When it comes to understanding the complex development of organisms, germ layers play a crucial role. Germ layers are the primary layers of cells that form during embryonic development and give rise to all the tissues and organs in an organism’s body. These layers are fascinating in their ability to transform into a diverse array of structures, allowing organisms to function and thrive.
In this article, we will delve into 9 astounding facts about germ layers that will shed light on their importance and incredible versatility. From their role in determining the body plan of an organism to their ability to give rise to various tissue types, germ layers are a fundamental aspect of biology that deserves our attention and admiration.
Key Takeaways:
- Germ layers are like the building blocks of life, forming the foundation for our organs and tissues during embryonic development. They determine what our bodies will become!
- Scientists are studying germ layers to unlock the secrets of regenerative medicine and prevent birth defects. Understanding these layers helps us explore the wonders of life and biology.
Three Primary Germ Layers
Germ layers are divided into three main categories: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Each layer plays a crucial role in the formation of specific tissues and organs in the developing embryo.
Ectoderm: Building the Nervous System
The ectoderm gives rise to the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. It also forms the epidermis, hair, nails, and tooth enamel.
Mesoderm: The Middle Layer
The mesoderm is responsible for developing muscle, bone, connective tissues, blood vessels, and the circulatory system. It also contributes to the formation of the kidneys and reproductive organs.
Endoderm: Essential Organs
The endoderm develops into vital organs such as the lungs, liver, pancreas, and the lining of the digestive system. It plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
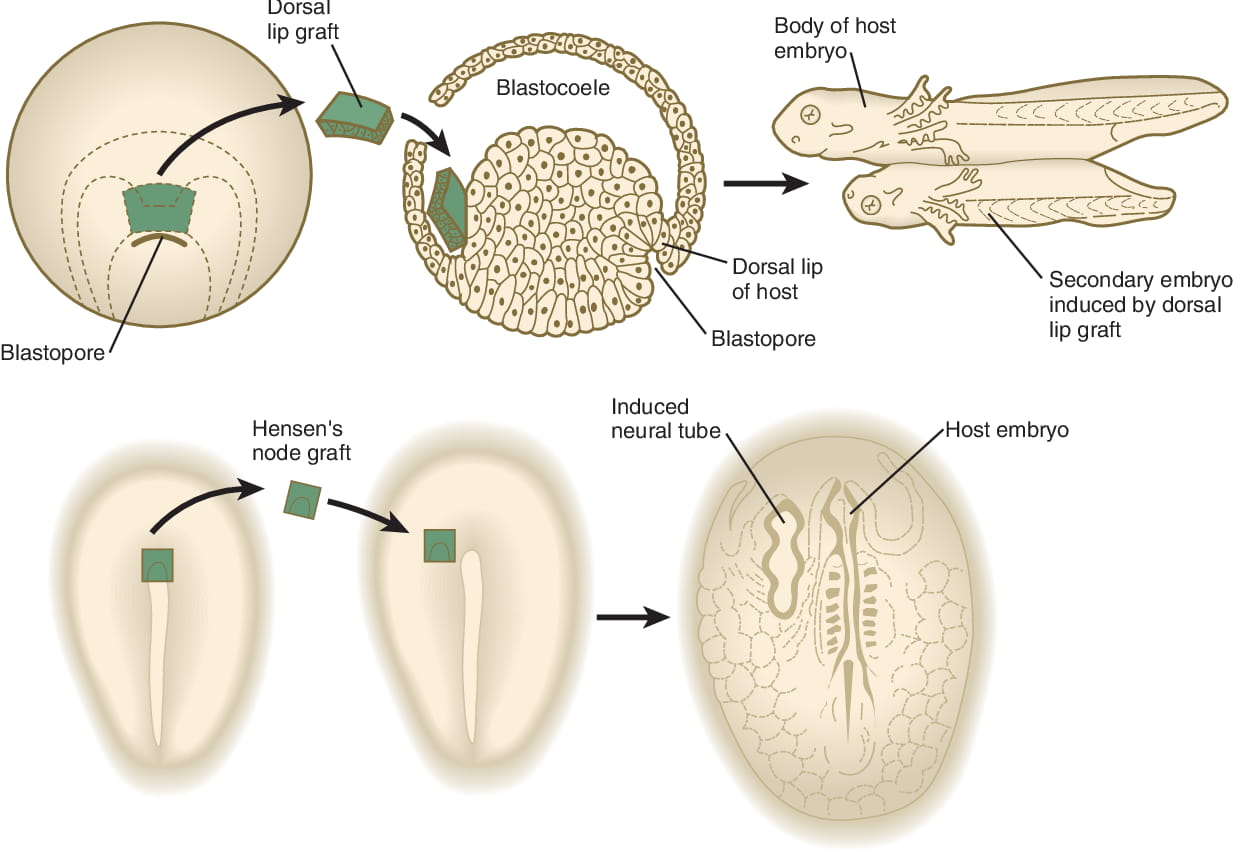
Gastrulation: Germ Layer Formation
Germ layers are formed during gastrulation, a key process in embryonic development. During gastrulation, the single-layered embryo transforms into a multi-layered structure with the formation of the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Germ Layers Determine Organ Development
The interactions between the germ layers create a complex signaling network that determines the specific fate of cells and leads to the development of various organs and structures in the body.
Germ Layers and Regenerative Medicine
Understanding germ layer development is crucial for the field of regenerative medicine. Researchers aim to use this knowledge to regenerate damaged tissues and organs by manipulating and guiding the behavior of cells derived from specific germ layers.
Germ Layers and Birth Defects
Abnormalities in germ layer development can lead to birth defects. By studying germ layer formation and identifying the causes of developmental disorders, scientists hope to find ways to prevent or treat these conditions.
Germ Layer Evolution
Germ layers have not always been present in all organisms. The development of germ layers is considered a significant evolutionary event, marking the transition from simple organisms to more complex multicellular organisms.
These 9 astounding facts about germ layers highlight their crucial role in embryonic development and the formation of tissues and organs in animals. Understanding the intricacies of germ layers allows scientists to delve deeper into the mysteries of life and explore new possibilities in medicine and biology.
Conclusion
Understanding germ layers is essential in comprehending the development and complexity of organisms. These distinct layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm – play a crucial role in the formation of tissues, organs, and body systems. From their origin in the early stages of embryonic development to their specialization into different cell types, germ layers lay the foundation for the structure and function of multicellular organisms.
As we delve deeper into the study of biology, the intricate processes occurring within the germ layers continue to amaze us. From the formation of the nervous system to the development of vital organs, the journey of the germ layers is a testament to the incredible complexity of life itself.
By exploring the astounding facts about germ layers, we gain a greater appreciation for the intricacies of embryonic development and the remarkable abilities of living organisms to self-organize and adapt. The study of germ layers offers a fascinating glimpse into the inner workings of life and paves the way for advancements in biology, medicine, and our understanding of the world around us.
FAQs
1. What are germ layers?
Germ layers are distinct cell layers that form during embryonic development. They are the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
2. What is the role of germ layers in embryonic development?
Germ layers give rise to various tissues, organs, and body systems in multicellular organisms. They are responsible for the development of specialized cell types and the formation of the overall body plan.
3. How do germ layers differentiate?
Germ layers differentiate through a process called gastrulation, where cells in the early embryo rearrange themselves into distinct layers. Each layer then develops into specific tissues and structures.
4. What organs develop from each germ layer?
The ectoderm gives rise to the skin, nervous system, and sensory structures. The mesoderm develops into muscles, bones, blood, and the circulatory system. The endoderm forms the digestive system, respiratory system, and other internal organs.
5. Can germ layers be regenerated in adults?
No, germ layers cannot be regenerated in adults. Once embryonic development is complete, the germ layers exist only in the early stages of life.
6. Are all organisms composed of germ layers?
No, not all organisms have germ layers. Germ layers are specific to complex multicellular organisms, such as animals.
7. Do all animals have the same number of germ layers?
Most animals have three germ layers, but some simpler organisms, like sponges, have fewer germ layers, while more complex organisms, like humans, have additional specialized layers.
8. How long does it take for germ layers to form in an embryo?
Germ layers begin to form during the early stages of embryonic development, typically within the first few weeks or months, depending on the species.
9. Can abnormalities in germ layer development cause birth defects?
Yes, disruptions in germ layer development can lead to various birth defects and developmental disorders. Issues with the formation or differentiation of germ layers can result in structural abnormalities or functional deficits in organs and systems.
Germ layers play a crucial role in shaping multicellular organisms, but their fascinating journey doesn't end there. Gastrulation, the process of germ layer formation, holds even more intriguing facts waiting to be explored. While you're at it, why not take a detour and learn about the surprising nutritional value of hulled barley? And if you're still hungry for knowledge, join us as we unravel the astounding world of embryogenesis, where germ layers work their magic to create life's building blocks.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


