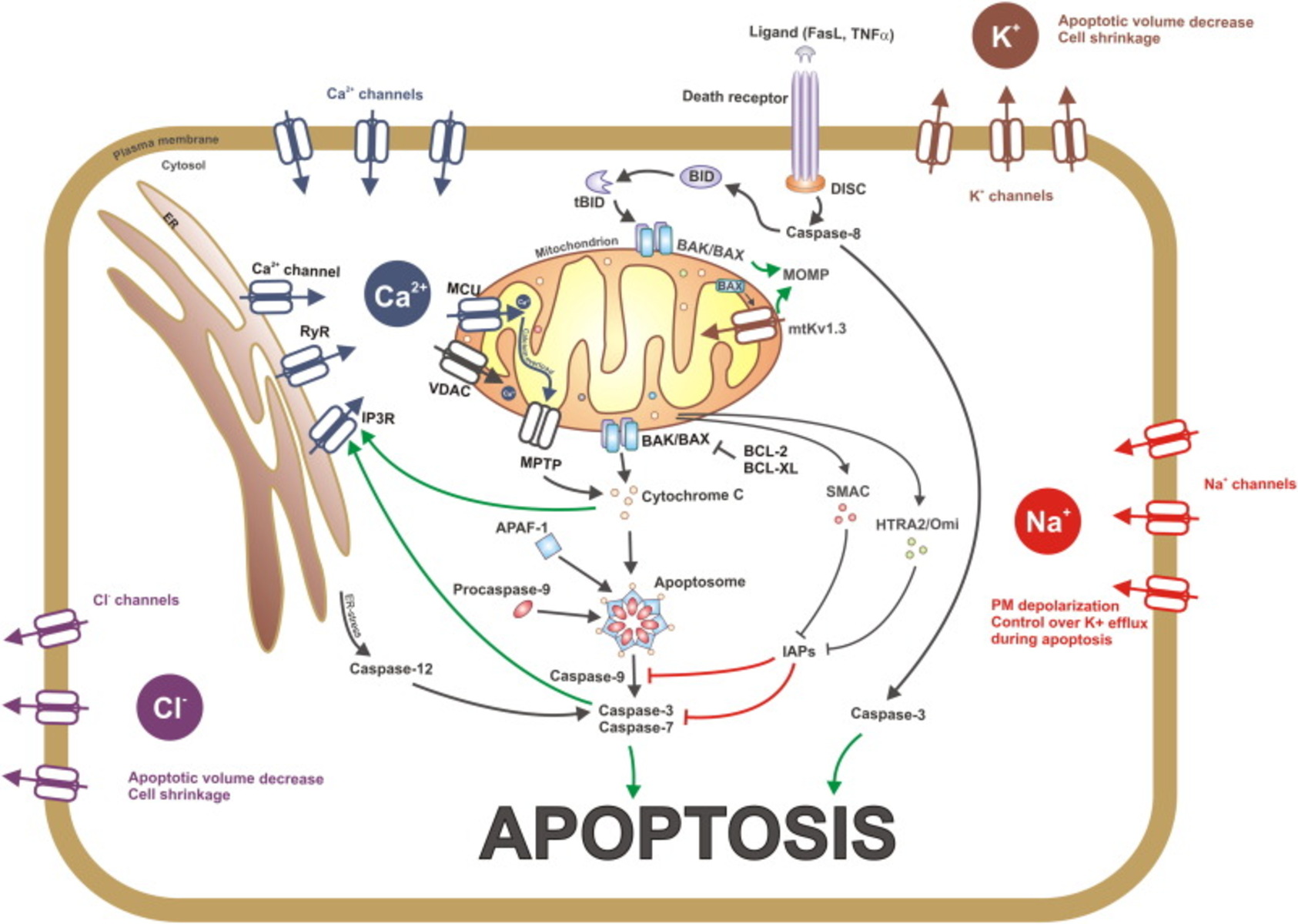
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a fundamental biological process that plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of cell population in multicellular organisms. It is a highly regulated and complex signaling pathway that involves a series of molecular events leading to the controlled elimination of cells. Understanding the intricate mechanisms underlying apoptosis signaling is of great importance in various fields, including cancer research, developmental biology, and immunology.
In this article, we will explore 13 enigmatic facts about apoptosis signaling that shed light on its significance and complexity. From the discovery of apoptosis to the intricate interplay of signaling molecules, we will delve into the fascinating world of this cell death process. So, let’s unravel the mysteries and gain a deeper understanding of apoptosis signaling and its impact on biological systems.
Key Takeaways:
- Apoptosis signaling is like a secret code that controls cell life and death. It helps keep our bodies healthy by getting rid of bad cells and shaping our organs during development.
- Understanding apoptosis signaling can help scientists develop new treatments for diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. It’s like finding the key to unlock potential cures!
The Fundamental Mechanism
Apoptosis signaling is a highly regulated process that involves a cascade of molecular events orchestrated by a series of proteins. It serves as a fundamental mechanism for eliminating unwanted or damaged cells.
Dual Nature of Apoptosis
Apoptosis signaling can act as both a safeguard and a weapon in the cellular landscape. It plays a crucial role during development, tissue homeostasis, and as a defense mechanism against pathogens, while also contributing to various diseases if dysregulated.
Initiators and Effectors
Apoptosis signaling is initiated by both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Extrinsic factors, such as death receptors, trigger apoptosis signaling through the activation of distinct pathways. In contrast, intrinsic factors, such as DNA damage or cellular stress, provoke apoptosis through mitochondrial-mediated pathways.
The Role of Caspases
Caspases are key players in apoptosis signaling. These proteases act as the executioners and dismantle crucial cellular components during cell death. They are responsible for the characteristic morphological and biochemical changes observed in apoptotic cells.
Cross-talk with Survival Pathways
Apoptosis signaling is intricately intertwined with survival pathways, creating a delicate balance between life and death decisions within the cell. Survival pathways such as the PI3K/Akt pathway and the Bcl-2 family of proteins regulate apoptosis signaling and determine cellular fate.
Death Receptors and Ligands
Death receptors, including Fas, TNF receptor, and TRAIL receptor, play a crucial role in initiating apoptosis signaling. Binding of their respective ligands triggers a cascade of events that ultimately leads to cell death.
Mitochondrial Control
The mitochondria act as a central hub in controlling apoptosis signaling. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) is a critical step in releasing apoptogenic factors into the cytoplasm, triggering the activation of caspases and subsequent cell death.
Apoptosis and Cancer
Dysregulation of apoptosis signaling is closely associated with the development and progression of cancer. Mutations in key apoptotic regulators, such as p53, Bcl-2, or Caspases, can disrupt the delicate balance between cell survival and death, leading to uncontrolled proliferation and tumor formation.
Apoptosis and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Defects in apoptosis signaling have also been implicated in various neurodegenerative diseases. Abnormalities in protein aggregation, failure to clear damaged neurons, and impaired apoptotic signaling can contribute to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.
Apoptosis and Development
Apoptosis signaling plays a pivotal role during embryogenesis and development. It helps sculpt organs, eliminate unnecessary tissues, and establish proper connections within the nervous system. Disturbances in apoptosis during development can lead to developmental abnormalities and birth defects.
Apoptosis and Immune Regulation
Apoptosis signaling is vital for maintaining immune homeostasis by eliminating excessive or autoreactive immune cells. It plays a crucial role in shaping the immune system and preventing autoimmunity.
Apoptosis and Therapeutics
The understanding of apoptosis signaling has opened doors to novel therapeutic strategies. Targeting specific apoptotic signaling components has shown promise in cancer treatment and combating certain diseases.
Apoptosis and Regeneration
Contrary to popular belief, apoptosis signaling also plays a role in tissue regeneration. Controlled cell death is essential for tissue remodeling and eliminating damaged cells to pave the way for new cell growth.
The discovery and ongoing research into apoptosis signaling continue to unravel its mysteries. Understanding its complex mechanisms and dysregulation in diseases provides valuable insights for therapeutic development. The “13 Enigmatic Facts About Apoptosis Signaling” shed light on the fascinating nature of this intricate process, fueling further exploration and innovation in the field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, apoptosis signaling is a fascinating and complex process that plays a crucial role in various biological processes. From its discovery to the understanding of the intricate signaling pathways involved, researchers have made significant advancements in unraveling the mysteries of apoptosis. The 13 enigmatic facts about apoptosis signaling highlight the diverse mechanisms and regulatory elements at play. From the importance of caspases to the role of mitochondria, these facts shed light on the intricacies of this fundamental biological process.As we continue to delve deeper into the world of apoptosis, it becomes clear that there is still much to be uncovered. The ongoing research in this field not only enhances our understanding of normal cell development and tissue maintenance but also opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions in diseases such as cancer.
FAQs
1. What is apoptosis signaling?
Apoptosis signaling is a highly regulated cellular process that determines whether a cell will live or die.
2. What are the key players in apoptosis signaling?
The key players in apoptosis signaling are caspases, mitochondria, and various molecular signaling pathways involving death receptors.
3. What is the purpose of apoptosis in the body?
Apoptosis plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis, eliminating damaged or infected cells, and regulating developmental processes.
4. How can apoptosis signaling be dysregulated?
Apoptosis signaling can be dysregulated by genetic mutations, alterations in signaling pathways, or external factors such as toxins or viruses.
5. Are there any diseases associated with dysregulated apoptosis signaling?
Yes, dysregulated apoptosis signaling has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
6. Can apoptosis be induced or inhibited?
Yes, apoptosis can be induced through different stimuli, such as chemotherapy drugs, radiation, or immune system activation. Conversely, it can also be inhibited by certain proteins or mutations that prevent cell death.
7. Is apoptosis important for normal development?
Yes, apoptosis is crucial for normal development as it helps shape tissues and organs by eliminating unwanted or excess cells.
8. Can apoptosis be targeted for therapeutic purposes?
Yes, targeting apoptosis signaling is a promising avenue for developing novel therapies, particularly in cancer treatment.
9. Can apoptosis signaling be regulated by diet or lifestyle?
There is evidence to suggest that certain dietary factors and lifestyle choices can influence apoptosis signaling. However, more research is needed to fully understand these relationships.
10. How is apoptosis different from necrosis?
Apoptosis is a programmed cell death process that occurs in a controlled and orderly manner. In contrast, necrosis is a form of cell death caused by external factors, often resulting in tissue damage and inflammation.
11. Does every cell undergo apoptosis?
No, not every cell undergoes apoptosis. Some cells, such as neurons, can be resistant to apoptosis under normal circumstances.
12. Can apoptosis signaling be used as a biomarker?
Yes, certain apoptotic markers can be used as biomarkers to assess cellular health and disease progression.
13. Are there any ethical implications associated with manipulating apoptosis signaling?
There may be ethical considerations associated with manipulating apoptosis signaling, particularly in the context of gene editing or selective cell death.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
