ATP production is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in sustaining life. ATP, short for adenosine triphosphate, is often referred to as the “energy currency” of cells. It is responsible for providing the energy needed for all cellular processes, from muscle contraction to DNA replication.
In this article, we will delve into the world of ATP production and explore 18 extraordinary facts that highlight the complexity and importance of this biological process. From the intricate mechanisms involved in ATP synthesis to the diverse strategies employed by different organisms, ATP production is a subject that captivates scientists and holds the key to understanding the functioning of living systems.
So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and uncover some fascinating insights into ATP production!
Key Takeaways:
- ATP is like the cell’s energy money, made in the mitochondria. It’s super important for muscle movement, cell signaling, and keeping our brains sharp. Without it, our cells would be tired and sluggish!
- ATP production is like a busy factory in our cells, working hard to make energy. It’s affected by things like temperature and pH, and disruptions can lead to diseases. So, it’s crucial to keep our cellular factories running smoothly!
ATP is the primary source of cellular energy
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is often referred to as the “molecular currency” of the cell. It is produced during cellular respiration and serves as a vital energy source for various cellular processes.
ATP production occurs in specialized cell structures called mitochondria
The mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell. They house the enzymes and molecules necessary for ATP production through processes such as glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
The process of ATP production involves breaking down glucose
During cellular respiration, glucose molecules are broken down in a series of enzymatic reactions to release energy. This energy is then used to generate ATP molecules.
ATP production is an aerobic process
ATP production primarily occurs in the presence of oxygen, making it an aerobic process. Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, which is crucial for ATP synthesis.
ATP production can also occur in the absence of oxygen
In certain circumstances, such as during intense exercise or in the absence of oxygen, cells can generate ATP through anaerobic processes like fermentation. However, this method is less efficient and produces less ATP compared to aerobic respiration.
ATP production involves the electron transport chain
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It transfers electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
ATP production produces a net of 36 ATP molecules
Through the complete oxidation of one glucose molecule via aerobic respiration, cells can produce a net gain of approximately 36 ATP molecules. This process maximizes energy extraction from glucose.
ATP production is regulated by feedback mechanisms
Cells maintain a delicate balance in ATP production to meet their energy demands. Feedback mechanisms, such as the regulation of enzyme activity and ATP concentration, ensure that ATP production is tightly controlled.
ATP production can be influenced by various factors
Factors such as temperature, pH, and the availability of coenzymes and substrates can impact ATP production. Any disruptions in these factors can affect the efficiency of ATP synthesis.
ATP production is essential for muscle contraction
During muscle contraction, ATP provides the energy necessary for the sliding of actin and myosin filaments. Without ATP, muscles would not be able to contract and perform their functions.
ATP production is crucial for active transport processes
Active transport mechanisms, such as the sodium-potassium pump, rely on ATP to move ions against their concentration gradients. This allows cells to maintain proper ion balances and perform vital functions.
ATP production plays a role in cell signaling
ATP is involved in cell signaling pathways as a signaling molecule. It can be released from cells and activate purinergic receptors, leading to various physiological responses.
ATP production is affected in certain diseases
Disruptions in ATP production can contribute to the development of various diseases, such as mitochondrial disorders and metabolic diseases. These conditions often lead to impaired energy production and cellular dysfunction.
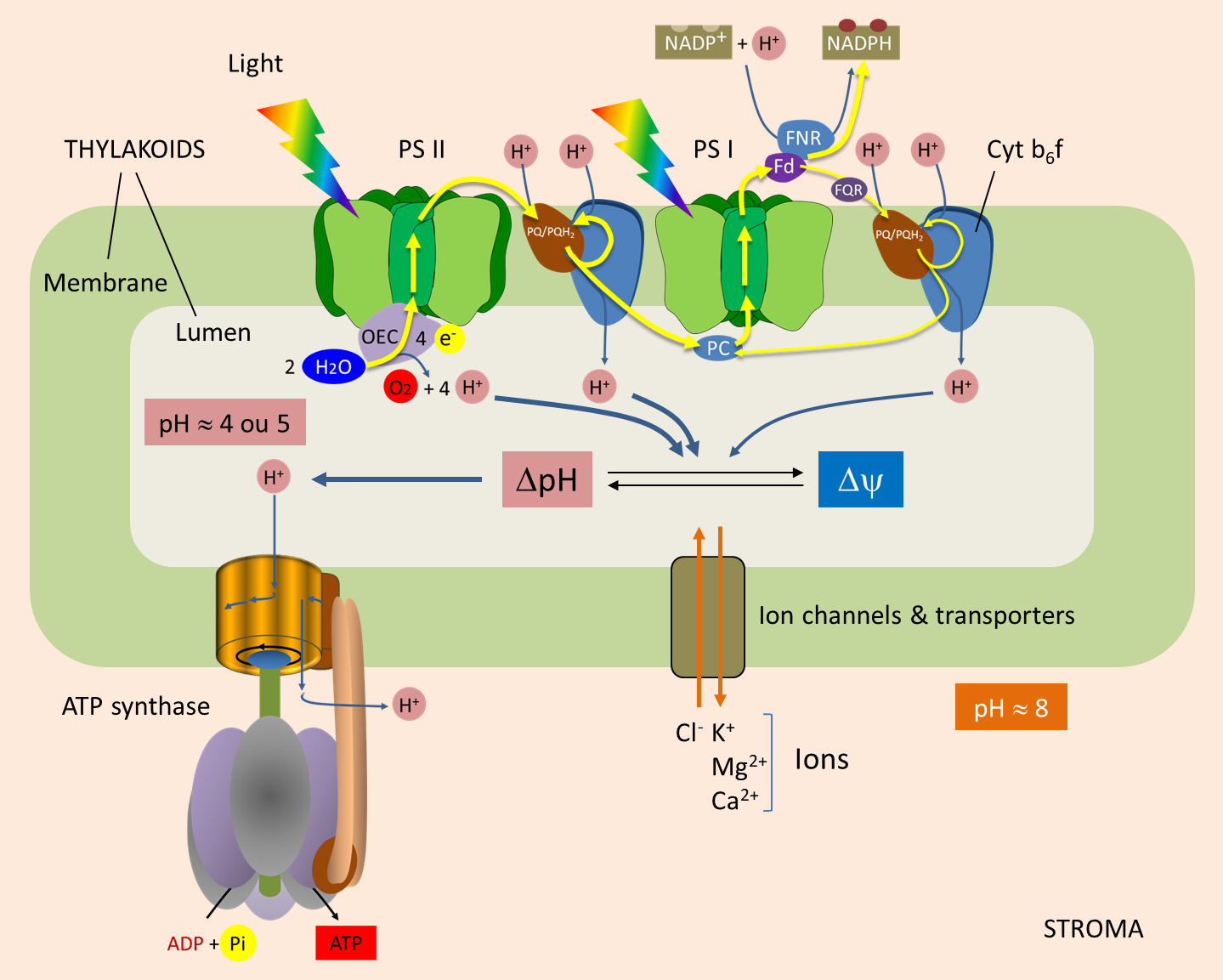
Photosynthesis is another major ATP production process
In plants and some microorganisms, ATP production occurs during photosynthesis. Light energy is converted into chemical energy, ultimately generating ATP along with glucose synthesis.
ATP production is an evolutionarily conserved process
The mechanisms of ATP production, such as oxidative phosphorylation and the electron transport chain, have been conserved throughout evolution. This highlights the fundamental importance of ATP as an energy source.
ATP production can be affected by drugs and toxins
Certain drugs and toxins can interfere with ATP production by targeting enzymes or disrupting mitochondrial function. These substances can have significant impacts on cellular metabolism and overall energy production.
ATP production is essential for brain function
The brain is one of the most energy-demanding organs in the body. ATP production is vital for proper brain function, influencing cognitive processes, neurotransmission, and overall neurological health.
ATP production is a dynamic process
ATP production is continuously occurring in cells to meet their energy needs. It responds to metabolic demands, adjusting production rates based on energy requirements and cellular conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ATP production is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the energy metabolism of all living organisms. These 18 extraordinary facts shed light on the intricacies and significance of ATP production. From the diversity of ATP synthesis methods in different organisms to the vital role of mitochondria in generating ATP, these facts highlight the complexity and efficiency of this fundamental biological process.
Understanding ATP production is not only important in biological research but also in various fields such as medicine, agriculture, and bioengineering. By unraveling the mechanisms behind ATP synthesis, scientists can develop innovative therapies, improve crop yield, and enhance renewable energy production.
Overall, ATP production is a remarkable process that underscores the remarkable adaptability and efficiency of life on Earth. Its discovery and ongoing study continue to shape our understanding of biology and have important implications for human health and the environment.
FAQs
1. What is ATP production?
ATP production is the process by which cells generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary molecule for storing and transferring energy within cells.
2. How is ATP produced in the body?
In the body, ATP is produced through cellular respiration, where glucose and oxygen are converted into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. This process primarily occurs in the mitochondria of cells.
3. Are there different methods of ATP production?
Yes, different organisms have different methods of ATP production. While most organisms use cellular respiration, some bacteria and archaea produce ATP through processes like fermentation and anaerobic respiration.
4. What role do mitochondria play in ATP production?
Mitochondria are often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell because they are responsible for the majority of ATP production through cellular respiration.
5. What happens if ATP production is disrupted?
If ATP production is disrupted, cells will lack the necessary energy to carry out essential functions, leading to various health issues and potentially life-threatening conditions.
ATP production is a complex process that keeps our cells functioning optimally. Understanding how this energy currency is generated can help us appreciate the intricacies of cellular metabolism. If you're curious to learn more about the fascinating world of energy production, our article on energy metabolism delves into eight intriguing facts that will leave you amazed.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
