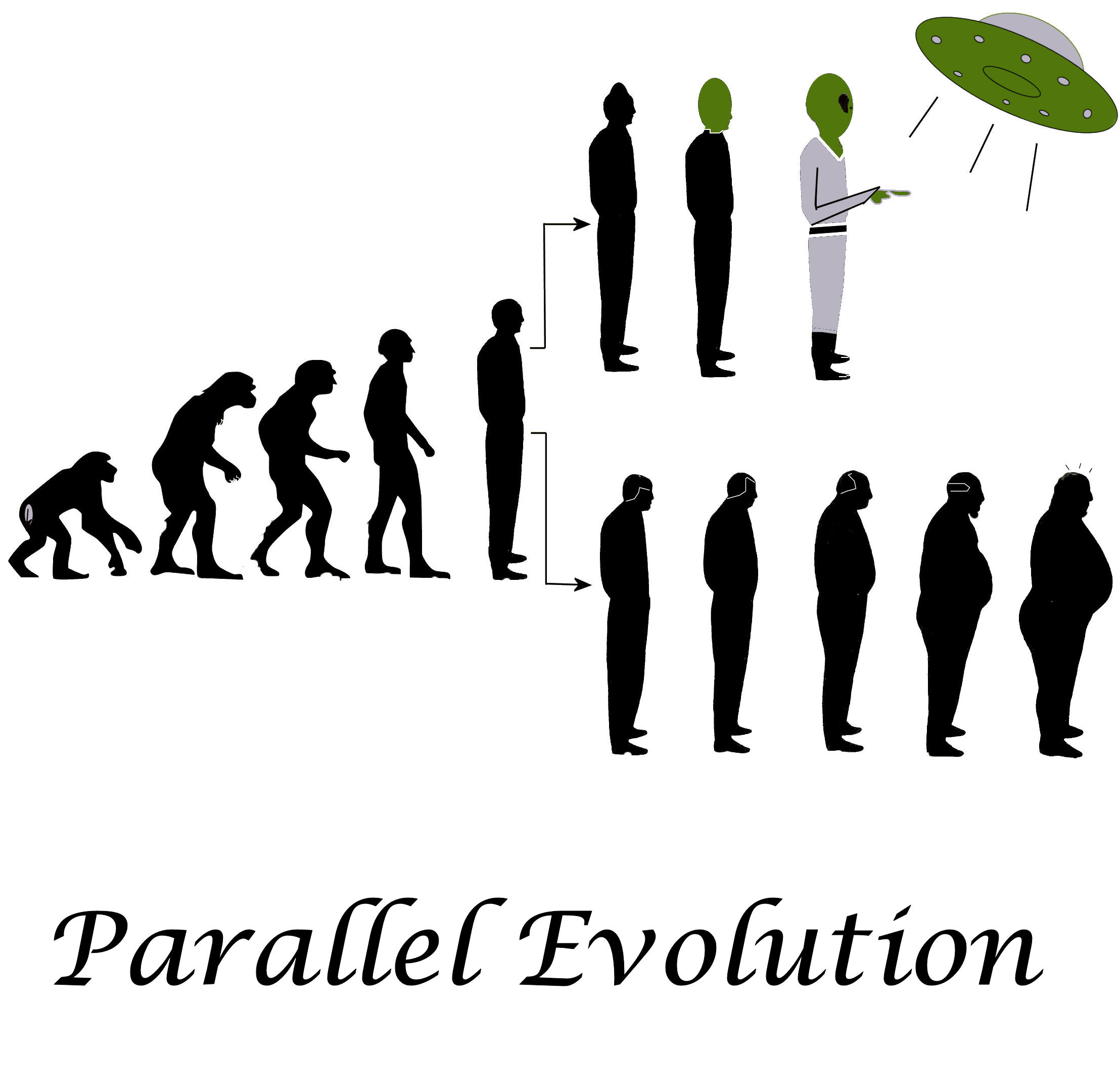
Parallel evolution is a fascinating concept that highlights the remarkable adaptability of living organisms. It refers to the independent emergence of similar traits in different species that are not closely related, but inhabit similar environments. This phenomenon showcases the power of natural selection in shaping the diversity of life on Earth.
Parallel evolution challenges the idea that evolution is always a result of common ancestry. Instead, it demonstrates that organisms can evolve similar characteristics in response to similar selective pressures. From convergent evolution in mammals and birds to analogous traits in plants and insects, parallel evolution offers a glimpse into the dynamic and unpredictable nature of the evolutionary process.
In this article, we will explore 14 mind-blowing facts about parallel evolution. Get ready to be amazed by the incredible examples of similar adaptations that have arisen independently in different species, reflecting the remarkable ways in which life on our planet has adapted and thrived.
Key Takeaways:
- Parallel evolution shows how different species can develop similar traits independently, revealing the amazing adaptability of life on Earth to similar environments.
- Understanding parallel evolution helps scientists protect vulnerable species facing similar threats and unlocks the mysteries of evolution, showcasing the incredible diversity of life.
Diverse Similarities
Parallel evolution refers to the process where different species independently evolve similar traits or features as adaptations to similar environmental conditions. It is a fascinating phenomenon that showcases the power of natural selection and the adaptive nature of life on Earth.
Convergent Evolution
Parallel evolution is often synonymous with convergent evolution, which occurs when unrelated species develop analogous traits due to similar selective pressures. This process leads to remarkable similarities between species that are not closely related on the phylogenetic tree.
Multiple Origins
Parallel evolution involves the independent emergence of similar traits in different lineages, suggesting that these traits have evolved multiple times in separate populations. This challenges the assumption that all shared characteristics among species stem from a common ancestor.
Various Examples
Parallel evolution can be observed in various organisms across different habitats. Examples include the evolution of streamlined body shapes in dolphins and sharks for efficient swimming, and the development of similar long tongues in hummingbirds and some nectar-feeding bats for accessing floral nectar.
Adaptation to Environments
Parallel evolution often occurs in response to similar environmental challenges. For instance, plants in arid environments may independently evolve the ability to store water or develop succulent leaves, showcasing a remarkable convergence in their adaptations to survive in dry conditions.
Rapid Evolution
Parallel evolution can sometimes occur relatively quickly, especially when the selective pressures are strong. This rapid pace of evolution enables species to adapt to new environments or exploit novel resources, leading to the emergence of diverse and functionally similar traits.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Parallel evolution is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. While genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection, similar environmental conditions drive the selection of certain traits, leading to the independent evolution of parallel features.
Not Always Identical
Although parallel evolution may result in the development of similar traits, the underlying genetic mechanisms can vary. Different genetic changes or mutations in separate populations can give rise to similar functional adaptations, demonstrating the flexibility of evolution.
Predominance in Science Fiction
Parallel evolution has captured the imagination of science fiction writers and filmmakers, often depicted in creative ways. The concept of alien species evolving similar characteristics to humans or Earth-based creatures has been a recurring theme, exploring the possibilities of life beyond our planet.
Cultural Significance
Parallel evolution has played a significant role in shaping cultural beliefs and practices. The occurrence of similar mythological creatures or folklore across different cultures could be attributed to parallel evolution, as common environmental experiences may have led to the creation of similar legends.
Evolutionary Analogies
Parallel evolution provides powerful evidence for evolutionary theory and helps us understand the underlying mechanisms of adaptation. By studying independently evolved traits in different lineages, scientists gain insights into the predictability and repeatability of evolutionary processes.
Key to Conservation
Understanding parallel evolution is crucial for conservation efforts. By recognizing how similar traits can arise independently, conservationists can identify vulnerable species facing similar threats and develop effective strategies to protect and preserve their habitats.
The Role of Chance
Parallel evolution is not solely driven by natural selection, but chance events also play a role. Random genetic mutations and the availability of certain ecological niches can influence the direction and outcome of parallel evolution, adding an element of unpredictability to the process.
Unlocking Evolutionary Mysteries
Studying parallel evolution helps uncover the mysteries of evolution and offers a deeper understanding of the complex web of life on our planet. Through unraveling the patterns and processes of parallel evolution, scientists gain insights into the evolutionary potential of organisms and the vast array of possibilities that exist in nature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, parallel evolution is a fascinating concept that highlights the ingenuity and adaptability of life on Earth. The fact that different species can independently develop similar traits and characteristics in response to similar environmental pressures is truly mind-blowing. From the convergent evolution of wings in birds and bats to the striking resemblance between dolphins and sharks, parallel evolution has shaped the biodiversity we see today.By studying parallel evolution, scientists are able to gain a better understanding of how species respond to their environment and how certain traits are advantageous for survival. This knowledge not only deepens our appreciation for the complexity of life but also has practical applications in fields such as medicine and conservation.As we continue to unravel the mysteries of parallel evolution, we are constantly amazed at the remarkable ways in which different species can evolve similar solutions to the challenges they face. It is a testament to the remarkable diversity and resilience of life, and a reminder that nature is full of surprises.
FAQs
1. What is parallel evolution?
Parallel evolution refers to the independent development of similar traits or characteristics in different species that are not closely related. It occurs when species face similar environmental pressures and independently evolve similar solutions.
2. How is parallel evolution different from convergent evolution?
Parallel evolution and convergent evolution are similar concepts, but there is a subtle difference. Convergent evolution refers to the development of similar traits in species that are not closely related, while parallel evolution specifically refers to the independent development of similar traits in related species.
3. Can you give an example of parallel evolution?
One example of parallel evolution is the evolution of wings in bats and birds. Bats and birds belong to different evolutionary lineages but independently evolved wings, allowing them to fly. This is a classic example of parallel evolution.
4. How does parallel evolution contribute to biodiversity?
Parallel evolution contributes to biodiversity by creating similar traits in different species. This allows species to occupy similar ecological niches and adapt to similar environmental challenges, resulting in a more diverse range of species in an ecosystem.
5. Why is parallel evolution important to study?
Studying parallel evolution helps us understand how species adapt to their environment and how certain traits evolve independently. This knowledge has practical applications in various fields, including medicine, conservation, and the understanding of evolutionary processes.
Parallel evolution's fascinating, but it's just one piece of the evolutionary puzzle. Speciation creates new species through reproductive isolation, while adaptive radiation explains how single ancestors diversify into many species. Convergent evolution, on the other hand, shows how unrelated species develop similar traits under comparable environmental pressures. Dive deeper into evolution's marvels by exploring these captivating concepts.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.