Protista, the diverse kingdom of eukaryotic organisms, is a fascinating and often overlooked group in the biological world. Comprising a wide array of single-celled and multicellular organisms, protists exhibit a remarkable range of characteristics and behaviors. From the dazzling bioluminescence of dinoflagellates to the complex life cycles of parasitic protozoa, the world of protists is filled with captivating wonders. In this article, we will explore 11 intriguing facts about protists that showcase their incredible diversity and significance in the natural world. So, let's dive into the captivating realm of protista and uncover some of the most captivating and fun facts about these remarkable organisms.
Key Takeaways:
- Protista, a diverse group of single-celled organisms, play vital roles in ecosystems as food sources and nutrient recyclers, showcasing their remarkable adaptability and ecological significance.
- Some protists, like algae, contribute to global oxygen production through photosynthesis, while others, like Plasmodium, can cause diseases, highlighting their complex and impactful nature.
Protista are a diverse group of organisms.
Protista is a unique kingdom in the domain Eukarya, encompassing a wide array of single-celled organisms. This diverse group includes algae, protozoa, and slime molds, each with distinct characteristics and ecological roles.
Protists are found in various habitats.
From freshwater ponds to the depths of the ocean, protists thrive in diverse environments. They play crucial roles in aquatic ecosystems, serving as primary producers and forming the base of the food web in many ecosystems.
Some protists are capable of photosynthesis.
Algae, a prominent group within the Protista kingdom, possess chloroplasts and can harness the energy of sunlight to produce their own food through photosynthesis. This ability contributes significantly to the global oxygen production and carbon dioxide fixation.
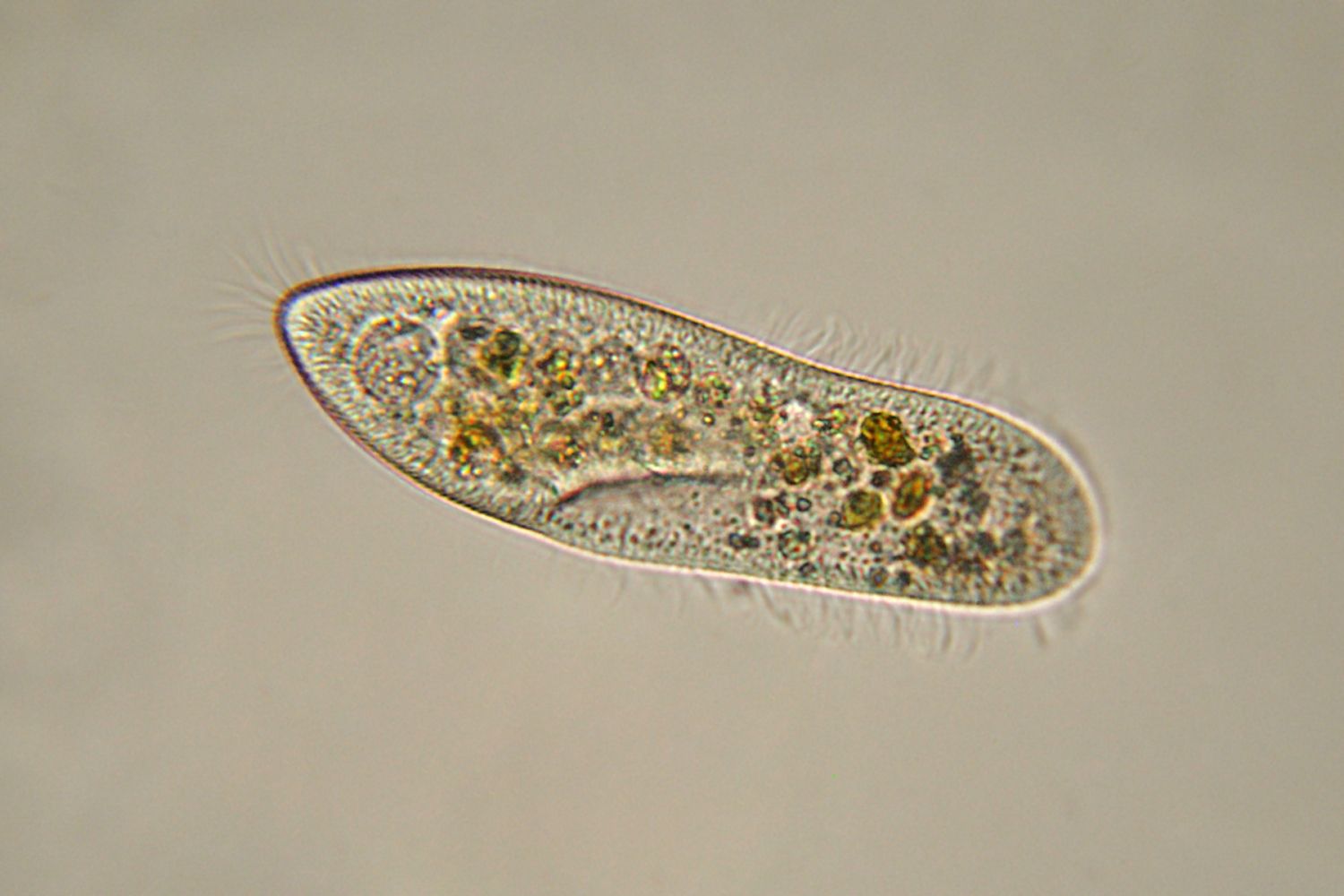
Protists exhibit remarkable diversity in size and complexity.
From unicellular organisms such as Paramecium and Amoeba to the giant kelp, which forms massive underwater forests, protists showcase a remarkable range in size and complexity, challenging the traditional notion of single-celled organisms.
Protists serve as food for various organisms.
Many aquatic organisms, including small fish and invertebrates, rely on protists as a primary food source. This pivotal role in the food chain highlights the ecological significance of these often-overlooked organisms.
Some protists are associated with diseases.
While the majority of protists are harmless, certain species can cause diseases in humans and other animals. For example, Plasmodium, the causative agent of malaria, is a well-known pathogenic protist with significant global health implications.
Protists have complex life cycles.
Several protist species exhibit intricate life cycles, involving both sexual and asexual reproductive phases. These diverse reproductive strategies contribute to the adaptability and resilience of protist populations in various environments.
Protists have unique locomotion mechanisms.
From the graceful movement of Euglena propelled by flagella to the amoeboid motion of organisms like Dictyostelium, protists employ a fascinating array of locomotion mechanisms, showcasing their remarkable adaptability and diversity.
Protists play a crucial role in nutrient cycling.
As primary producers and decomposers, protists contribute significantly to nutrient cycling in ecosystems. They aid in the breakdown of organic matter and facilitate the recycling of essential nutrients, playing a vital role in sustaining ecological balance.
Some protists form symbiotic relationships.
Protists engage in symbiotic associations with various organisms, ranging from corals to termites. These mutually beneficial relationships underscore the ecological interconnectedness and the intricate web of interactions within diverse ecosystems.
Protists have contributed to scientific advancements.
Studying protists has led to significant scientific breakthroughs, including the elucidation of fundamental biological processes such as cellular differentiation and organelle evolution. Their unique biological features continue to inspire innovative research in fields ranging from ecology to biotechnology.
Conclusion
Protists are a fascinating and diverse group of organisms that play crucial roles in various ecosystems. From their unique characteristics to their vital contributions to the environment, it’s clear that protists deserve our attention and appreciation. As we continue to explore and study these remarkable organisms, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of life on Earth. Whether it’s their evolutionary significance, ecological impact, or potential applications in biotechnology, protists continue to captivate scientists and enthusiasts alike. By delving into the world of protists, we not only expand our understanding of biology but also gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible diversity of life that surrounds us.
FAQs
What are protists?
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms that are not plants, animals, or fungi. They can be unicellular, colonial, or multicellular and are found in various aquatic and moist environments.
What are some examples of protists?
Common examples of protists include algae, amoebas, paramecia, and euglenas. These organisms exhibit a wide range of characteristics and behaviors, highlighting the diversity within the protist kingdom.
How do protists contribute to the environment?
Protists play essential roles in ecosystems as primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. They are crucial in nutrient cycling, food webs, and oxygen production, impacting the balance and sustainability of natural environments.
Can protists cause diseases?
Yes, some protists are pathogenic and can cause diseases in humans, animals, and plants. Examples include Plasmodium, the causative agent of malaria, and various species of protozoa responsible for gastrointestinal infections.
Are protists important for scientific research?
Absolutely. Protists have been instrumental in numerous areas of research, including evolutionary biology, cell biology, and biotechnology. Their unique features and biological processes provide valuable insights for various scientific disciplines.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


