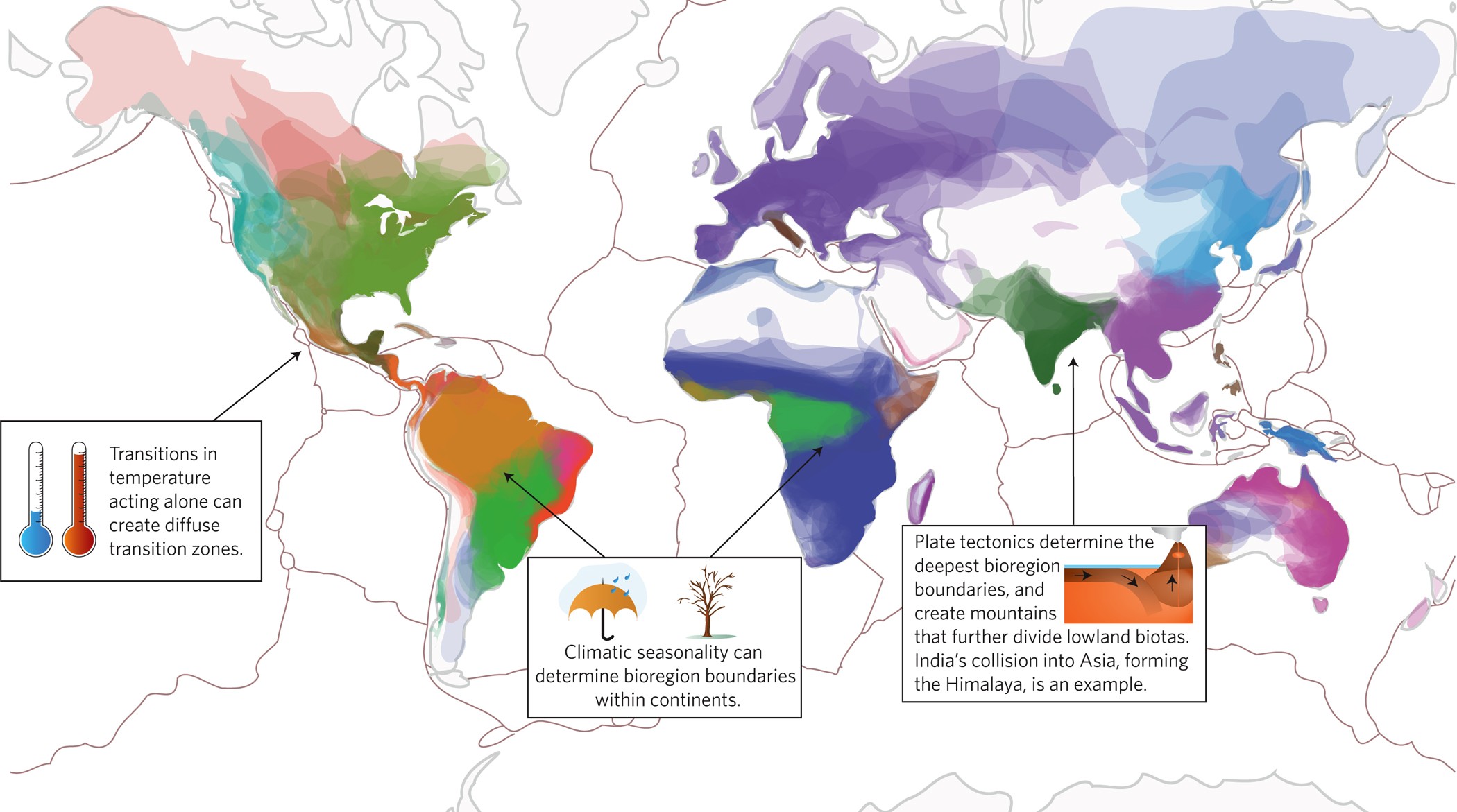
The concept of bioregion refers to a geographical area defined by its unique combination of ecological, environmental, and cultural characteristics. These regions are not limited by political boundaries but rather defined by natural features such as watersheds, climate patterns, and biodiversity. Exploring the wonders of bioregions can be truly awe-inspiring, as they are often home to an incredible array of flora and fauna, and are rich in natural resources.
In this article, we will delve into 10 astonishing facts about bioregions that will provide you with a glimpse of the remarkable diversity and interconnectedness of our planet’s ecosystems. From the breathtaking landscapes to the fascinating adaptations of species, bioregions offer a unique perspective on the intricate web of life on Earth. So, let us embark on this journey of discovery and marvel at the wonders that exist within these remarkable geographical areas!
Key Takeaways:
- Bioregions are special areas that connect nature and culture, promoting sustainable living and community involvement. They’re not limited by borders and encourage people to protect and cherish their environment.
- Indigenous knowledge and community engagement are crucial in bioregionalism, fostering a deep connection to the environment and promoting biodiversity conservation. It’s all about working together for a sustainable and harmonious relationship with nature.
The concept of bioregion focuses on the interconnectedness of ecology and culture.
Bioregion refers to a geographic area defined by its distinct ecological characteristics, such as climate, topography, and biodiversity. However, it goes beyond purely ecological aspects and includes the cultural and social systems that are shaped by and interact with the environment.
Bioregions promote sustainable living and environmental stewardship.
By recognizing the unique ecological features and cultural heritage of a specific region, bioregionalism encourages communities to adopt sustainable practices that respect and preserve the natural resources and ecosystems within their bioregion. This includes sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and conservation initiatives.
Bioregions are not bound by political boundaries.
Unlike traditional administrative divisions, bioregions transcend political boundaries and are defined by the natural characteristics of the area. This holistic understanding of a region allows for a more comprehensive and interconnected approach to environmental management and conservation.
Indigenous knowledge plays a crucial role in bioregionalism.
Indigenous communities have long understood and lived in harmony with their bioregional environments. Their traditional knowledge and practices provide invaluable insights into sustainable land and resource management, biodiversity conservation, and regenerative practices.
Bioregions foster a sense of place and belonging.
By recognizing and honoring the unique ecological and cultural characteristics of a bioregion, individuals and communities develop a deeper connection to their surroundings. This sense of place fosters a greater appreciation for the environment and a desire to protect and restore its ecological integrity.
Bioregional planning promotes self-sufficiency and resilience.
Through bioregional planning, communities are encouraged to prioritize local resources and develop self-sufficient systems to meet their needs. This includes promoting local agriculture, renewable energy generation, and decentralization of economic activities, reducing dependence on external sources.
Bioregionalism emphasizes the importance of biodiversity conservation.
As bioregions are defined by their distinct ecological characteristics, protecting and conserving biodiversity is a primary concern. Preserving diverse ecosystems within a bioregion is crucial for maintaining ecological balance, ensuring the survival of species, and supporting overall ecosystem health.
Bioregions drive community engagement and participation.
The bioregional approach recognizes the importance of community involvement in decision-making processes related to land use, resource management, and environmental policies. This promotes a sense of ownership and empowerment within communities, leading to more sustainable and locally supported initiatives.
Bioregionalism encourages interdisciplinary collaboration.
Given the complex nature of bioregions, addressing environmental and social challenges requires collaboration across different disciplines. Bioregionalism fosters partnerships between scientists, policymakers, community leaders, and indigenous knowledge holders to develop holistic solutions for sustainable development and environmental conservation.
Bioregions are dynamic and ever-evolving.
Bioregions are not static entities but are subject to natural and human-induced changes. Recognizing the dynamic nature of bioregions allows for adaptive management strategies that respond to emerging ecological, social, and economic realities, ensuring long-term sustainability.
Overall, the concept of bioregion highlights the interconnectedness between ecology, culture, and sustainability. By understanding and embracing the unique characteristics of a bioregion, communities can work towards a more harmonious and sustainable relationship with their natural surroundings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bioregions are fascinating and complex ecosystems that deserve our attention and protection. They provide a unique perspective on the interconnectedness of nature and the importance of preserving biodiversity. From the incredible range of species they support to the essential role they play in regulating our climate, bioregions are truly astonishing.By understanding and appreciating the intricacies of bioregions, we can make informed decisions about how to best preserve and conserve these vital habitats. Whether it’s through sustainable farming practices, responsible tourism, or conservation efforts, we all have a part to play in protecting and enhancing the health of our bioregions.So, let’s celebrate the wonders of bioregions and work together to ensure that future generations can continue to be amazed by the incredible biodiversity and natural beauty they offer.
FAQs
1. What is a bioregion?
A bioregion is a distinct geographical area defined by its unique combination of climate, topography, flora, and fauna. It encompasses a range of ecosystems that are interconnected and influence each other’s dynamics.
2. How are bioregions different from ecosystems?
While ecosystems refer to specific habitats or communities of organisms, bioregions encompass larger geographical areas and encompass multiple ecosystems. Bioregions consider the broader environmental factors that shape the characteristics of ecosystems within them.
3. What are some examples of bioregions?
Examples of bioregions include the Amazon Rainforest in South America, the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, the Serengeti in Tanzania, and the Arctic Tundra. These regions have distinct ecological features and support unique biodiversity.
4. How do bioregions benefit us?
Bioregions provide numerous benefits, including clean air and water, climate regulation, food production, and cultural significance. They also offer opportunities for recreation, education, and scientific research.
5. What are the threats to bioregions?
Some of the major threats to bioregions include deforestation, habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and invasive species. These factors can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems and lead to the loss of biodiversity.
6. How can we preserve and protect bioregions?
We can protect bioregions by promoting sustainable practices, supporting conservation efforts, and advocating for responsible land use policies. It’s crucial to raise awareness about the importance of bioregions and take action to mitigate the threats they face.
7. Can individuals make a difference in bioregion conservation?
Absolutely! Individuals can make a significant impact by adopting eco-friendly behaviors, supporting local conservation organizations, volunteering, and spreading awareness about the importance of bioregions. Every small action counts!
8. How can tourism and bioregion conservation coexist?
Tourism can play a positive role in bioregion conservation when managed responsibly. By implementing sustainable tourism practices, minimizing negative environmental impacts, and supporting local communities, tourism can contribute to the economic viability and protection of bioregions.
9. Are there any regulations in place to protect bioregions?
Many countries have established protected areas, such as national parks and nature reserves, to safeguard bioregions. Additionally, international agreements and conventions aim to promote the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity in bioregions worldwide.
10. Why should we care about bioregions?
We should care about bioregions because they are essential for the health and well-being of our planet and future generations. They provide critical ecosystem services, support biodiversity, and offer immense beauty and inspiration. Preserving bioregions is crucial for the sustainable future of our planet.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
