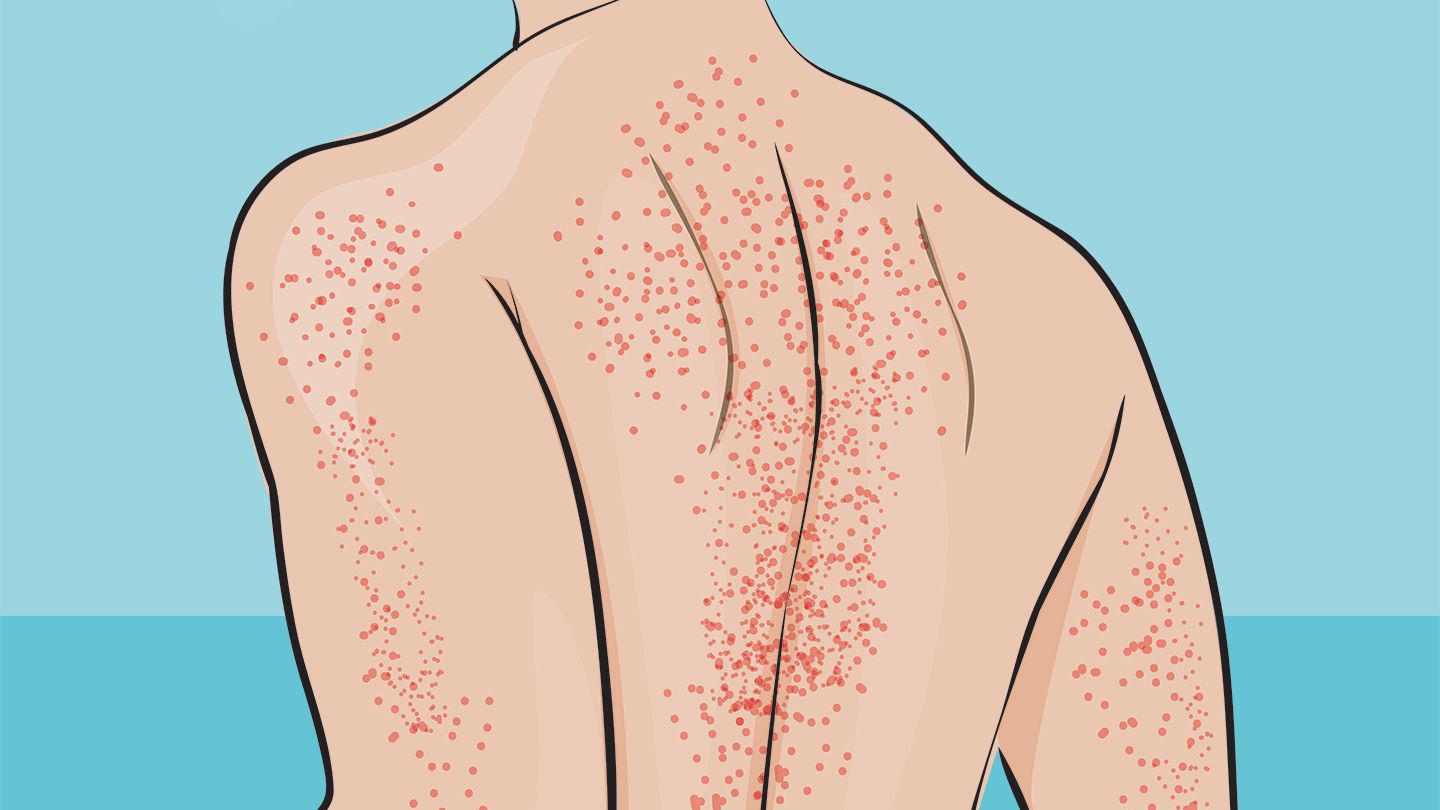
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a rare blood disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks platelets, which are crucial for blood clotting. Did you know that ITP can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender? While some people might experience mild symptoms, others could face severe complications. Understanding ITP is vital for managing it effectively. This condition can be triggered by infections, medications, or even other autoimmune diseases. Symptoms often include easy bruising, frequent nosebleeds, and tiny red spots on the skin called petechiae. Treatment options range from medications to boost platelet count to more intensive therapies like splenectomy. Living with ITP requires regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments to minimize bleeding risks. Stay informed and proactive to navigate this challenging condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a disorder that causes low platelet count, leading to bruising and bleeding. It can be triggered by infections and requires regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments.
- Diagnosis and treatment of ITP involve blood tests, steroids, and other medications. Living with ITP requires avoiding certain medications, moderating physical activity, and seeking emotional support.
What is Immune Thrombocytopenia?
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a disorder that affects the blood. It causes a low platelet count, which can lead to easy or excessive bruising and bleeding. Here are some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
ITP stands for Immune Thrombocytopenia Purpura. The term "purpura" refers to the purple-colored spots and patches that appear on the skin due to bleeding underneath.
-
ITP is an autoimmune disorder. The body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets, which are essential for blood clotting.
-
Two types of ITP exist: acute and chronic. Acute ITP is more common in children and often resolves on its own, while chronic ITP lasts longer and is more common in adults.
-
Symptoms can vary widely. Some people may have no symptoms, while others may experience severe bleeding, bruising, or petechiae (tiny red spots on the skin).
-
ITP can be triggered by infections. Viral infections like the flu or chickenpox can sometimes lead to the development of ITP.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and treating ITP involves several steps and methods. Understanding these can help manage the condition more effectively.
-
Blood tests are essential for diagnosis. A complete blood count (CBC) is used to measure platelet levels and rule out other conditions.
-
Bone marrow tests may be needed. In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy is performed to ensure the bone marrow is producing enough platelets.
-
Steroids are a common treatment. Corticosteroids like prednisone can help increase platelet counts by suppressing the immune system.
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is another option. IVIG can temporarily increase platelet counts by blocking the immune system's destruction of platelets.
-
Splenectomy may be necessary. Removing the spleen can help some patients because the spleen is where platelets are often destroyed.
Living with ITP
Living with ITP requires lifestyle adjustments and regular medical care. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Regular monitoring is crucial. Frequent blood tests are needed to keep track of platelet levels and adjust treatments as necessary.
-
Avoiding certain medications is important. Drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen can increase the risk of bleeding and should be avoided.
-
Physical activity should be moderated. High-impact sports or activities that could lead to injury should be avoided to reduce the risk of bleeding.
-
Diet can play a role. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall health and potentially improve platelet function.
-
Support groups can be beneficial. Connecting with others who have ITP can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving the understanding and treatment of ITP. Here are some exciting developments.
-
New medications are being developed. Researchers are working on drugs that target specific pathways involved in platelet destruction.
-
Genetic studies are underway. Understanding the genetic factors that contribute to ITP can lead to more personalized treatments.
-
Clinical trials offer hope. Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
-
Biomarkers are being identified. Finding specific biomarkers can help predict disease severity and response to treatment.
-
Patient registries are valuable. Collecting data from large groups of ITP patients can help identify trends and improve care strategies.
Impact on Daily Life
ITP can affect many aspects of daily life. Here are some ways it can impact individuals and their families.
-
Fatigue is a common issue. Low platelet counts can lead to tiredness and reduced energy levels.
-
Emotional health can be affected. Living with a chronic condition can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress.
-
Work and school may be impacted. Frequent medical appointments and the need to avoid certain activities can interfere with daily responsibilities.
-
Travel requires extra planning. Ensuring access to medical care and avoiding risky activities are important considerations when traveling.
-
Family dynamics can change. Family members may need to provide additional support and care, which can affect relationships.
Pediatric ITP
Children with ITP face unique challenges. Here are some facts specific to pediatric cases.
-
Acute ITP is more common in children. Most cases in children are acute and resolve within six months.
-
Vaccinations can sometimes trigger ITP. In rare cases, vaccines like the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine can lead to ITP.
-
Children often recover without treatment. Many pediatric cases resolve on their own without the need for medical intervention.
-
School activities may need adjustment. Parents and teachers should work together to ensure children avoid activities that could lead to injury.
-
Emotional support is crucial. Helping children understand their condition and providing emotional support can improve their quality of life.
ITP in Adults
Adult ITP presents different challenges compared to pediatric cases. Here are some important points.
-
Chronic ITP is more common in adults. Unlike children, adults are more likely to develop chronic ITP that requires ongoing management.
-
Women are more affected than men. Adult women are more likely to develop ITP, particularly during their reproductive years.
-
Pregnancy can complicate ITP. Pregnant women with ITP need careful monitoring to manage both their health and the health of their baby.
-
Age can affect treatment options. Older adults may have other health conditions that complicate treatment choices.
-
Workplace accommodations may be needed. Adults with ITP may need adjustments in their work environment to reduce the risk of injury.
Complications and Risks
ITP can lead to various complications and risks. Understanding these can help in managing the condition more effectively.
-
Bleeding is the primary risk. Low platelet counts increase the risk of bleeding, which can be life-threatening in severe cases.
-
Intracranial hemorrhage is rare but serious. Bleeding in the brain is a rare but potentially fatal complication of ITP.
-
Infections can be a concern. Treatments that suppress the immune system can increase the risk of infections.
-
Bone density may be affected. Long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
-
Mental health issues are common. Anxiety and depression are common among people with ITP due to the chronic nature of the condition.
Support and Resources
Access to support and resources can make a significant difference for those living with ITP. Here are some valuable options.
-
Patient advocacy groups are helpful. Organizations like the Platelet Disorder Support Association provide information and support for ITP patients.
-
Online forums offer community. Connecting with others online can provide a sense of community and shared experience.
-
Educational materials are available. Many organizations offer brochures, videos, and other materials to help patients understand their condition.
-
Financial assistance programs exist. Some organizations offer financial help for medical expenses related to ITP.
-
Counseling services can be beneficial. Professional counseling can help patients and their families cope with the emotional challenges of ITP.
Advances in Technology
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in the management of ITP. Here are some ways it is making a difference.
-
Telemedicine is expanding access. Virtual appointments can make it easier for patients to consult with specialists without traveling.
-
Mobile apps can track symptoms. Apps designed for ITP patients can help track symptoms, medication, and platelet counts.
-
Wearable devices monitor health. Wearables can track vital signs and alert patients to potential issues.
-
Electronic health records improve care. Digital records make it easier for healthcare providers to access and share patient information.
-
Research databases are growing. Large databases of patient information are helping researchers identify new trends and treatment options.
Final Thoughts on Immune Thrombocytopenia
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) can be a complex condition, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can make a big difference. From bruising and bleeding to fatigue, recognizing the signs early helps in managing the condition effectively. Autoimmune disorders, infections, and even certain medications can trigger ITP. Treatments range from steroids and immunoglobulins to more advanced options like splenectomy or thrombopoietin receptor agonists. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers ensures the best possible outcomes. Remember, while ITP can be challenging, many people lead full, active lives with proper care. Keep these facts in mind, and don't hesitate to seek medical advice if you notice any unusual symptoms. Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to managing health conditions like ITP.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
