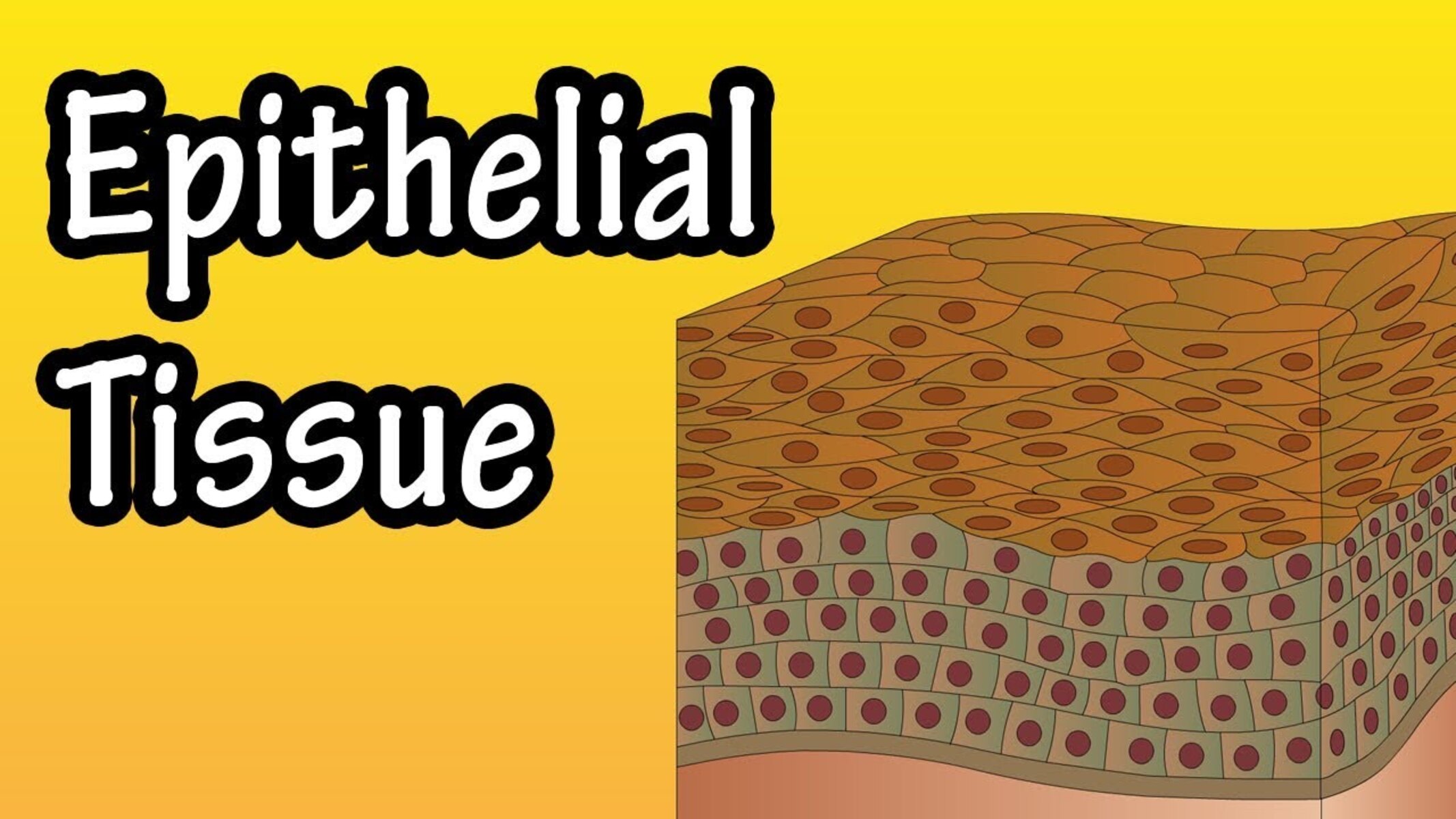
Epithelial tissues are a fascinating and vital component of the human body, playing a crucial role in its structure and function. They are found both on the body’s external surfaces and lining various organs and internal cavities. These tissues act as a protective barrier, preventing the entry of pathogens and foreign substances while allowing the exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products.
In this article, we will explore 18 astounding facts about epithelial tissues that will deepen our understanding of their importance. From their diverse types and specialized functions to their regenerative abilities and involvement in diseases, epithelial tissues truly have a captivating story to tell. So, let’s dive in and uncover the remarkable world of epithelial tissues!
Key Takeaways:
- Epithelial tissues are like the body’s protective armor, shielding organs and blood vessels from harm, absorbing nutrients, and even helping with temperature regulation and wound healing.
- These tissues are like the superheroes of the body, with diverse functions in different organs, playing a crucial role in immune responses, fluid balance, and even contributing to the development of organs during embryonic stages.
Epithelial tissues are one of the four major tissue types in the human body.
Epithelial tissues encompass a wide range of structures, including the outer layer of the skin, the lining of the respiratory tract, and the inner lining of organs and blood vessels.
Epithelial tissues act as a protective barrier.
These tissues form a barrier that protects the underlying tissues and organs from mechanical injury, pathogens, and harmful substances.
Epithelial tissues are involved in absorption and secretion.
They play a crucial role in the absorption of nutrients, ions, and water from the digestive tract and the secretion of substances such as hormones and enzymes.
Epithelial tissues have distinct cell-cell adhesion structures.
The cells in epithelial tissues are tightly connected through specialized junctions, including tight junctions, adherens junctions, and desmosomes, which help maintain tissue integrity.
Epithelial tissues have polarity.
Epithelial cells have an apical surface that faces a lumen or the external environment, and a basal surface that is in contact with the underlying connective tissue.
Epithelial tissues can be classified based on their shape.
Epithelial cells can be squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube-shaped), or columnar (rectangular), giving rise to different types of epithelial tissues.
Epithelial tissues are highly regenerative.
These tissues have a high turnover rate and can continuously regenerate to repair damage and maintain their function.
Epithelial tissues are avascular.
Since they lack blood vessels, epithelial tissues rely on diffusion from nearby blood vessels for their nutrient and oxygen supply.
Epithelial tissues provide sensory functions.
Epithelial cells in specialized sensory organs, such as the taste buds and olfactory epithelium, are responsible for detecting and transmitting sensory information.
Epithelial tissues play a role in temperature regulation.
The sweat glands in the skin, which are made up of epithelial cells, help regulate body temperature through the production of sweat.
Epithelial tissues contribute to the formation of glands.
Certain epithelial tissues can differentiate and give rise to specialized glands, such as sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands.
Epithelial tissues have diverse functions in different organs.
From lining the small intestine to forming the alveoli of the lungs, epithelial tissues adapt to the specific functions of various organs.
Epithelial tissues can undergo hyperplasia and metaplasia.
In response to injury or certain stimuli, epithelial cells can increase in number (hyperplasia) or change their phenotype (metaplasia).
Epithelial tissues play a key role in wound healing.
When an injury occurs, epithelial cells migrate and proliferate to cover the wound, facilitating the healing process.
Epithelial tissues participate in immune responses.
Epithelial cells lining the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts act as a barrier against pathogens and contribute to the immune response.
Epithelial tissues can undergo malignant transformation.
Abnormal changes in epithelial cells can lead to the development of various types of cancer, such as skin cancer and lung cancer.
Epithelial tissues are involved in fluid and electrolyte balance.
Epithelial cells in the kidneys are responsible for reabsorbing water and electrolytes and maintaining proper balance within the body.
Epithelial tissues have a crucial role in embryonic development.
During embryogenesis, epithelial cells undergo complex morphogenetic processes to form the different layers and structures of developing organs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, epithelial tissues play a vital role in the functioning of our body. From forming protective barriers to facilitating transportation of substances, these tissues are truly remarkable. Their diverse characteristics and functions make them a subject of great interest in the field of biology. Understanding the intricacies of epithelial tissues can help us gain deeper insights into human anatomy and physiology.With their ability to regenerate and adapt, epithelial tissues have the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine. Researchers are constantly exploring ways to harness the power of these tissues in healing wounds, treating diseases, and even growing organs for transplantation. As our understanding of epithelial tissues continues to expand, we can expect further breakthroughs in the field of regenerative medicine.Overall, the study of epithelial tissues is a fascinating journey into the intricacies of our own bodies. By delving deeper into their structure, function, and remarkable properties, we can appreciate the beauty and complexity of the biological systems that make us who we are.
FAQs
Q: What are epithelial tissues?
A: Epithelial tissues are flat, thin layers of cells that cover the surfaces of organs and line the cavities of the body.
Q: What are the different types of epithelial tissues?
A: The different types of epithelial tissues include simple squamous, stratified squamous, cuboidal, columnar, and transitional epithelium.
Q: What are the functions of epithelial tissues?
A: Epithelial tissues have various functions, including protection, absorption, secretion, and transportation of substances.
Q: Where are epithelial tissues found in the body?
A: Epithelial tissues are found in the skin, blood vessels, respiratory tract, digestive tract, urinary tract, and other organs.
Q: Can epithelial tissues regenerate?
A: Yes, epithelial tissues have a high regenerative capacity. They can repair and replace damaged cells to maintain tissue integrity.
Q: Can epithelial tissues become cancerous?
A: Yes, epithelial tissues can develop cancerous growths, known as carcinomas. Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes.
Epithelial tissues are truly remarkable, playing crucial roles in protecting, absorbing, secreting, and sensing within our bodies. Their adaptability and regenerative capabilities make them essential for maintaining healthy organs and systems. If you found these facts captivating, continue your exploration of the wonders of epithelial tissues with our article "20 Unbelievable Facts About Epithelial Tissue." Prepare to be amazed by the incredible world of these microscopic marvels and their impact on our overall well-being.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
