Parallel circuits are an integral part of our everyday lives, despite many people not realizing it. These circuits are the foundation of modern electrical systems, ensuring that electricity flows efficiently and reliably to power our homes, gadgets, and devices. Understanding the principles behind parallel circuits is fascinating and can unlock a whole new level of comprehension about the electronic devices we use on a daily basis.
In this article, we will dive deep into the world of parallel circuits and unravel 19 captivating facts that will broaden your knowledge about how they work. From the basic concepts to the practical applications, we will explore the intricacies of parallel circuits and shed light on their importance in various industries. So, let’s embark on this electrifying journey and discover the secrets behind parallel circuits!
Key Takeaways:
- Parallel circuits allow multiple devices to share electricity without affecting each other. If one device fails, the others keep working, making them reliable and convenient for everyday use.
- Parallel circuits are like teamwork for electricity, dividing the current and ensuring efficient performance. They’re used in everything from household wiring to Christmas lights, making our lives brighter and easier.
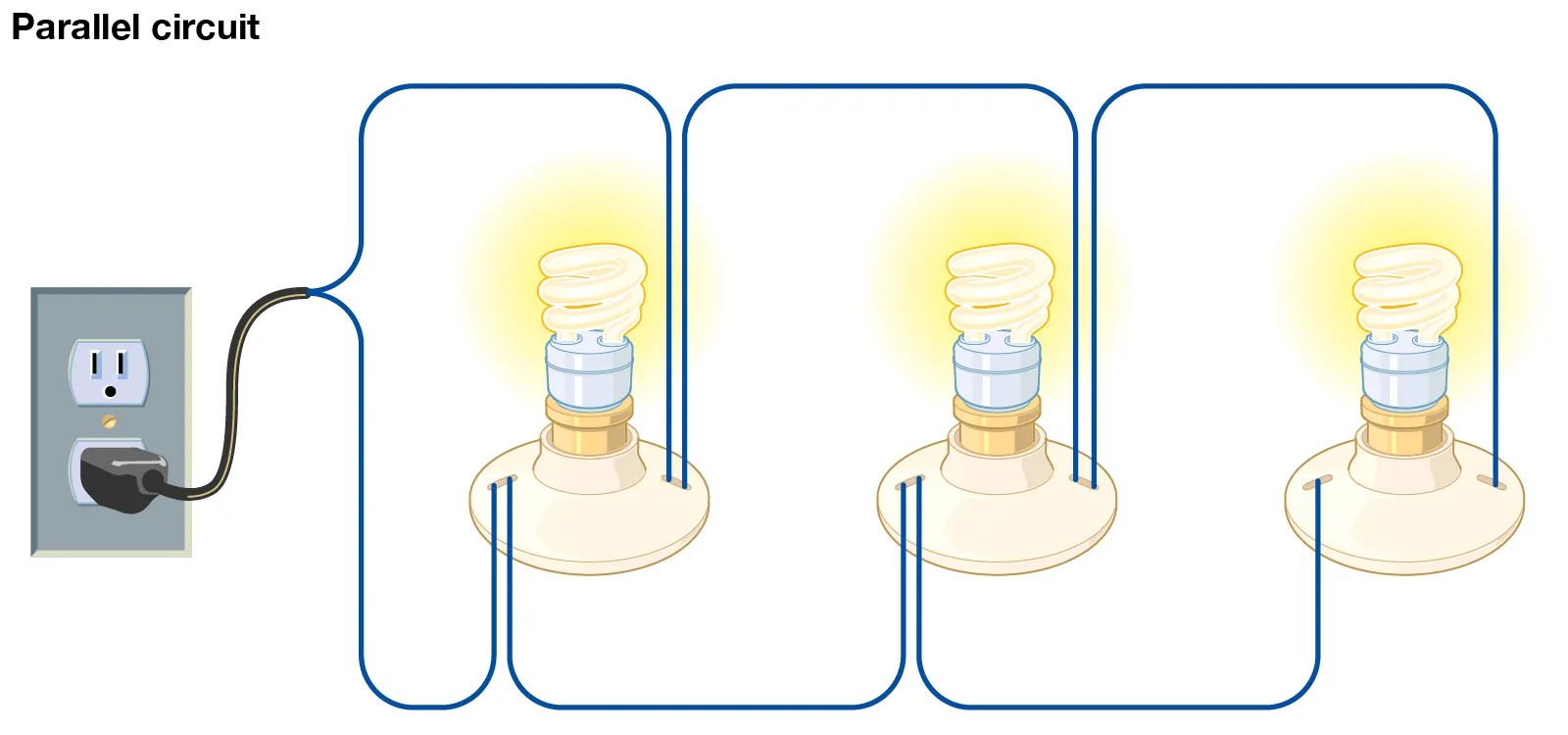
Captivating What is a Parallel Circuit?
A parallel circuit is an electrical circuit where the components are connected in a way that allows the current to flow along multiple paths simultaneously. It is commonly used in various applications, such as household wiring, electrical appliances, and automotive systems.
Captivating The Magic of Voltage Distribution
In a parallel circuit, each component receives the same voltage across its terminals. This means that even if one component fails or is disconnected, the other components will continue to receive the required voltage, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Captivating Current Sharing is Caring
In a parallel circuit, the current is divided among the branches or individual components. Each component draws only the amount of current it needs, preventing overload and ensuring efficient performance.
Captivating The Power Multiplier Effect
Parallel circuits have the unique ability to increase the overall power capacity. When components are connected in parallel, the total power available is the sum of the individual power ratings.
Captivating Plug-and-Play Convenience
Parallel circuits offer the advantage of easy installation and modification. This means that components can be added or removed from the circuit without affecting the operation of the other components.
Captivating Lighting Up Lives with Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits are commonly used in lighting fixtures and lamps. If one light bulb in a parallel circuit burns out, the other bulbs will remain lit, thanks to the independent path of current flow.
Captivating Parallel Circuits in Everyday Electronics
Many electronic devices we use daily, such as televisions, computers, and smartphones, utilize parallel circuits to power various components, ensuring reliable operation and efficient use of electricity.
Captivating Balancing Act with Parallel Resistors
Parallel resistors have the ability to balance the overall resistance in a circuit. By adding more resistors in parallel, the total resistance decreases, allowing for higher current flow.
Captivating Parallel Circuits and Homes
Parallel circuits are extensively used in residential wiring. They allow for multiple outlets and appliances to be used simultaneously without affecting the voltage supply to each individual device.
Captivating Fault Tolerance in Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits offer a level of fault tolerance. If one component fails, the other components will continue to function normally, preventing a complete loss of power.
Captivating The Breadth of Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits are not limited to just electrical systems; they are also prevalent in plumbing and hydraulics, allowing for the efficient distribution and regulation of fluid flow.
Captivating Parallel Circuits and Amplifiers
Audio amplifiers commonly utilize parallel circuits to enhance sound quality and increase the overall power output. By connecting multiple transistors in parallel, they can handle higher currents and deliver better performance.
Captivating Parallel Circuits in Renewable Energy
Parallel circuits play a vital role in solar power systems, where multiple solar panels are connected in parallel to increase the current capacity and maximize the energy output.
Captivating Quick Troubleshooting in Parallel Circuits
Fault finding in parallel circuits is often easier compared to series circuits. By isolating each component or branch, it becomes straightforward to identify and address any issues that may arise.
Captivating Parallel Circuits and Christmas Lights
Christmas lights often utilize parallel circuits, ensuring that if one bulb burns out or is removed, the other bulbs will continue to shine brightly, adding joy and festive cheer.
Captivating Parallel Circuits and Reliable Networks
In computer networks, parallel circuits are used for data transmission. They provide redundancy and fault tolerance, ensuring reliable and uninterrupted communication between devices.
Captivating The Efficiency of Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits are known for their high efficiency. As the current is divided among multiple paths, each component can operate at its optimal current level, minimizing power wastage and heat generation.
Captivating Parallel Circuits in Automotive Wiring
The wiring system in automobiles employs parallel circuits to power various electrical components, such as headlights, taillights, and interior lighting, allowing for independent control and improved safety.
Captivating The Versatility of Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits offer unparalleled flexibility and adaptability. They can be found in diverse applications, from simple household circuits to complex industrial machinery, providing reliable and efficient electrical distribution.
Conclusion
Parallel circuits are an integral part of our everyday lives, whether we realize it or not. Understanding how they work and their various applications can enhance our appreciation for the world of physics. From powering our homes to enabling complex electrical systems, parallel circuits play a crucial role in modern technology.
By exploring the captivating facts about parallel circuits, we have discovered their unique properties and advantages. From their ability to divide current evenly to their ability to maintain the flow of electricity when one component fails, parallel circuits are truly remarkable.
Whether you’re an electrical engineer, a physics enthusiast, or simply curious about the inner workings of electrical systems, learning about parallel circuits can be both educational and fascinating. With their widespread use and endless applications, parallel circuits continue to shape the world around us.
FAQs
1. What is a parallel circuit?
A parallel circuit is a type of electrical circuit where multiple components are connected in such a way that each component has its own separate connection to the power source. This allows current to flow through each component independently.
2. How does a parallel circuit differ from a series circuit?
In a parallel circuit, the current has multiple paths to follow, whereas in a series circuit, the current has only one path. This means that in a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component remains the same, while in a series circuit, the voltage is divided among the components.
3. What are the advantages of using parallel circuits?
One advantage of using parallel circuits is that if one component fails, the flow of electricity is not disrupted to the other components. Additionally, parallel circuits allow for the independent operation of each component, making them suitable for applications that require multiple devices to work simultaneously.
4. Can the total resistance in a parallel circuit ever be greater than the individual resistances?
No, the total resistance in a parallel circuit is always less than the smallest individual resistance. This is because the current has multiple paths to follow, reducing the overall resistance.
5. Where are parallel circuits commonly used?
Parallel circuits are used in various applications, including household electrical wiring, lighting systems, computer circuits, and many electronic devices. They are also commonly used in industrial settings for powering machinery and equipment.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
