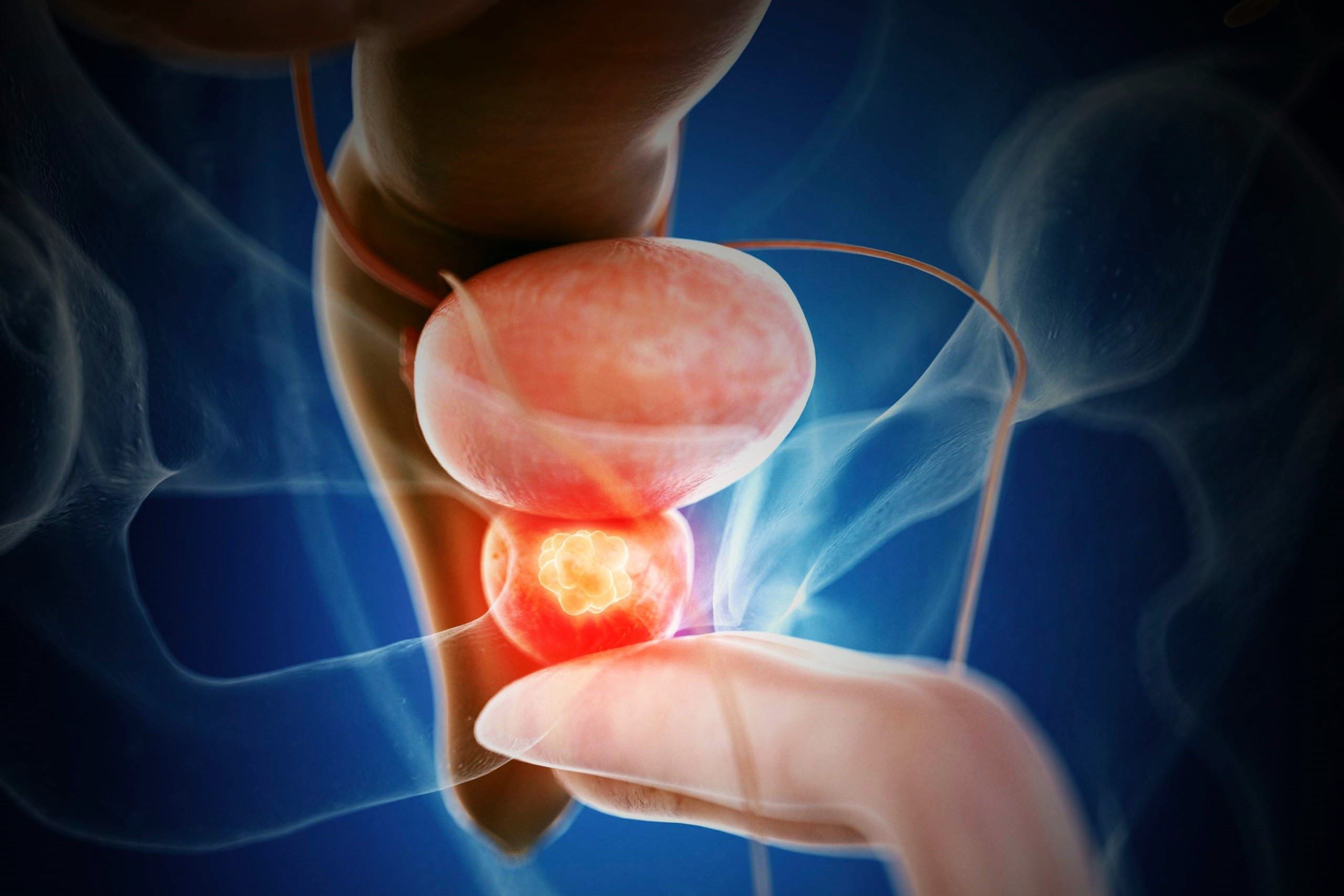
Did you know that prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men? Understanding this disease is crucial for early detection and treatment. Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped organ that produces seminal fluid. Most cases grow slowly, but some can be aggressive. Risk factors include age, family history, and ethnicity, with African American men at higher risk. Symptoms might not appear until the cancer is advanced, making regular screenings vital. Treatment options vary from active surveillance to surgery and radiation. Knowing these facts can help in making informed decisions about health. Stay informed and proactive about prostate health.
Key Takeaways:
- Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men, so regular screenings are crucial for early detection and treatment. Age, family history, and ethnicity are important risk factors to consider.
- Symptoms of prostate cancer may not appear until the disease is advanced, making regular screenings even more important. Lifestyle choices, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can also influence the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a significant health concern for men worldwide. It affects the prostate gland, a small organ that produces seminal fluid. Knowing more about this disease can help in early detection and treatment.
-
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men. Only skin cancer is more prevalent. This highlights the importance of regular screenings.
-
The prostate is about the size of a walnut. Despite its small size, the prostate plays a crucial role in male reproductive health.
-
Age is a major risk factor. Men over 50 are more likely to develop prostate cancer, with risk increasing as they age.
-
Family history matters. Having a father or brother with prostate cancer more than doubles a man's risk of developing it.
-
African American men are at higher risk. They are more likely to develop prostate cancer and have a higher mortality rate from the disease.
Symptoms and Detection
Recognizing the signs of prostate cancer early can lead to better outcomes. However, symptoms often don't appear until the cancer is advanced.
-
Early-stage prostate cancer may not cause symptoms. This makes regular screenings vital for early detection.
-
Common symptoms include difficulty urinating. This can manifest as a weak stream or frequent urination, especially at night.
-
Blood in urine or semen can be a warning sign. Although not always indicative of cancer, it should prompt a medical evaluation.
-
Pain in the hips, back, or chest may occur. This can happen if cancer has spread to the bones.
-
PSA tests help in detection. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test measures the level of PSA in the blood, which can be elevated in men with prostate cancer.
Treatment Options
Various treatments are available, depending on the stage and severity of the cancer. Each has its benefits and potential side effects.
-
Active surveillance is an option for some. This involves closely monitoring the cancer without immediate treatment, suitable for slow-growing cancers.
-
Surgery can remove the prostate. A prostatectomy is often recommended for localized cancer.
-
Radiation therapy targets cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
-
Hormone therapy reduces testosterone levels. Since prostate cancer cells rely on testosterone to grow, this can slow the cancer's progression.
-
Chemotherapy is used for advanced cancer. It involves using drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
Lifestyle and Prevention
While some risk factors like age and genetics can't be changed, lifestyle choices can influence prostate cancer risk.
-
A healthy diet may lower risk. Consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is beneficial.
-
Regular exercise is important. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, which can reduce cancer risk.
-
Limiting red meat and dairy intake might help. Some studies suggest these foods could increase prostate cancer risk.
-
Smoking cessation is crucial. Smoking is linked to a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
-
Regular screenings are key. Men should discuss with their doctors when to start screenings based on their risk factors.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to improve our understanding and treatment of prostate cancer.
-
Genetic testing can identify risk. Tests can reveal inherited mutations that increase prostate cancer risk.
-
New drugs are being developed. These aim to target cancer cells more precisely, minimizing side effects.
-
Immunotherapy is a promising field. It involves using the body's immune system to fight cancer.
-
Liquid biopsies are emerging. These tests detect cancer cells or DNA in the blood, offering a less invasive diagnostic option.
-
Prostate cancer vaccines are in development. These aim to prevent cancer or stop its progression by boosting the immune response.
Support and Resources
Dealing with prostate cancer can be challenging, but support is available for patients and their families.
-
Support groups provide community. They offer a space to share experiences and advice.
-
Counseling can help with emotional challenges. Professional support can assist in coping with the diagnosis and treatment.
-
Educational resources are widely available. Many organizations provide information on prostate cancer and treatment options.
-
Financial assistance programs exist. These can help cover the costs of treatment and related expenses.
-
Family involvement is beneficial. Having a strong support system can improve outcomes and quality of life.
Global Impact
Prostate cancer affects men worldwide, with varying incidence and mortality rates across different regions.
-
Prostate cancer rates vary globally. Western countries generally report higher rates, possibly due to better screening practices.
-
Access to healthcare influences outcomes. In regions with limited healthcare access, prostate cancer is often diagnosed at a later stage.
-
Cultural factors affect awareness. In some cultures, discussing prostate health is taboo, leading to lower screening rates.
-
International collaborations are crucial. Global partnerships help advance research and improve treatment options.
-
Awareness campaigns are increasing. Efforts to educate men about prostate cancer are growing worldwide.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding prostate cancer that can lead to confusion and fear.
-
Prostate cancer is not always fatal. Many men live long, healthy lives after treatment.
-
Only older men get prostate cancer. While age is a factor, younger men can also be diagnosed.
-
Prostate cancer always causes symptoms. Many cases are asymptomatic, especially in the early stages.
-
A high PSA level always means cancer. Elevated PSA can result from other conditions, such as an enlarged prostate or infection.
-
Surgery always leads to impotence. While there is a risk, many men regain sexual function after recovery.
Future Directions
The future of prostate cancer treatment and prevention looks promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements.
-
Personalized medicine is on the rise. Tailoring treatment to individual genetic profiles can improve outcomes.
-
Artificial intelligence aids in diagnosis. AI technology helps analyze medical images and predict cancer progression.
-
Nanotechnology offers new treatment methods. Tiny particles can deliver drugs directly to cancer cells, reducing side effects.
-
Telemedicine expands access to care. Virtual consultations make it easier for patients to receive expert advice.
-
Public health initiatives focus on prevention. Efforts to promote healthy lifestyles aim to reduce prostate cancer incidence.
Living with Prostate Cancer
Managing life with prostate cancer involves addressing both physical and emotional challenges.
-
Maintaining a positive outlook is important. A hopeful attitude can improve quality of life and treatment outcomes.
-
Diet and exercise support recovery. Staying active and eating well can help manage side effects and boost energy levels.
-
Open communication with healthcare providers is key. Discussing concerns and treatment options ensures the best care.
-
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques can reduce stress. Practices like meditation and yoga promote mental well-being.
-
Planning for the future provides peace of mind. Setting goals and making plans can help patients focus on living life to the fullest.
Final Thoughts on Prostate Cancer Facts
Understanding prostate cancer is crucial for awareness and prevention. These 50 facts highlight the importance of early detection and the role of screening in saving lives. Prostate cancer affects millions globally, yet many remain unaware of its symptoms and risk factors. Regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers can make a significant difference. Lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, also play a part in reducing risk. Knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Sharing this information can help others stay informed and proactive. Remember, early detection is key, and being informed is the first step toward prevention. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and encourage others to do the same. By spreading awareness, we can work together to reduce the impact of prostate cancer on individuals and families worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
