Hormones play a crucial role in our body, orchestrating various physiological processes and maintaining balance. They are essential chemical messengers that regulate everything from growth and development to metabolism and reproduction. The process of hormone synthesis, where these vital molecules are produced, is a fascinating and intricate one that involves multiple organs and intricate biochemical pathways.
In this article, we will delve into 17 intriguing facts about hormone synthesis, shedding light on the remarkable mechanisms that govern this vital process. From the production of hormones in specialized glands to the complex signaling pathways that ensure their release into the bloodstream, we will explore the intricate dance of molecules that regulates our body’s functions. So, let’s dive deep into the world of hormone synthesis and discover the captivating secrets behind this fundamental aspect of our biological machinery.
Key Takeaways:
- Hormone synthesis is a fascinating process that involves specialized cells, enzymes, and feedback mechanisms to produce chemical messengers for regulating bodily functions and maintaining balance.
- Factors like stress, nutrition, and genetic variations can influence hormone synthesis, impacting our health and well-being. Understanding hormone synthesis helps us appreciate the complexity of our bodies.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by the endocrine glands.
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions and maintaining homeostasis.
The process of hormone synthesis occurs in specialized cells within the endocrine glands.
These cells contain specific enzymes and machinery responsible for synthesizing hormones.
Hormones can be synthesized from various precursor molecules.
Depending on the specific hormone, precursors can include cholesterol, amino acids, or other hormones.
The synthesis of hormones is tightly regulated by feedback mechanisms.
These mechanisms ensure that hormone production is adjusted according to the body’s needs.
Many hormones are synthesized in multiple steps.
This involves the conversion of precursor molecules into intermediate compounds before the final hormone is produced.
Enzymes play a crucial role in hormone synthesis.
Specific enzymes are responsible for catalyzing the reactions involved in converting precursor molecules into hormones.
Hormones are often synthesized and stored in endocrine glands until they are needed.
Upon stimulation, these stored hormones are released into the bloodstream to exert their effects.
Hormone synthesis can be influenced by various factors, including stress, nutrition, and other hormones.
External and internal factors can modulate the rate of hormone synthesis and secretion.
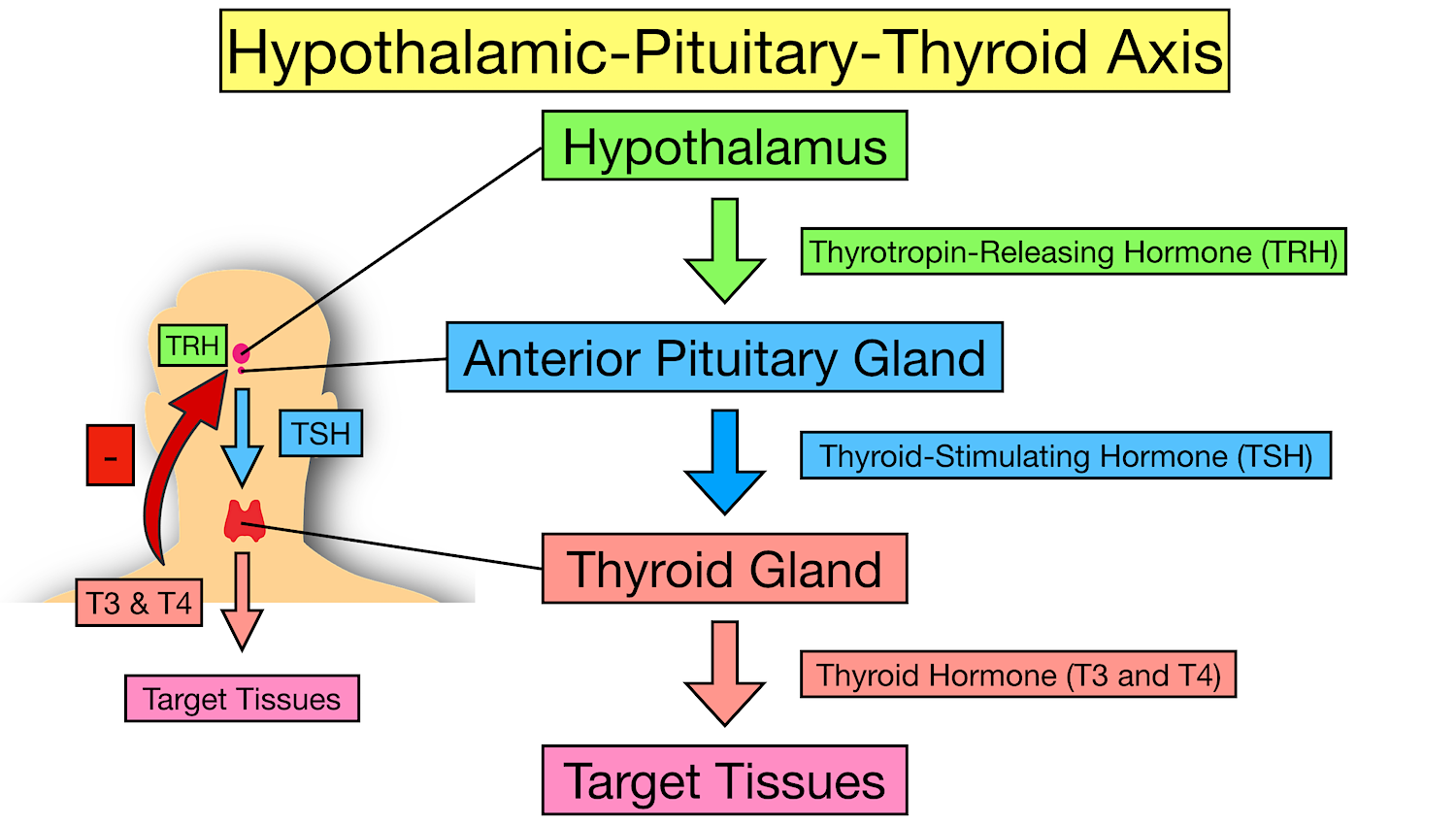
Different endocrine glands specialize in the synthesis of specific hormones.
For example, the thyroid gland synthesizes thyroid hormones, while the adrenal glands produce cortisol and adrenaline.
Hormone synthesis can be disrupted by certain diseases or conditions.
Disorders such as hypothyroidism or adrenal insufficiency can impair the production of specific hormones.
Hormones can have both short-term and long-term effects on target cells.
Some hormones act rapidly to elicit immediate responses, while others have slower, long-lasting impacts.
The synthesis of steroid hormones involves cholesterol as a crucial precursor.
Cholesterol serves as the building block for the synthesis of hormones such as cortisol and testosterone.
Hormone synthesis can be affected by genetic factors.
Genetic mutations or variations can impact the enzymes involved in hormone synthesis, leading to hormonal disorders.
Feedback loops involving hormones play a significant role in maintaining hormonal balance.
Negative feedback loops help regulate hormone synthesis by inhibiting or stimulating production as needed.
Hormones can act locally or systemically.
Some hormones exert their effects only on nearby cells, while others travel through the bloodstream to reach distant target cells.
Hormone synthesis can be modulated by certain medications or hormone replacement therapies.
These interventions can help restore hormonal balance in individuals with deficiencies or imbalances.
Hormone synthesis is a complex and fascinating process that is still being extensively studied.
Scientists continue to unravel the intricate mechanisms involved in hormone synthesis, leading to new insights and discoveries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hormone synthesis is a fascinating and intricate process that plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall balance and function. From the multiple glands involved to the complex pathways and feedback loops, hormones regulate various physiological processes and help coordinate the body’s activities.
Understanding the synthesis of hormones is essential for grasping the underlying mechanisms of many biological functions. Through continuous research and advancement, scientists are uncovering new insights into hormone synthesis, paving the way for improved diagnostics and treatments for hormonal imbalances and related disorders.
With its profound impact on our health and well-being, hormone synthesis remains an intriguing area of study, promising to unravel more secrets of our complex biological system in the years to come.
FAQs
Q: What is hormone synthesis?
A: Hormone synthesis refers to the process by which hormones are produced within the body. It involves various organs and glands that synthesize, regulate, and release these chemical messengers into the bloodstream to exert their specific effects on target tissues and organs.
Q: What are the key glands involved in hormone synthesis?
A: Several glands are involved in hormone synthesis, including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries (in females), and testes (in males). Each gland has a specific role in producing and regulating different hormones.
Q: How are hormones synthesized?
A: Hormones are synthesized through a series of complex biochemical reactions within the cells of the glands. The process starts with the synthesis of hormone precursor molecules, which are then modified and transformed into active hormones through enzymatic reactions. These hormones are then released into the bloodstream where they travel to target tissues and exert their effects.
Q: What factors influence hormone synthesis?
A: Hormone synthesis is influenced by various factors, including genetic factors, environmental cues, feedback mechanisms, and hormonal signals from other glands. Additionally, factors such as stress, diet, exercise, and sleep patterns can also impact hormone synthesis and balance in the body.
Q: Can hormone synthesis be disrupted?
A: Yes, hormone synthesis can be disrupted due to various reasons, including genetic disorders, tumors or dysfunctions of the glands involved, certain medications, chronic stress, and lifestyle factors. Hormonal imbalances can lead to a wide range of health issues and may require medical intervention for proper diagnosis and management.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
