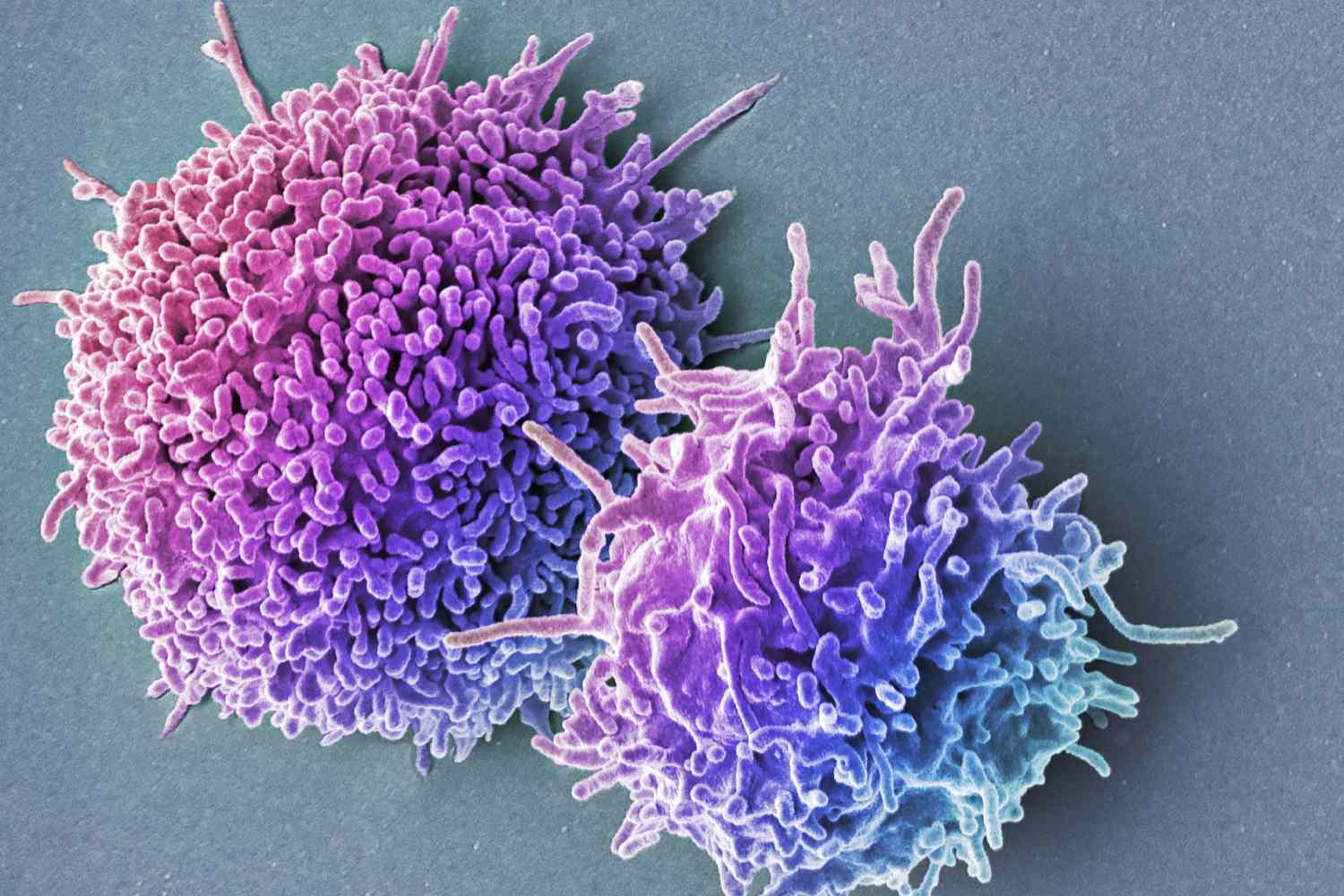
Welcome to the fascinating world of T lymphocytes! These remarkable cells are an integral part of our immune system and play a crucial role in protecting our bodies against harmful pathogens. T lymphocytes, also known as T cells, are a type of white blood cell that are responsible for orchestrating and coordinating immune responses.In this article, we will delve into 18 unbelievable facts about T lymphocytes that will not only amaze you, but also deepen your understanding of their importance in maintaining our health. From their diverse types and functions to their amazing capabilities and interactions with other immune cells, buckle up for a journey through the incredible world of T lymphocytes.So, let’s dive in and explore the extraordinary characteristics and abilities of these T cells that are instrumental in our body’s defense against infections and diseases.
Key Takeaways:
- T lymphocytes, or T cells, are immune system superheroes with memory, diversity, and longevity, playing vital roles in fighting infections and maintaining overall health.
- T cells can remember previous infections, differentiate into different types, and even help in cancer treatment, showcasing their incredible versatility and potential for medical advancements.
Facts 1: T Lymphocytes Are Key Players in the Immune System
T lymphocytes, also known as T cells, are a vital component of the immune system, playing a crucial role in adaptive immunity. They are responsible for recognizing specific foreign antigens and triggering immune responses to eliminate them from the body.
Facts 2: T Lymphocytes Originate from the Thymus Gland
T lymphocytes derive their name from the thymus gland, where they undergo maturation and acquire their unique antigen receptor repertoire. The thymus gland is located in the chest, just above the heart.
Facts 3: T Lymphocytes Have Diverse Functions
T cells have various functions, including the ability to directly kill infected cells, activate other immune cells, and regulate the immune response. They play a critical role in both cell-mediated and humoral immune responses.
Facts 4: T Lymphocytes Recognize Antigens Through T Cell Receptors
T lymphocytes identify specific antigens through their T cell receptors (TCRs). These receptors are highly diverse and allow T cells to recognize a wide range of foreign substances, including viruses, bacteria, and cancer cells.
Facts 5: T Lymphocytes Differentiate into Helper T Cells and Cytotoxic T Cells
Upon activation, T lymphocytes differentiate into two main subsets: helper T cells (Th) and cytotoxic T cells (Tc). Helper T cells assist in coordinating immune responses, while cytotoxic T cells directly kill infected or abnormal cells.
Facts 6: T Lymphocytes Can Remember Previous Infections
One of the remarkable features of T lymphocytes is their ability to remember previous encounters with specific antigens. This memory allows for a faster and more potent immune response upon re-exposure to the same pathogen.
Facts 7: T Lymphocytes Play a Role in Autoimmune Diseases
In certain cases, T lymphocytes can mistakenly target healthy cells and tissues, leading to autoimmune diseases. Examples of autoimmune disorders include rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes.
Facts 8: T Lymphocytes Interact with Antigen-Presenting Cells
T cells interact with antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. This interaction is necessary for the activation of T cells and initiation of immune responses against specific antigens.
Facts 9: T Lymphocytes Express Cell Surface Markers
T cells express specific cell surface markers, including CD4 and CDCD4 is primarily found on helper T cells, while CD8 is present on cytotoxic T cells. These markers help in distinguishing between different T cell subsets.
Facts 10: T Lymphocyte Development Requires Signals from Other Cells
The development and maturation of T lymphocytes require signals from various cells, including thymic epithelial cells and dendritic cells. These signals are crucial for shaping the T cell repertoire and ensuring proper immune function.
Facts 11: T Lymphocytes Have Longevity
T lymphocytes have the ability to persist in the body for a long time. Some memory T cells can survive for decades, providing long-term immunity against previously encountered pathogens.
Facts 12: T Lymphocytes Activate B Cells
T cells play a crucial role in activating B cells, another type of immune cell responsible for producing antibodies. This collaboration between T and B cells is essential for an effective immune response against pathogens.
Facts 13: T Lymphocytes Can Induce Immunological Tolerance
T regulatory cells (Tregs), a subset of T lymphocytes, have the ability to suppress immune responses and promote tolerance. They help prevent excessive immune reactions against self-antigens and maintain immune system balance.
Facts 14: T Lymphocytes Have Differentiation Pathways
T cells can differentiate into various effector subsets, each with specialized functions. Examples include Th1 cells, Th2 cells, Th17 cells, and regulatory T cells. These subsets contribute to different aspects of immune responses.
Facts 15: T Lymphocytes Provide Immune Surveillance
T lymphocytes continuously patrol tissues and lymphoid organs, providing immune surveillance for the detection and elimination of infected or abnormal cells. This surveillance helps maintain overall immune system integrity.
Facts 16: T Lymphocytes Can Be Engineered for Immunotherapy
Recent advances in immunotherapy have led to the development of techniques to engineer T lymphocytes, such as CAR-T cell therapy. These engineered T cells have shown promising results in the treatment of certain types of cancer.
Facts 17: T Lymphocytes Play a Role in Graft Rejection
During organ transplantation, T lymphocytes can recognize the transplanted tissue as foreign and initiate an immune response, leading to graft rejection. Immunosuppressive medications are often used to prevent this rejection.
Facts 18: T Lymphocytes Are Essential for Vaccination
T lymphocytes are crucial for the success of vaccination. They help recognize vaccine antigens and generate long-lasting immune memory, providing protection against future infections.
Conclusion
T lymphocytes, also known as T cells, are a crucial component of the immune system. These remarkable cells play a pivotal role in defending the body against various pathogens and foreign substances. From their formation in the thymus to their specific interactions with antigens, T lymphocytes display a fascinating array of functions and characteristics.
Throughout this article, we have explored 18 unbelievable facts about T lymphocytes. We have delved into their diverse subsets, such as helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells, and examined their ability to recognize and eliminate infected cells. We have also discussed their involvement in autoimmune diseases and their potential in cancer immunotherapy.
By understanding the intricacies of T lymphocytes, we gain a deeper appreciation for the astounding complexity of our immune system. These tiny cells work tirelessly to keep us healthy and protected. As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries of T lymphocytes, we can look forward to advancements in immunology and the development of innovative therapeutic strategies.
FAQs
1. What are T lymphocytes?
T lymphocytes, or T cells, are a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system’s defense against infections and diseases.
2. How are T lymphocytes formed?
T lymphocytes are formed in the bone marrow and undergo maturation in the thymus gland.
3. What are the subsets of T lymphocytes and their functions?
There are several subsets of T lymphocytes, including helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, and regulatory T cells. Helper T cells assist other immune cells in mounting an immune response, cytotoxic T cells kill infected or abnormal cells, and regulatory T cells help prevent an overactive immune response.
4. How do T lymphocytes recognize antigens?
T lymphocytes possess specific receptors on their surface called T cell receptors (TCRs) that enable them to recognize antigens presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
5. Are T lymphocytes involved in autoimmune diseases?
Yes, T lymphocytes can contribute to autoimmune diseases by mistakenly targeting healthy cells and tissues in the body.
6. Can T lymphocytes be used in cancer treatment?
Yes, T lymphocytes can be harnessed in cancer immunotherapy, such as adoptive cell therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors, to enhance the body’s ability to recognize and kill cancer cells.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
