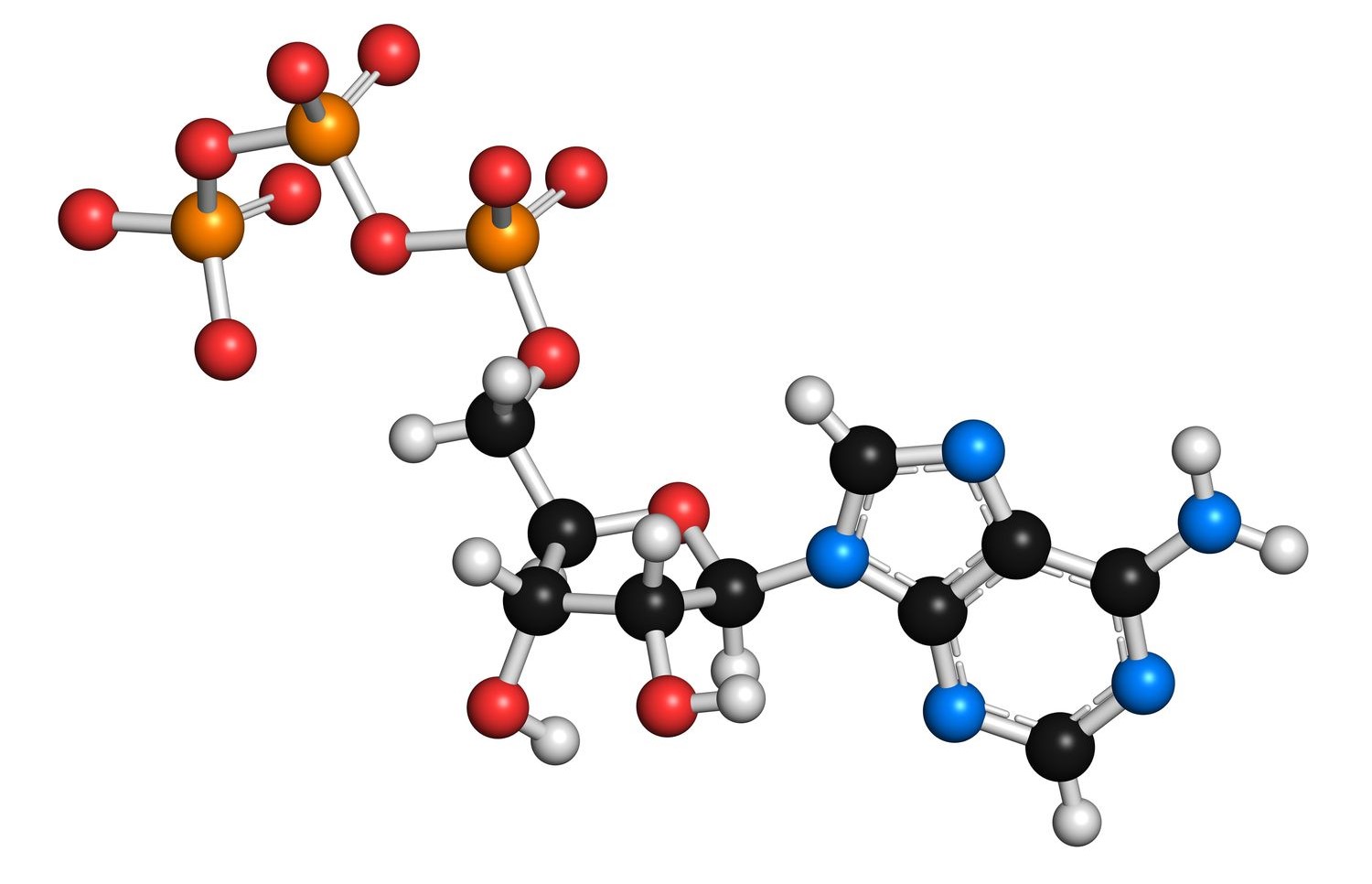
Energy metabolism is a fascinating and vital process that occurs within the cells of all living organisms. It is responsible for converting the food we consume into the energy our bodies need to function properly. This complex process involves various biochemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouses of the cells.
In this article, we will uncover eight intriguing facts about energy metabolism that will shed light on its importance and the incredible mechanisms at play. From the role of enzymes in breaking down molecules to the efficiency of ATP production, these facts will give you a deeper understanding of this fundamental biological process.
So, buckle up and get ready to delve into the intricacies of energy metabolism as we explore these fascinating facts that will leave you amazed by the wonders happening inside our cells.
Key Takeaways:
- Energy metabolism is like a cell’s power plant, producing ATP to fuel all its activities. Without ATP, cells wouldn’t be able to function properly, so it’s super important!
- Genetics can affect how efficiently our bodies produce and use energy. This can impact weight, metabolism, and even our risk for certain health conditions. It’s like our body’s unique energy blueprint!
The Key Role of ATP
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is often referred to as the “energy currency” of the cell. It is the molecule responsible for storing and transferring energy within living organisms. ATP is crucial for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and biochemical reactions. Without ATP, cells would not be able to function properly.
The Powerhouse of the Cell: Mitochondria
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for producing the majority of ATP through cellular respiration. These small, double-membraned organelles convert nutrients into ATP, providing the energy needed for cellular activities. Interestingly, mitochondria have their own DNA and are thought to have once been independent organisms that entered into a symbiotic relationship with cells.
The Metabolic Pathways
Energy metabolism encompasses a series of interconnected chemical reactions called metabolic pathways. These pathways involve the breakdown of complex molecules, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, to release energy. The energy is then stored in ATP molecules for later use. Examples of metabolic pathways include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
The Role of Enzymes in Energy Metabolism
Enzymes play a vital role in energy metabolism by facilitating chemical reactions. They act as catalysts, speeding up the rate of metabolic reactions without being consumed in the process. Enzymes are highly specific, meaning they can recognize and bind to specific molecules. Without enzymes, the metabolic pathways involved in energy metabolism would not be able to proceed efficiently.
The Impact of Exercise on Energy Metabolism
Engaging in physical exercise can have a significant impact on energy metabolism. During exercise, the body’s demand for energy increases, leading to an increased rate of ATP production. The body utilizes different energy sources depending on the intensity and duration of the exercise, including carbohydrates, fats, and even stored glycogen. Regular exercise can also enhance the efficiency of energy metabolism in the body.
The Link Between Energy Metabolism and Weight Gain
Energy metabolism plays a crucial role in weight regulation. When the body consumes more calories than it needs, the excess energy is stored as fat. On the other hand, if the body does not receive enough calories, it will break down stored fat to obtain the energy it requires. Balancing energy intake and expenditure is essential for maintaining a healthy weight.
The Influence of Genetics on Energy Metabolism
Genetics can impact individual variations in energy metabolism. Certain genetic variations can affect the efficiency of metabolic pathways, leading to differences in how efficiently energy is produced and utilized in the body. These genetic factors may contribute to variations in weight gain or susceptibility to metabolic disorders such as diabetes.
The Role of Energy Metabolism in Ageing
Energy metabolism has been linked to the ageing process. As we age, the efficiency of energy metabolism can decrease, resulting in a decline in ATP production. This decline may contribute to age-related diseases, reduced physical performance, and overall ageing. Understanding the mechanisms behind age-related changes in energy metabolism is an active area of research.
Conclusion
In conclusion, energy metabolism is a fascinating and crucial process in biology. It is responsible for converting the fuel we consume into energy that our cells can utilize. Through various biochemical reactions, energy is generated and harnessed, enabling our bodies to function and carry out essential processes like growth, repair, and reproduction.Understanding the intricacies of energy metabolism is essential not only for scientists and researchers but also for individuals seeking to optimize their health and well-being. By learning about the factors that influence energy production and expenditure, we can make informed choices about our diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits.From the role of mitochondria as the powerhouses of the cell to the complex interplay between different metabolic pathways, energy metabolism is a captivating field that continues to be studied and unraveled. As our understanding of this process expands, so does the potential for innovative treatments and interventions targeting metabolic disorders and diseases.So, next time you feel a surge of energy or wonder why you’re feeling fatigued after a long day, remember that it all comes down to the captivating world of energy metabolism.
FAQs
1. What is energy metabolism?
Energy metabolism is the process through which our bodies convert the food we consume into energy that can be utilized by our cells. It involves a series of biochemical reactions that occur in various organs and tissues, ultimately generating the energy needed for essential bodily functions.
2. What factors influence energy metabolism?
Several factors affect energy metabolism, including age, body composition, physical activity level, and hormonal balance. Genetic factors and certain medical conditions can also play a role in individual variations in energy metabolism.
3. How can I optimize my energy metabolism?
To enhance energy metabolism, it is important to maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and ensure adequate rest and sleep. Choosing nutrient-rich foods, managing stress levels, and staying hydrated are also beneficial for optimizing energy metabolism.
4. Can energy metabolism be affected by medical conditions?
Yes, certain medical conditions such as metabolic disorders, thyroid dysfunction, and diabetes can impact energy metabolism. In these cases, seeking medical advice and treatment is crucial for managing and improving energy metabolism.
5. Are there any supplements or foods that can boost energy metabolism?
While some supplements claim to enhance energy metabolism, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements. Certain foods, such as those rich in antioxidants and B vitamins, may support energy metabolism, but a balanced diet overall is key for optimal energy production.
Energy metabolism is a captivating subject, but it's just the tip of the iceberg. Delve deeper into cellular processes by exploring the roles of GTP guanosine triphosphate, a crucial molecule for protein synthesis and cell signaling. Unravel the secrets of NAD nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a coenzyme essential for energy production, DNA repair, and cell death regulation. Finally, uncover the fascinating mechanism of chemiosmotic coupling, which harnesses the power of proton gradients to generate ATP, the cell's energy currency. Embark on a journey through these intriguing topics and expand your knowledge of cellular biology.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
