Neurulation is a fascinating biological process that plays a crucial role in the development of the nervous system in vertebrate embryos. It is a complex series of events that transforms a simple sheet of cells into the intricate structure of the brain and spinal cord. Understanding neurulation not only sheds light on how our own nervous system forms but also provides insight into neurodevelopmental disorders and potential therapeutic interventions.
In this article, we will delve into the incredible world of neurulation and uncover 15 mind-blowing facts about this vital process. From the formation of the neural tube to the emergence of neural crest cells, we will explore the intricate mechanisms and highlight the remarkable milestones that occur during neurulation. So, get ready to expand your knowledge and embark on a journey through the mesmerizing world of neurulation!
Key Takeaways:
- Neurulation is the amazing process of forming the brain and spinal cord from the ectoderm during early embryonic development, and it’s guided by signaling pathways and the notochord.
- Neurulation is like a carefully choreographed dance, involving precise cellular movements and genetic influences, and it’s crucial for establishing the foundation of the central nervous system.
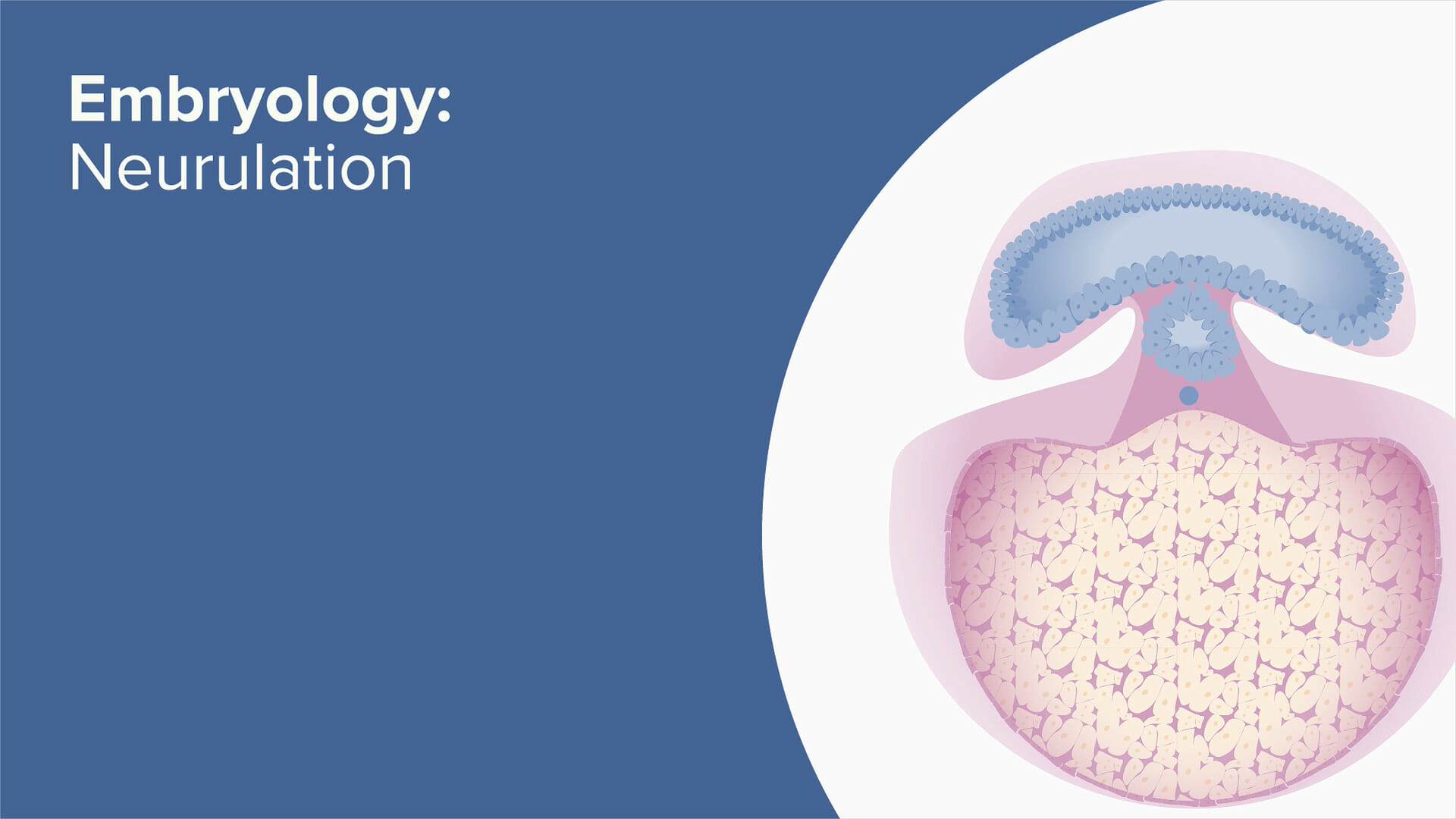
Neurulation is the process of neural tube formation.
Neurulation is an essential developmental process in vertebrates, where the neural tube, which later forms the brain and spinal cord, is formed from the ectoderm.
Neurulation begins during embryonic development.
During early embryonic development, neurulation starts with the formation of the neural plate, which then folds and fuses to create the neural tube.
Neurulation is regulated by various signaling pathways.
Several crucial signaling pathways, such as the Wnt and BMP pathways, play a significant role in orchestrating the processes involved in neurulation.
The notochord is a critical structure during neurulation.
The notochord, a rod-like structure, provides signals that induce the formation of the neural plate and guide the neural tube formation.
Neurulation establishes the basic structure of the central nervous system.
Through neurulation, the neural tube gives rise to the brain and spinal cord, establishing the foundation for the complex central nervous system.
Neurulation is a highly coordinated process.
Precise coordination of cell proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenetic movements is essential for successful neurulation.
Neurulation defects can lead to severe developmental abnormalities.
Disruptions in the neurulation process can result in neural tube defects, such as spina bifida and anencephaly, which can have severe consequences on the affected individuals.
Neurulation occurs in a cranio-caudal direction.
The process of neurulation starts from the cranial region and progresses towards the caudal region, ensuring the proper development of the entire neural tube.
Neurulation involves complex cellular rearrangements.
During neurulation, cells undergo dynamic movements, including convergent extension and apical constriction, to shape the neural tube.
Neurulation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
Both genetic factors, such as specific gene mutations, and environmental factors, including folic acid deficiency, can affect neurulation and contribute to neural tube defects.
Neurulation is conserved across vertebrate species.
The process of neurulation is remarkably conserved across different vertebrate species, highlighting its fundamental importance in embryonic development.
Neurulation is a dynamic process.
The movement and shaping of neural tissue during neurulation involve intricate cellular dynamics driven by various molecular mechanisms.
Neurulation is guided by signaling gradients.
Signaling molecules, such as retinoic acid and sonic hedgehog, establish concentration gradients that provide positional information for proper neural tube formation.
Neurulation involves the formation of neural crest cells.
During neurulation, a group of cells called neural crest cells detach from the neural tube and give rise to diverse cell types, including neurons, glial cells, and pigment cells.
Neurulation marks the beginning of nervous system development.
Neurulation is a crucial milestone that sets the stage for the formation and subsequent development of the intricate nervous system.
Conclusion
Neurulation is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the development of the nervous system. From the formation of the neural tube to the intricate differentiation of neural crest cells, each step in neurulation contributes to the complexity and functionality of the nervous system.
By understanding the mind-blowing facts about neurulation, we gain insight into the remarkable intricacies of embryonic development. From the initiation of neurulation to the closure of the neural tube, these processes demonstrate the intricate coordination of cellular and molecular events that shape our nervous system.
As research and technology continue to advance, we can expect to uncover even more mind-blowing facts about neurulation and its significance in human development and health. Exploring the hidden wonders of neurulation not only expands our understanding of biology but also opens up possibilities for new insights and potential therapeutic interventions.
FAQs
1. What is neurulation?
Neurulation is the process by which the neural plate forms, folds, and eventually becomes the neural tube, which gives rise to the brain and spinal cord.
2. At what stage of development does neurulation occur?
Neurulation occurs during the early stages of embryonic development, typically between weeks three and four after fertilization.
3. What are neural crest cells?
Neural crest cells are a unique group of cells that arise from the developing neural tube and play a crucial role in the formation of various tissues, including the peripheral nervous system.
4. What happens if neurulation does not occur properly?
If neurulation does not occur properly, it can lead to severe developmental abnormalities known as neural tube defects, which can affect the brain, spinal cord, and other structures derived from the neural tube.
5. Are there any genetic factors that influence neurulation?
Yes, several genetic factors can influence neurulation, including mutations in genes involved in neural tube closure and neural crest cell differentiation.
Neurulation's mind-blowing facts have piqued your curiosity, but there's more to explore in the fascinating world of embryonic development. Unravel the mysteries of gastrulation/">developmental biology and gastrulation with our captivating articles on these crucial processes. Don't miss out on the opportunity to delve deeper into the awe-inspiring journey of embryonic development, where each stage holds its own wonders and surprises. Continue your exploration and expand your knowledge with these engaging reads.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


