Hormone feedback loops play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of hormones in our bodies. These intricate systems involve a complex interplay between various glands and their target organs, ensuring that hormone levels are regulated and adjusted as needed. Understanding how these feedback loops work can provide key insights into the functioning of our endocrine system. In this article, we will explore 11 intriguing facts about hormone feedback loops that shed light on their importance and fascinating mechanisms. From the precise timing of hormone release to the role of negative and positive feedback, these facts will deepen our understanding of how our bodies maintain hormonal equilibrium. So, let’s dive into the intricate world of hormone feedback loops and discover the wonders they hold.
Key Takeaways:
- Hormone feedback loops are like the body’s traffic controllers, keeping everything in balance and working smoothly. They can be affected by things like stress and diet, and can impact growth, metabolism, and overall health.
- Understanding hormone feedback loops is important for doctors who study hormones. These loops can affect things like the menstrual cycle, blood sugar levels, and growth. They can also cause health issues if they get out of balance.
Hormone feedback loops play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis.
In the complex world of biology, hormone feedback loops act as the body’s regulatory system to ensure that various physiological processes are kept in balance.
Hormone feedback loops can be either positive or negative.
Positive feedback loops amplify the initial signal, while negative feedback loops work to counteract or decrease the initial signal.
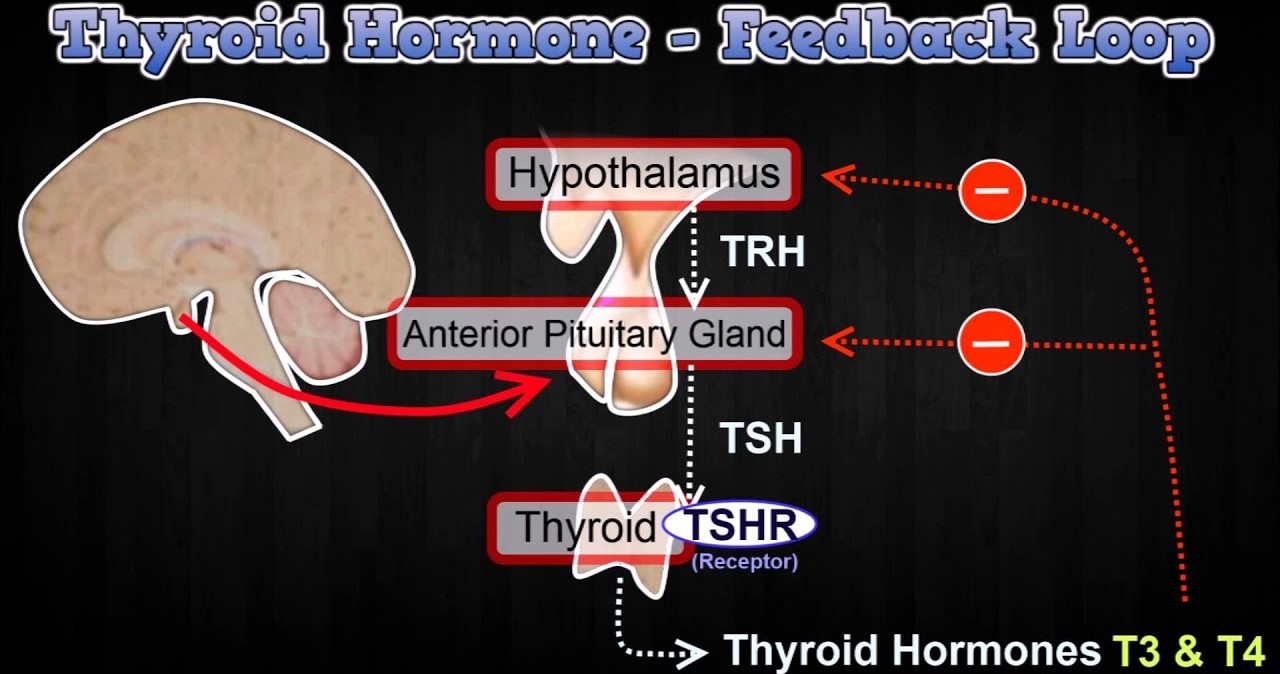
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key players in hormone feedback loops.
The hypothalamus releases hormones that stimulate or inhibit the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, which then controls the release of hormones from other endocrine glands.
Hormone feedback loops regulate the menstrual cycle in females.
Through a carefully orchestrated series of feedback loops involving hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, the female reproductive system undergoes regular cycles of ovulation and menstruation.
Hormone feedback loops are involved in the regulation of blood sugar levels.
The hormones insulin and glucagon work together in a feedback loop to maintain optimal blood glucose levels, ensuring that cells have enough energy for proper functioning.
Hormone feedback loops are crucial for growth and development.
Growth hormone, produced in the pituitary gland, plays a key role in stimulating growth and development in children and adolescents. Feedback loops ensure that growth occurs at a balanced and appropriate rate.
Imbalances in hormone feedback loops can lead to a variety of health issues.
Disruptions in hormone feedback loops can result in conditions such as hormonal imbalances, thyroid disorders, infertility, and metabolic disorders.
Hormone feedback loops are influenced by external factors.
Factors such as stress, diet, exercise, and environmental toxins can impact hormone feedback loops and disrupt their normal functioning.
Hormone feedback loops can exhibit long-term effects on the body.
Changes in hormone feedback loops can have profound and long-lasting effects on various biological processes, including metabolism, reproduction, and overall health.
Hormone feedback loops can vary between individuals and different stages of life.
The dynamics of hormone feedback loops can be influenced by genetic factors, age, and other individual variations, leading to differences in hormone levels and responses.
Understanding hormone feedback loops is crucial in the field of endocrinology.
Endocrinologists study hormone feedback loops to better understand and treat conditions related to hormonal regulation, contributing to advancements in medical knowledge and patient care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hormone feedback loops are essential for maintaining homeostasis in the body. These intricate systems play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes and ensuring the proper functioning of our organs and tissues.Understanding hormone feedback loops not only contributes to our knowledge of human biology but also has implications for treating hormonal imbalances and disorders. By comprehending the complexities of these feedback mechanisms, medical professionals can develop targeted therapies and interventions to restore hormonal balance and improve overall health.Hormone feedback loops are fascinating and dynamic, constantly adapting to changing conditions and stimuli. Exploring the intricate web of interactions between hormones, glands, and target organs reveals the remarkable complexity of the human body. By delving deeper into the world of hormone regulation, we can continue to unravel the mysteries of health and develop innovative treatments for hormonal disorders.
FAQs
1. What are hormone feedback loops?
Hormone feedback loops are complex physiological processes that involve the regulation and control of hormone levels in the body. They typically involve a feedback mechanism where a hormone acts on a target tissue or organ, which then provides feedback to the endocrine system to either stimulate or inhibit hormone secretion.
2. Why are hormone feedback loops important?
Hormone feedback loops are vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body, ensuring that hormone levels are properly regulated. They play a critical role in various physiological processes, including growth and development, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response.
3. How do hormone feedback loops work?
Hormone feedback loops involve a series of events where a hormone is released by an endocrine gland, travels through the bloodstream, and binds to specific receptors on target tissues or organs. This binding triggers a response in the target tissue or organ and provides feedback to the endocrine system, either inhibiting or stimulating hormone secretion.
4. Can hormone feedback loops be disrupted?
Yes, hormone feedback loops can be disrupted, leading to hormonal imbalances and disorders. Factors such as stress, genetics, environmental toxins, certain medications, and certain diseases can interfere with the normal functioning of these feedback mechanisms.
5. How are hormone feedback loops regulated?
Hormone feedback loops are regulated by various mechanisms, including negative feedback and positive feedback. Negative feedback helps maintain hormone levels within a certain range by reducing or inhibiting hormone production. Positive feedback, on the other hand, amplifies hormone production or secretion.
6. Are hormone feedback loops specific to humans?
No, hormone feedback loops are not specific to humans. They exist in various organisms, including animals, plants, and even some single-celled organisms. These feedback mechanisms are crucial for maintaining physiological balance and regulating essential functions across different species.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
