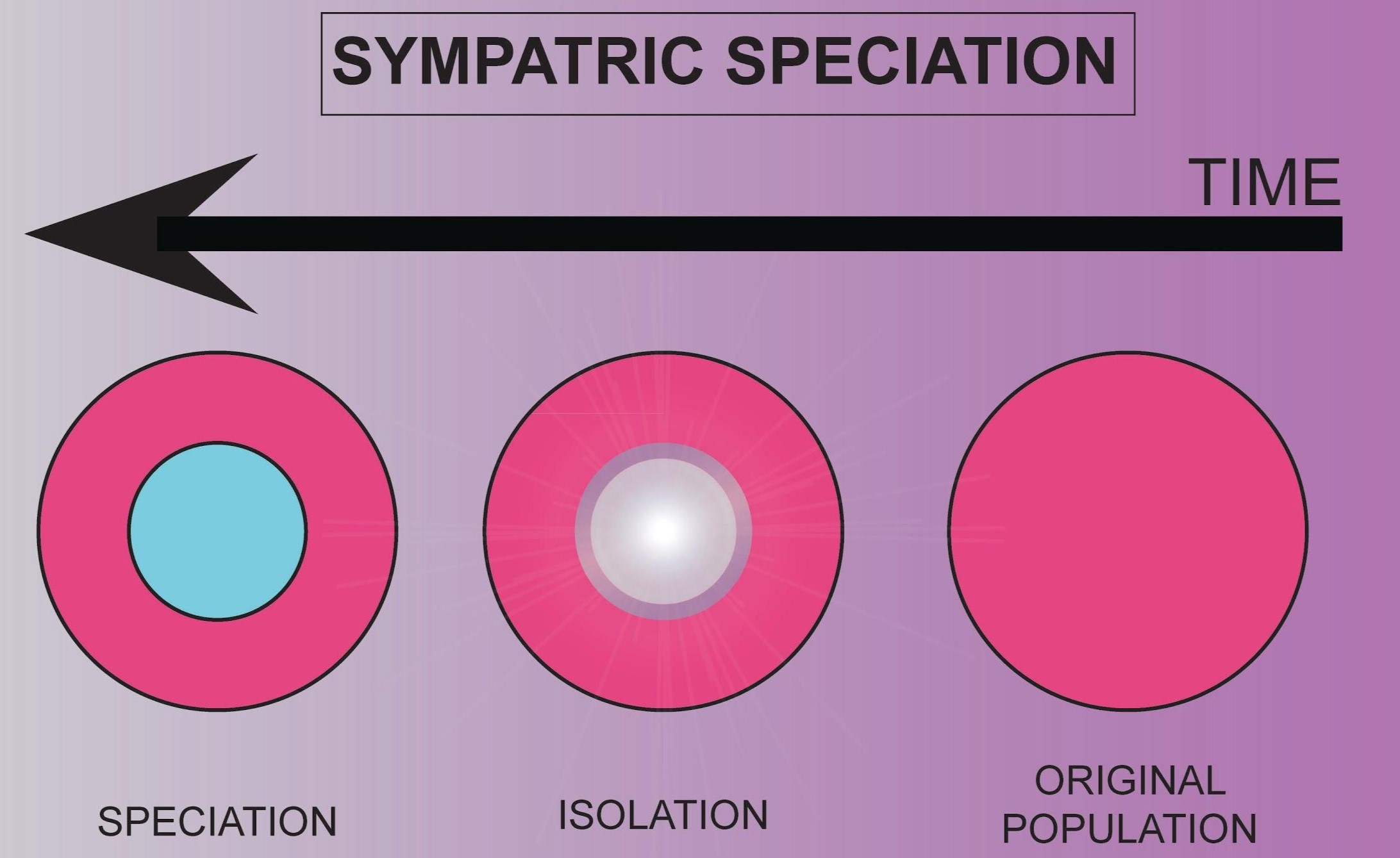
Sympatric speciation is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs when two or more species evolve from a common ancestor within the same geographical area, without any physical barriers separating them. This process challenges the traditional understanding of speciation, which often involves geographic isolation as a crucial factor. Instead, sympatric speciation relies on intriguing mechanisms such as ecological differentiation, disruptive selection, and sexual selection to drive the formation of distinct species. In this article, we will explore 20 enigmatic facts about sympatric speciation, shedding light on the complex dynamics that shape the evolution of biodiversity. From the origin of new species in the absence of physical barriers to the role of natural and sexual selection, prepare to delve into the captivating world of sympatric speciation and unravel some of its mysteries.
Key Takeaways:
- Sympatric speciation challenges the idea that species can only evolve in separate areas. It shows that new species can emerge in the same place, leading to a more dynamic and diverse natural world.
- Sympatric speciation can happen quickly and involves factors like environment, behavior, and genetics. It leads to the creation of new species with unique traits, challenging our understanding of how life evolves.
Sympatric speciation is a process that leads to the formation of new species within the same geographic area.
Sympatric speciation occurs when a single population fragments into two or more distinct populations without any physical barriers separating them.
It challenges the traditional notion that geographic isolation is necessary for speciation.
In sympatric speciation, speciation occurs despite the absence of physical barriers that would typically restrict gene flow between populations.
It can be driven by a variety of factors, including ecological, behavioral, and genetic factors.
This form of speciation can be triggered by changes in the environment, such as the availability of different food sources or the emergence of new mating behaviors.
Polyploidy, the presence of more than two sets of chromosomes, is a common mechanism of sympatric speciation.
Polyploidy can lead to reproductive isolation between individuals with different chromosome numbers, preventing them from successfully interbreeding.
Sympatric speciation is more likely to occur in plants than in animals.
Plants have a higher propensity for sympatric speciation due to their ability to self-fertilize or cross-pollinate with closely related species.
It can result in the formation of new species with distinct genetic and phenotypic characteristics.
Over time, populations undergoing sympatric speciation accumulate genetic variations that can lead to the development of unique traits and adaptations.
Sympatric speciation can happen rapidly, within a few generations.
In certain cases, environmental pressures and genetic mutations can drive rapid changes in a population, leading to the emergence of new species in a relatively short period.
The occurrence of sympatric speciation challenges the concept of a “species” as a fixed, immutable entity.
As new species arise within the same geographic area, the definition and boundaries of a species become more fluid and dynamic.
Sympatric speciation can result in the formation of hybrid zones.
Hybrid zones are regions where individuals from different species come into contact and occasionally interbreed, resulting in hybrid offspring.
In some cases, sympatric speciation can lead to the evolution of reproductive barriers.
Reproductive barriers, such as changes in mating behaviors or the timing of reproductive cycles, can reinforce speciation by preventing genetic mixing between populations.
The genetic changes that drive sympatric speciation can be influenced by natural selection.
Positive selection for specific traits can promote the divergence of populations within the same geographic area.
Hybridization between diverging populations can also contribute to sympatric speciation.
Hybridization can introduce novel combinations of genes and genetic variation, fueling the emergence of new species.
Sympatric speciation can lead to the adaptive radiation of a group of species.
As new species emerge, they can exploit different ecological niches and diversify, adapting to specific environmental conditions.
It can occur in both terrestrial and aquatic habitats.
Sympatric speciation is not limited to a particular type of habitat and can occur in various environments, including forests, grasslands, rivers, and lakes.
Sympatric speciation is still a topic of active research and debate among biologists.
The mechanisms and factors that drive sympatric speciation are complex and continue to be the focus of scientific investigations.
It has been observed in several organisms, including insects, fish, and plants.
Examples of sympatric speciation can be found in groups such as cichlid fish in African lakes and the apple maggot fly.
The study of sympatric speciation provides insights into the processes of evolutionary diversification.
Understanding the mechanisms behind sympatric speciation can shed light on how biodiversity arises and how new species emerge.
Sympatric speciation can occur through disruptive selection.
Disruptive selection favors extreme phenotypes, leading to the divergence of populations and eventually the formation of new species.
It can involve changes in mate preference and sexual selection.
Differences in mate preference can drive reproductive isolation and contribute to the formation of new species within a shared habitat.
The occurrence of sympatric speciation challenges our understanding of the boundaries between species.
As new species emerge within the same geographic area, it raises questions about how we define and classify species in a dynamic and ever-evolving natural world.
Overall, the phenomenon of sympatric speciation is a fascinating and enigmatic process that challenges long-standing assumptions about speciation. Through various genetic, ecological, and behavioral mechanisms, new species can arise within the same geographic area, leading to increased biodiversity and evolutionary diversification. The study of sympatric speciation provides valuable insights into the complex processes driving the emergence of new species and the ever-changing nature of life on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sympatric speciation is a fascinating process that occurs when new species evolve from a single ancestral species in the same geographic area. It involves the development of reproductive barriers that prevent gene flow between populations, leading to the formation of distinct species.
Throughout this article, we have explored 20 enigmatic facts about sympatric speciation. We have discussed how it can occur through disruptive selection, polyploidy, and sexual selection. We have also explored the role of genetic mutations and hybridization in driving speciation.
Understanding the mechanisms behind sympatric speciation is crucial for advancing our knowledge of biodiversity and evolutionary processes. By studying these enigmatic facts, scientists can gain valuable insights into the complex mechanisms that drive the formation of new species.
In conclusion, sympatric speciation is a dynamic and intricate process that continues to captivate scientists and inspire further research in the field of evolutionary biology.
FAQs
1. What is sympatric speciation?
Sympatric speciation refers to the formation of new species from a single ancestral species in the same geographic area, without the physical separation of populations.
2. What are the mechanisms of sympatric speciation?
Sympatric speciation can occur through processes like disruptive selection, polyploidy, sexual selection, genetic mutations, and hybridization.
3. How does disruptive selection lead to sympatric speciation?
Disruptive selection occurs when extreme phenotypes have a selective advantage over intermediate phenotypes within a population. This can lead to the evolution of distinct populations with different traits, eventually resulting in the formation of new species.
4. What is polyploidy and its role in sympatric speciation?
Polyploidy refers to the duplication of an entire set of chromosomes. It can lead to the formation of new species by instantly isolating the polyploid individual from the diploid population, preventing gene flow and allowing for the evolution of reproductive barriers.
5. How does sexual selection contribute to sympatric speciation?
Sexual selection occurs when individuals with certain traits have a higher likelihood of mating success. This can drive the evolution of distinct mating behaviors or physical characteristics, leading to reproductive isolation and the formation of new species.
6. Can sympatric speciation occur without genetic mutations?
Genetic mutations play a crucial role in sympatric speciation by introducing new genetic variation within populations. While speciation can occur without mutations, they significantly enhance the rate and likelihood of species formation.
7. How does hybridization contribute to sympatric speciation?
Hybridization occurs when individuals from different populations or species mate and produce offspring. Sometimes, hybridization can result in the formation of new, reproductively isolated species.
8. Is sympatric speciation a common phenomenon?
Sympatric speciation is considered relatively rare compared to allopatric speciation, where populations are geographically separated. However, recent research has provided evidence of sympatric speciation occurring in various organisms, suggesting that it may be more common than previously believed.
Sympatric speciation's enigmatic nature sparks curiosity about evolution's intricate mechanisms. Unraveling genetic drift's mysteries, discovering natural selection's astounding power, and exploring evolutionary biology's fascinating facts deepens understanding. Investigating these interconnected concepts illuminates life's incredible diversity, adaptations, and the complex processes shaping our world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.